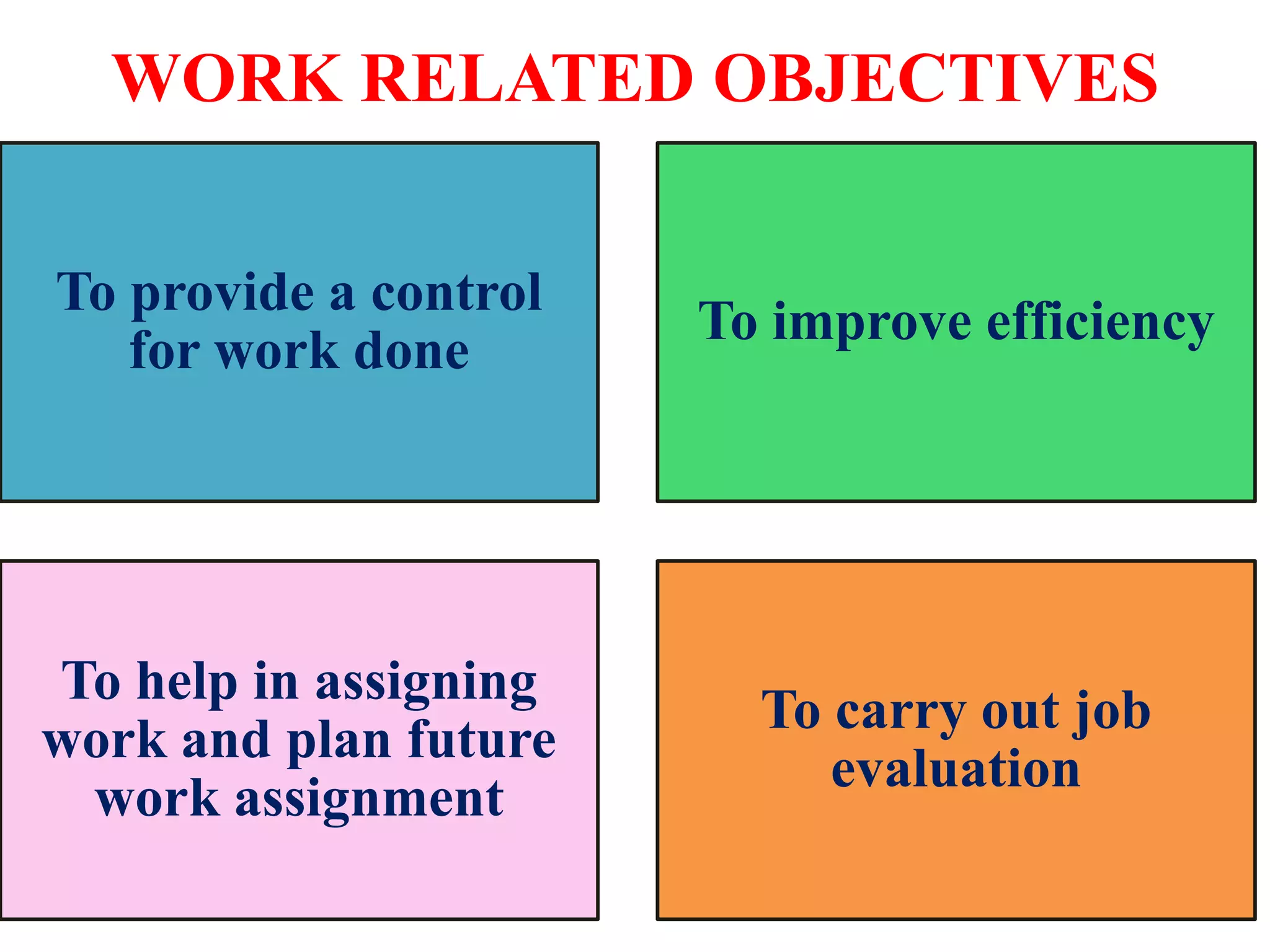
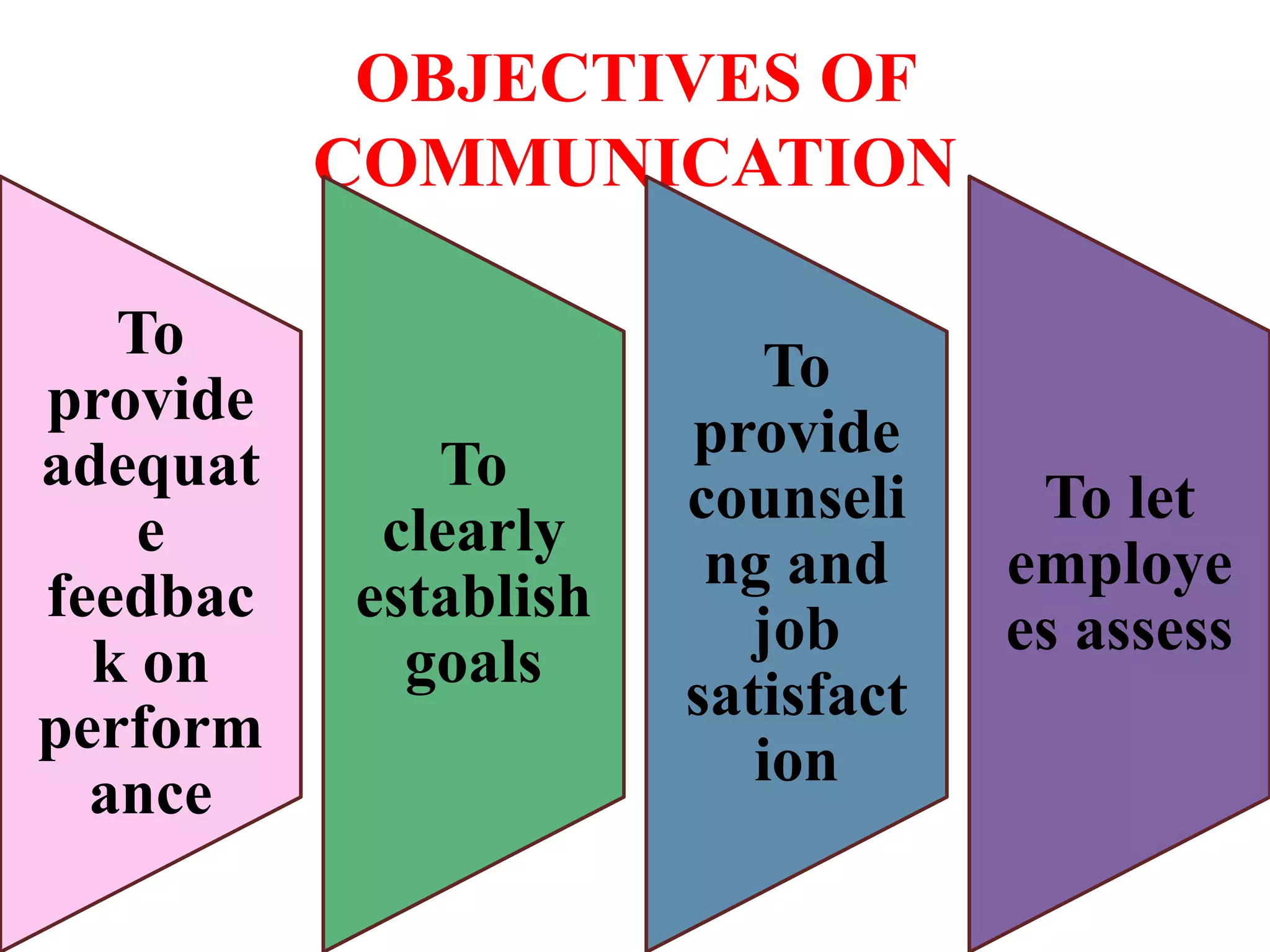
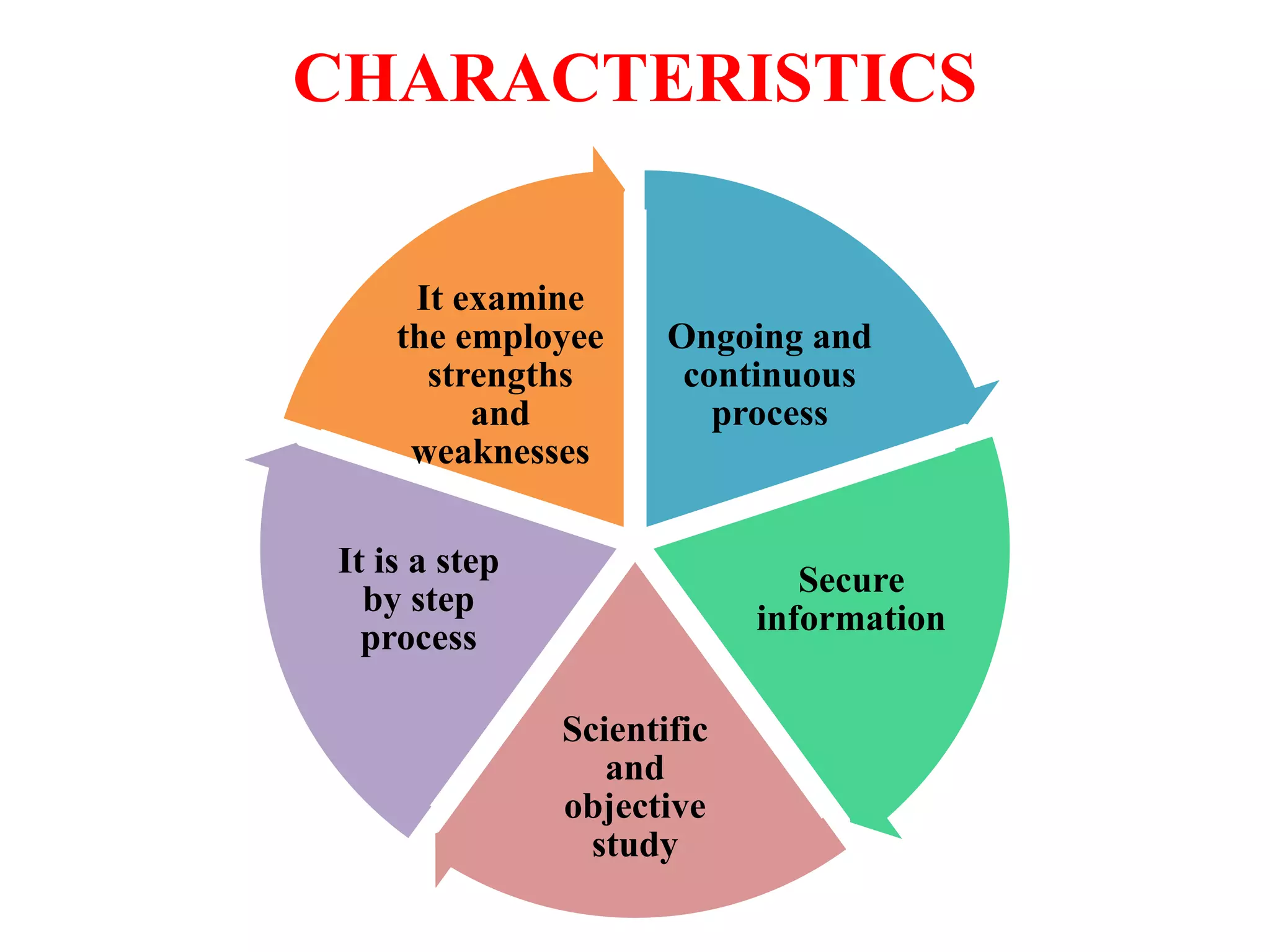
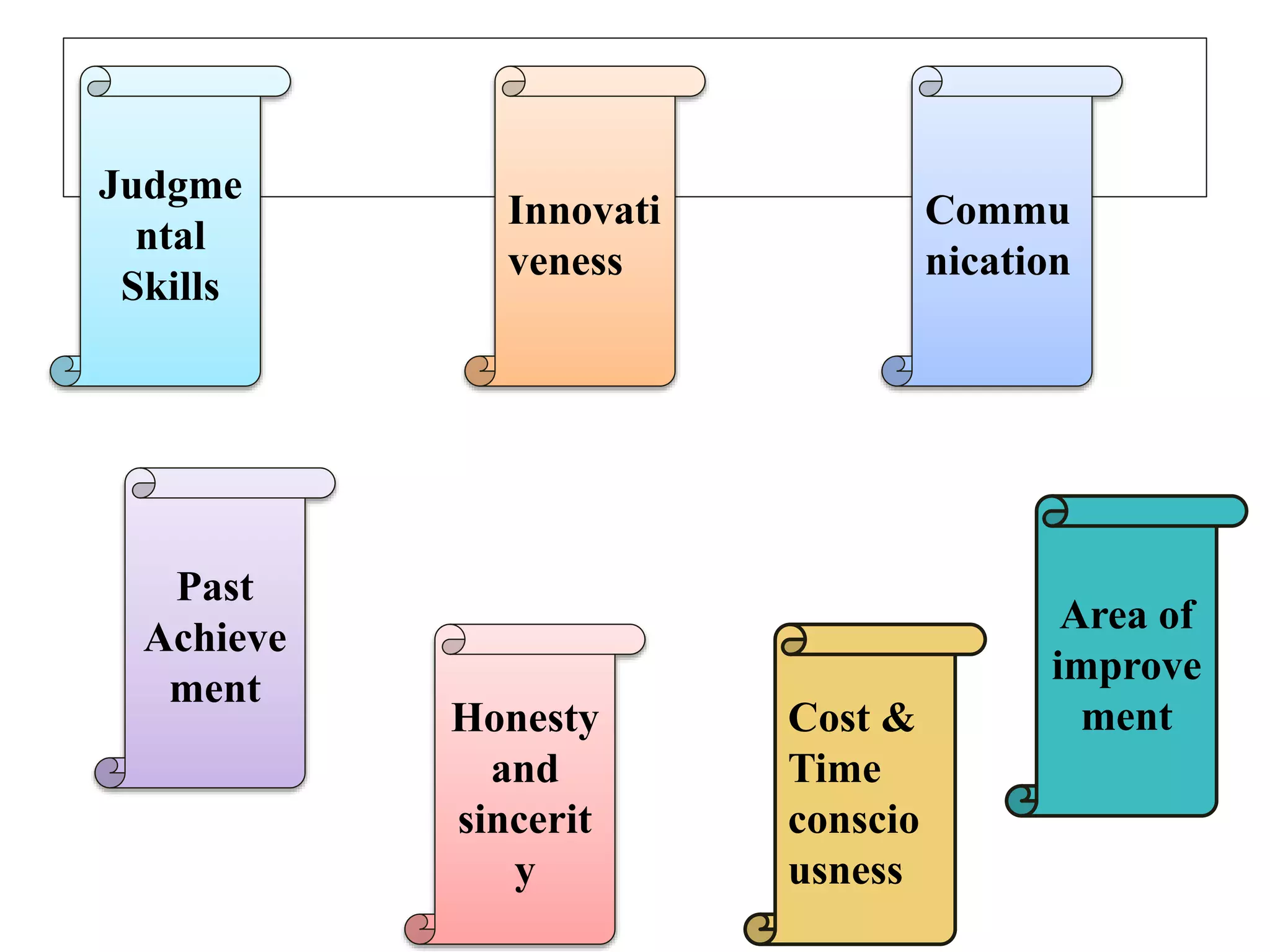
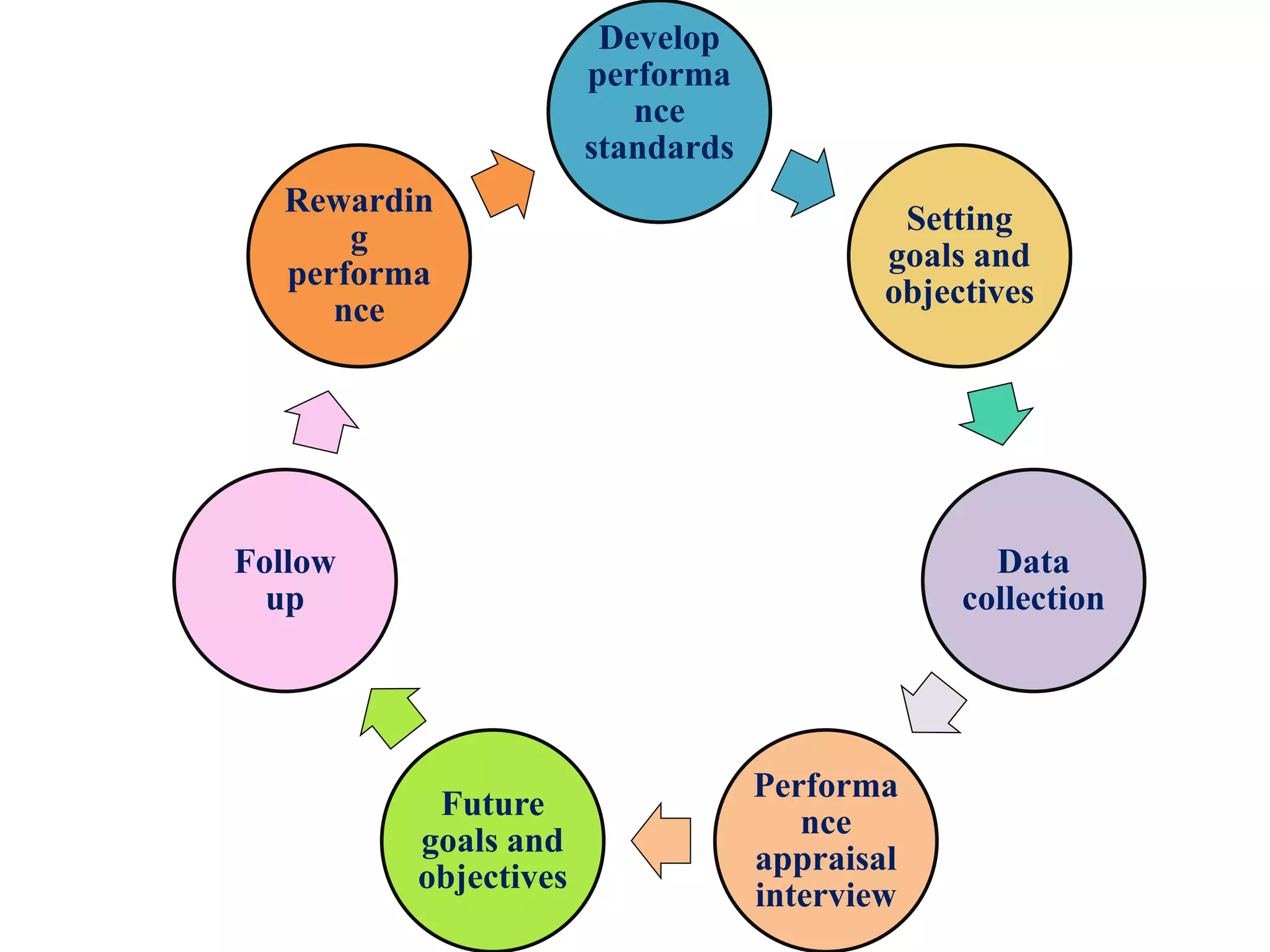
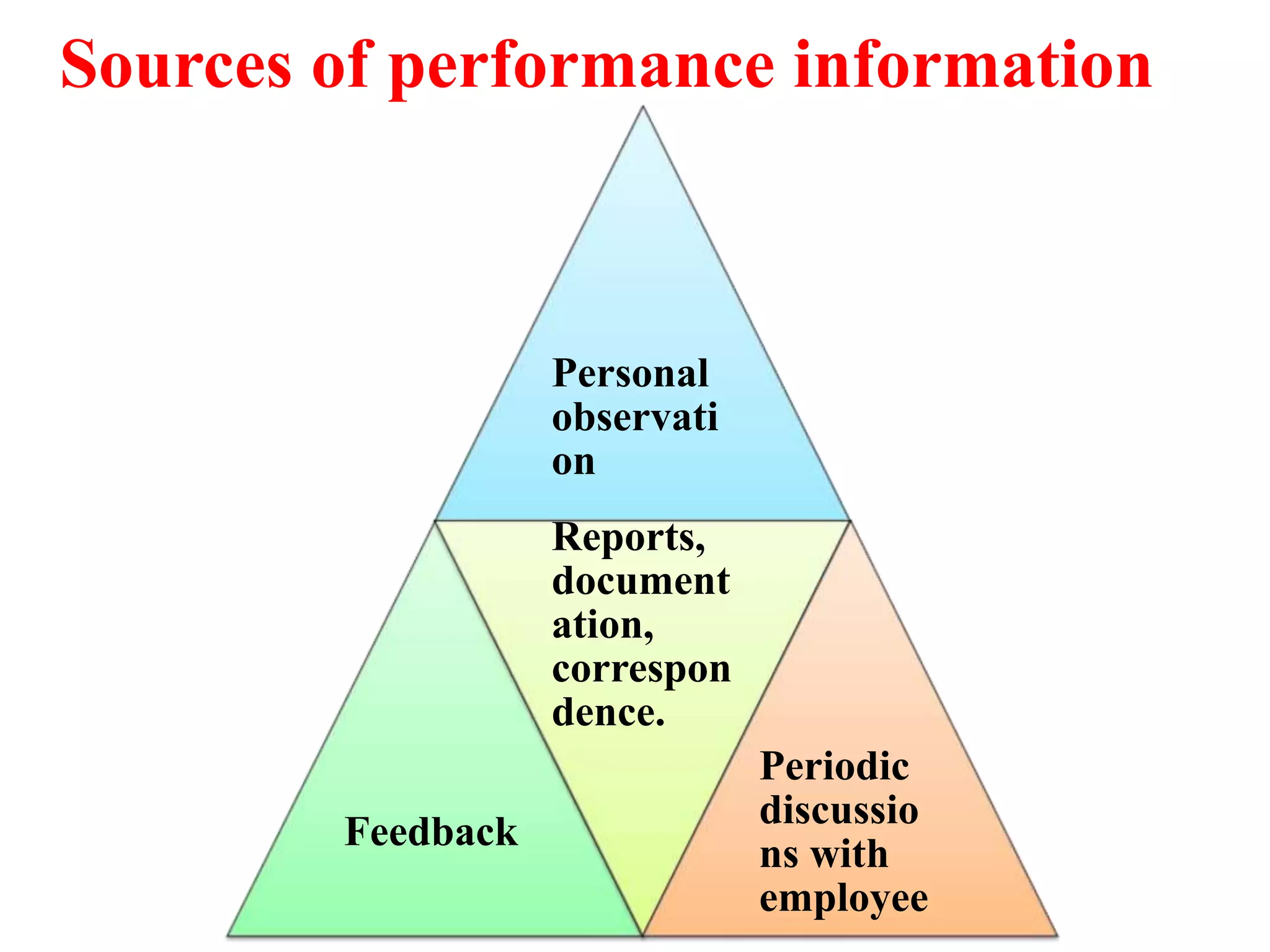
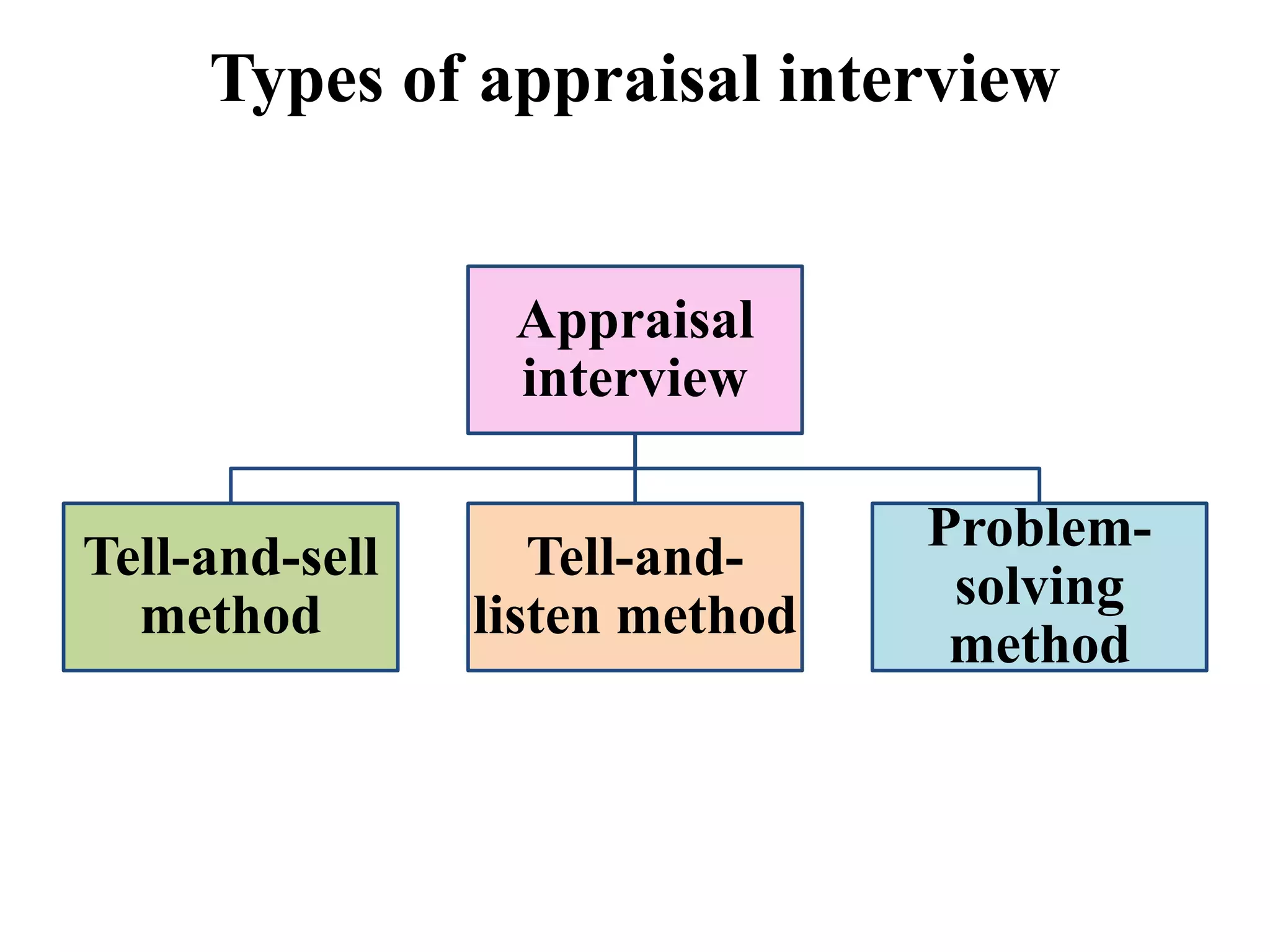
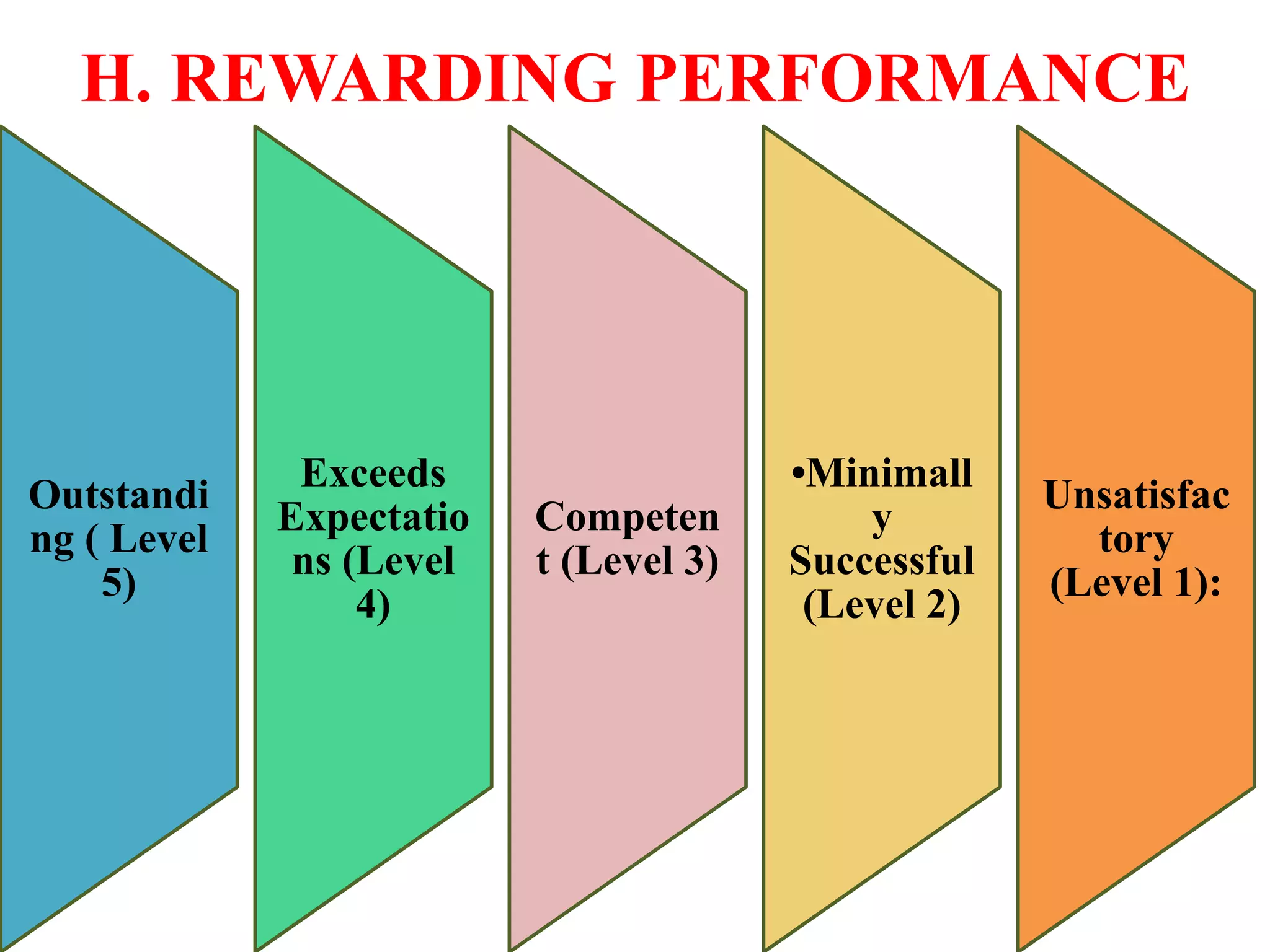
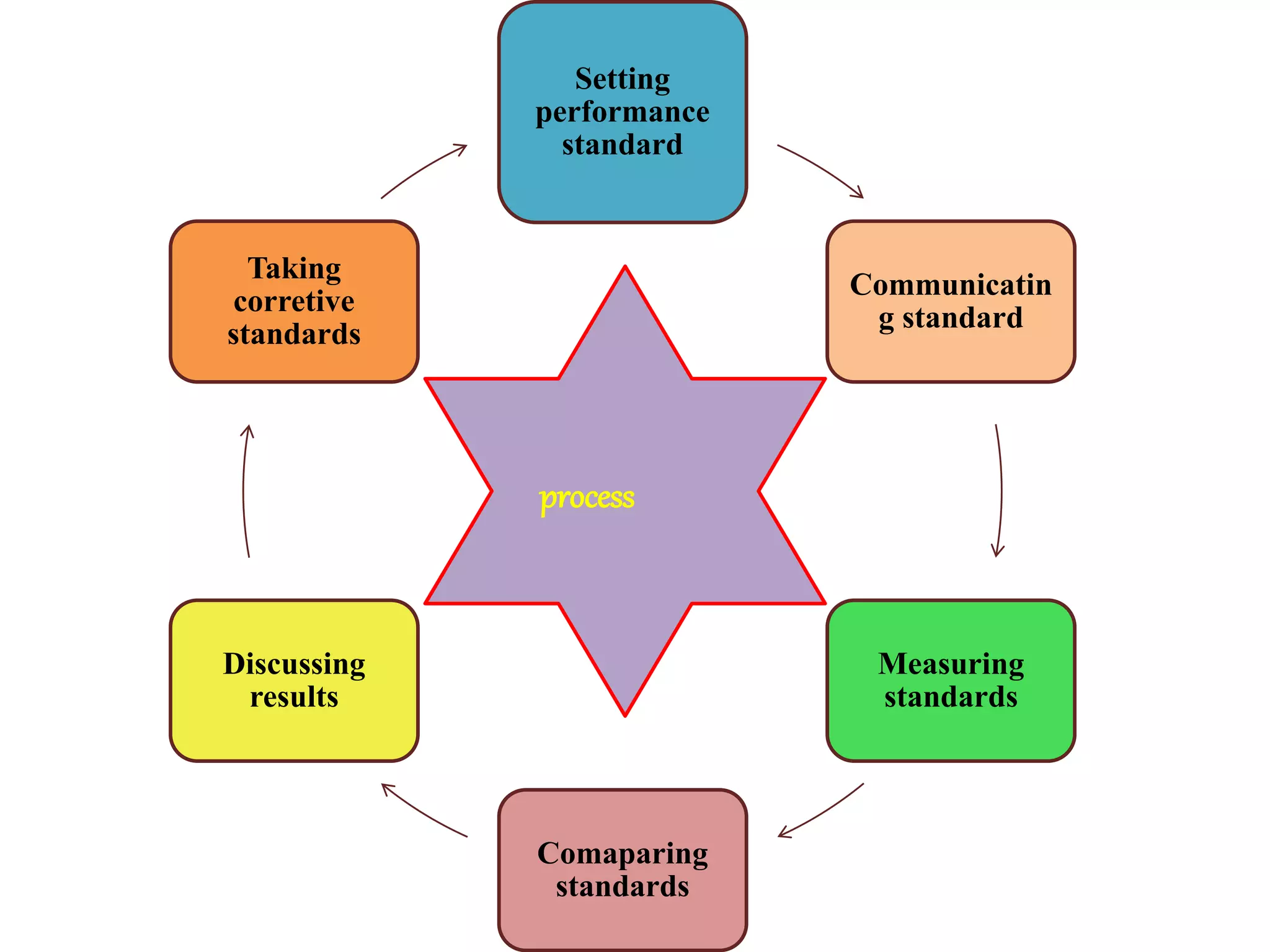
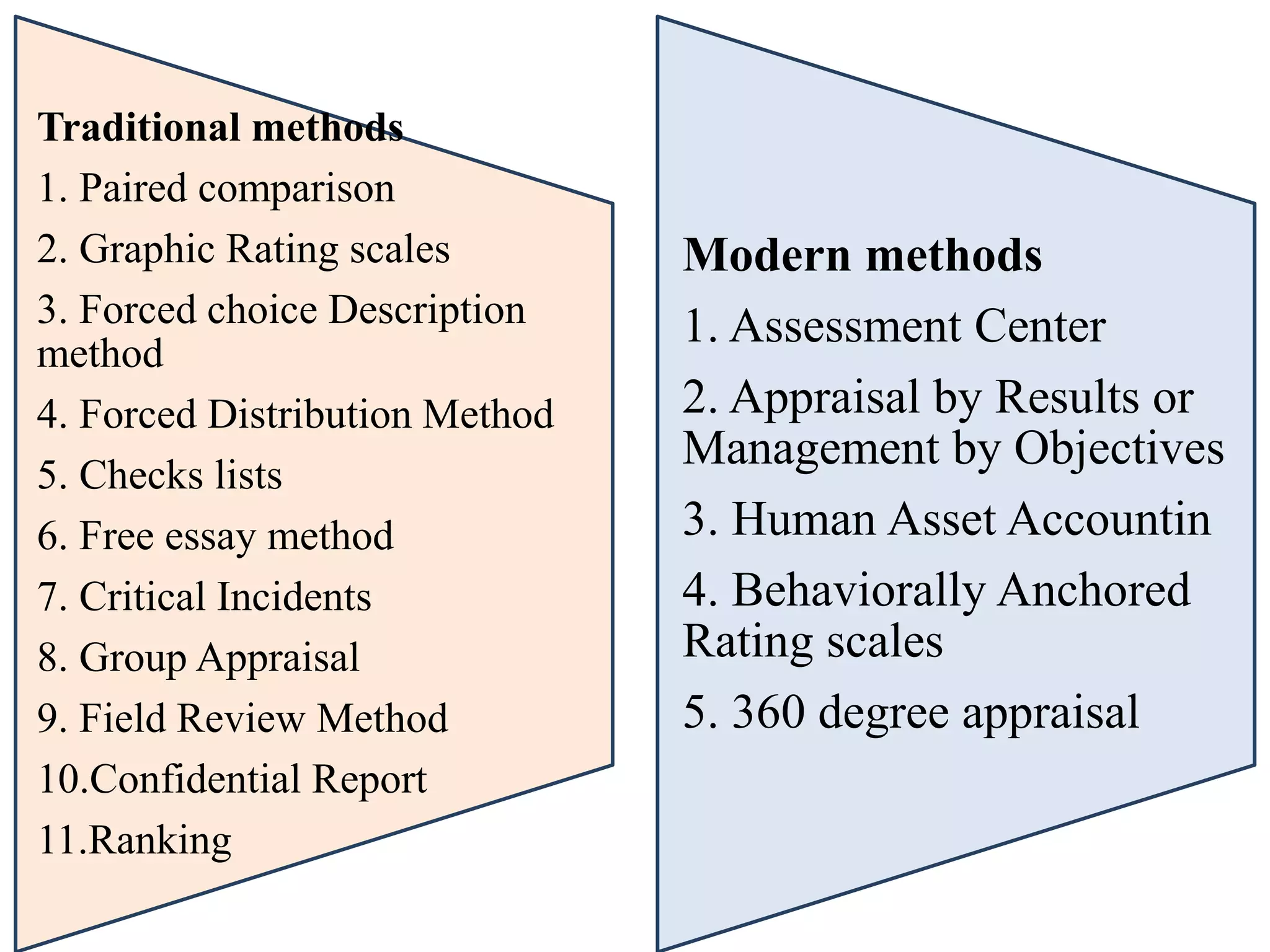
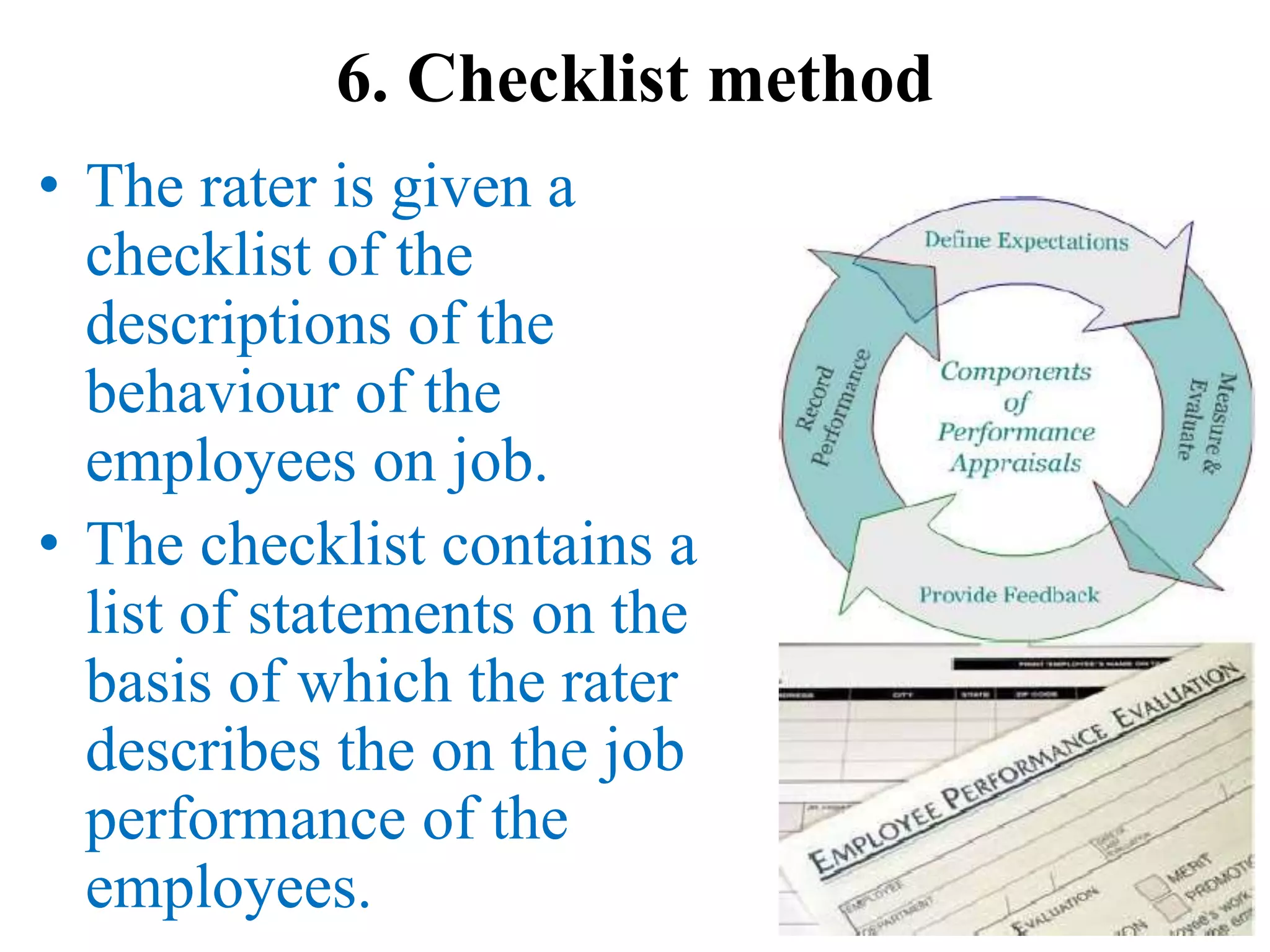
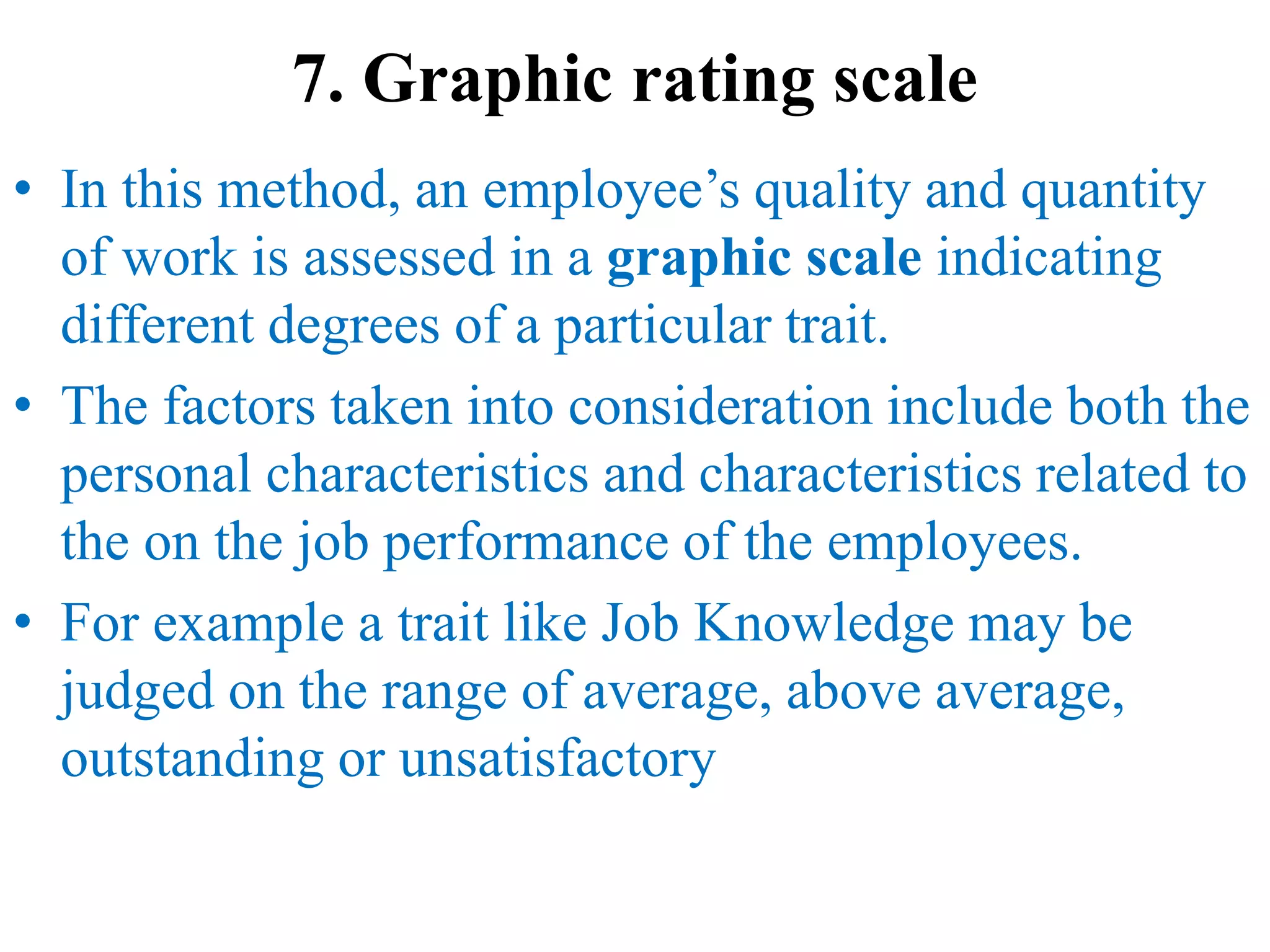
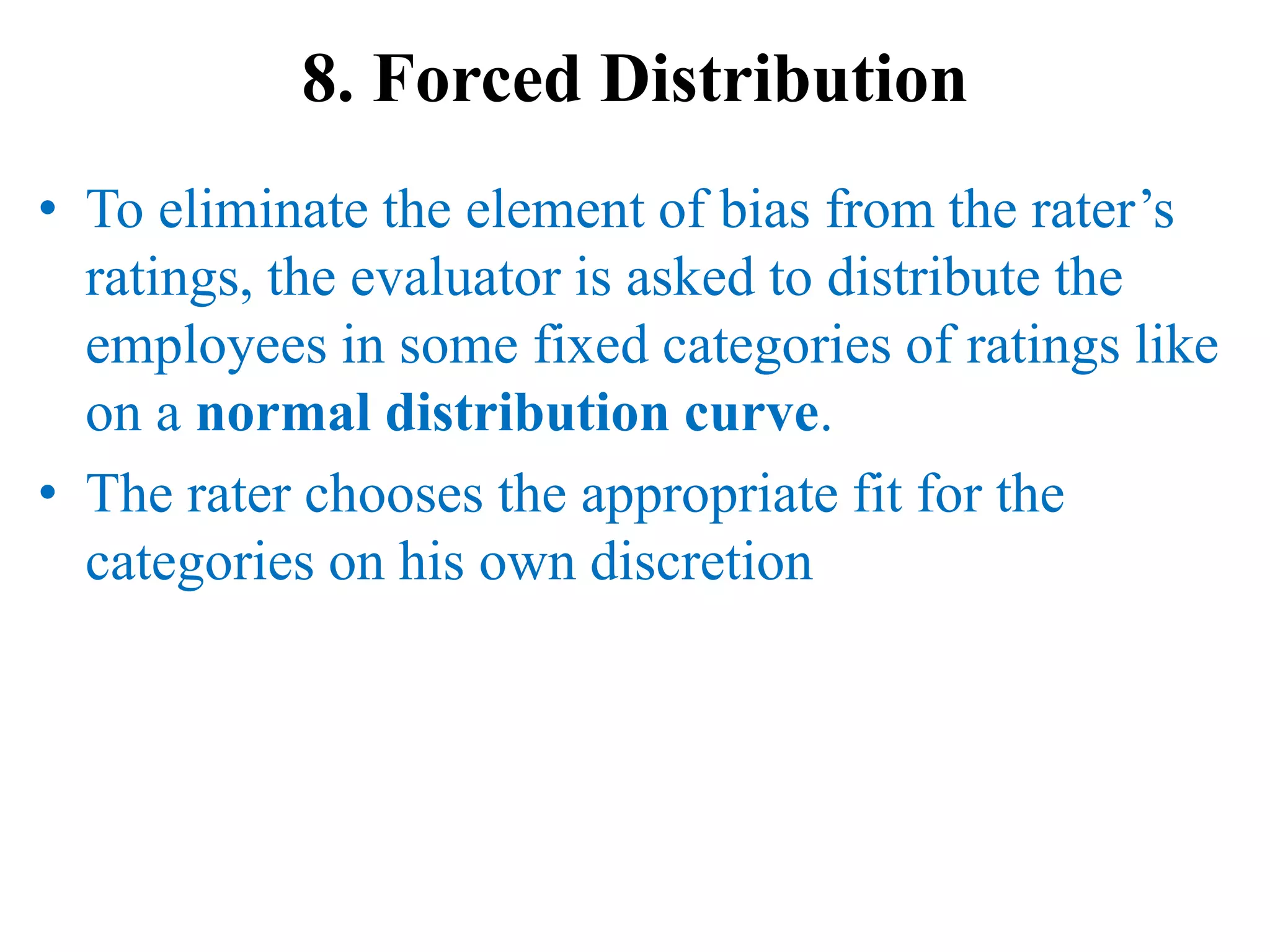
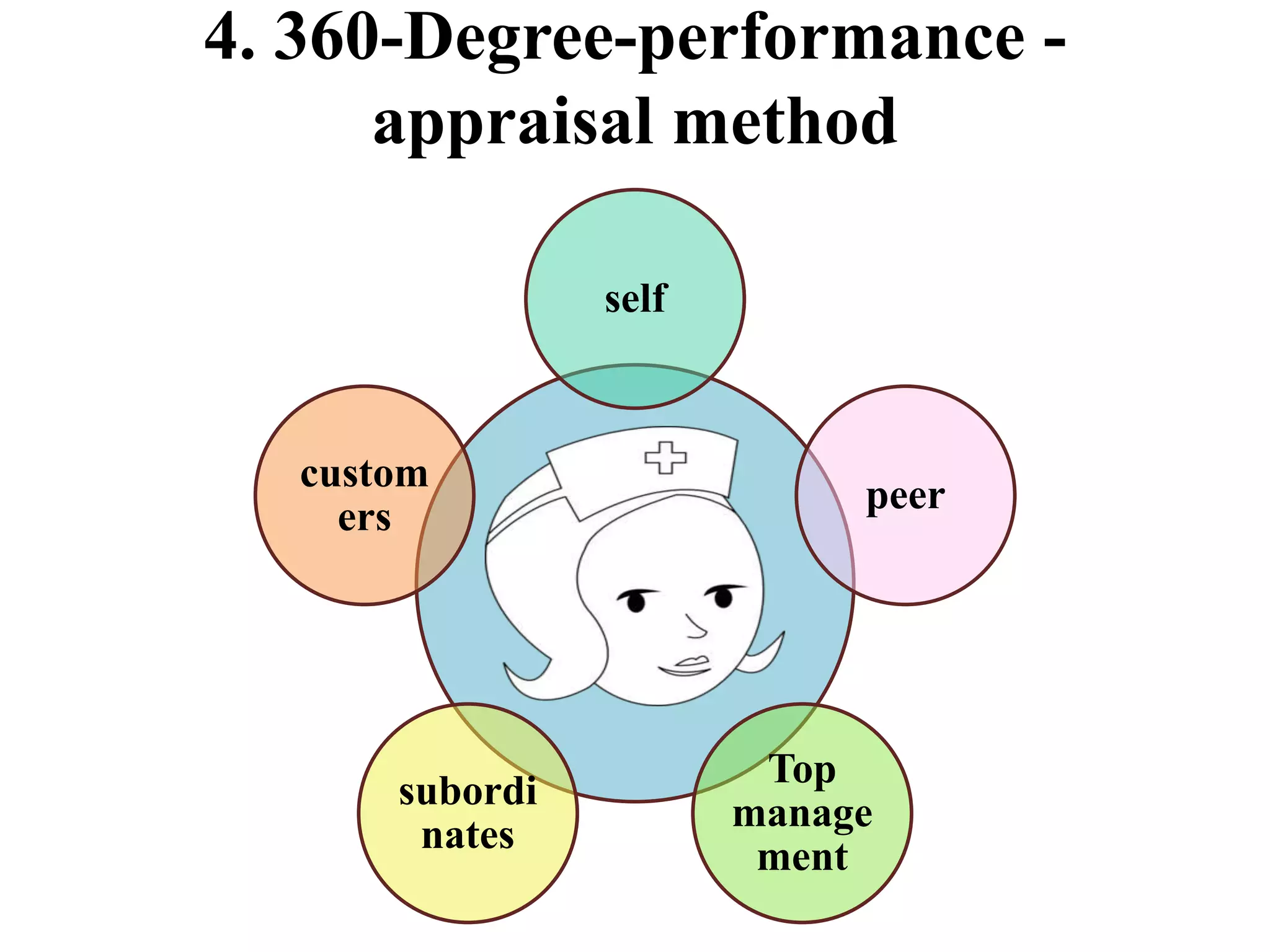
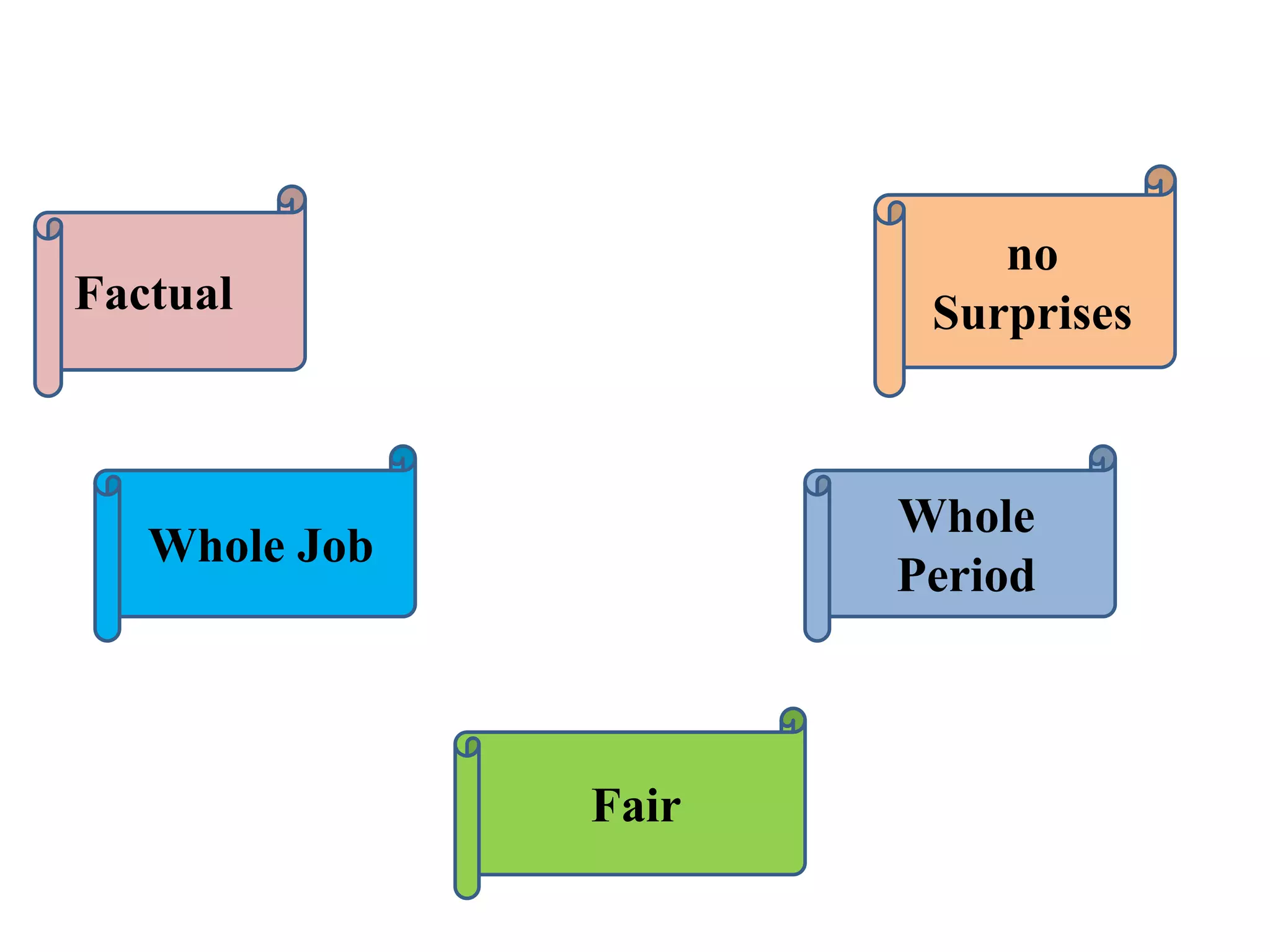
Performance appraisal is a method to evaluate an employee's job performance in terms of quality, quantity, cost, and time. It involves setting standards, collecting performance data, conducting appraisal interviews, setting future goals, and rewarding performance. There are traditional methods like essay, ranking, and checklists as well as modern methods like assessment centers, behaviorally anchored rating scales, and 360-degree feedback. An effective performance appraisal system should be simple, effective at improving performance, efficient to implement, and fair in its administration.