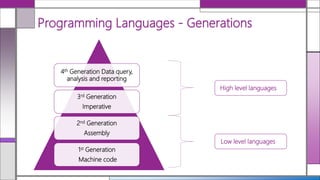
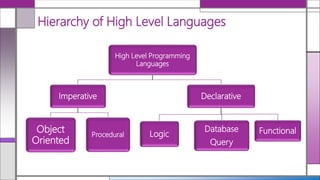
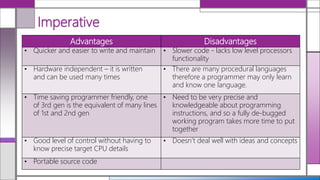
The document discusses various generations of programming languages, categorizing them into imperative, declarative, and object-oriented languages, each with specific characteristics and advantages. It highlights the functionalities and limitations of these high-level languages, emphasizing the organization around actions and data, the need for precise programming instructions, and their applicability in different programming contexts. Additionally, it describes the differences between logic and functional declarative languages and characterizes high-level programming's accessibility and maintainability.