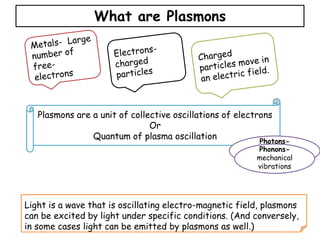
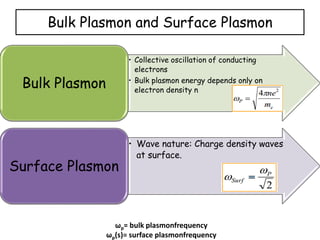
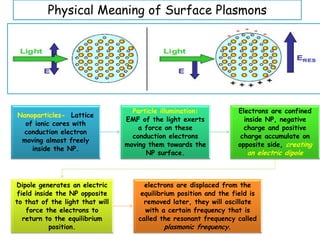
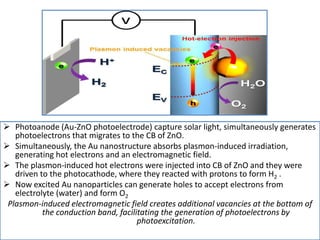
Plasmons are quanta of plasma oscillations that can be excited by light under certain conditions. There are two types of plasmons: bulk plasmons, which depend only on electron density, and surface plasmons, which are collective oscillations of electrons at a surface. Metallic nanoparticles support surface plasmons - when illuminated by light, the electromagnetic field causes electrons within the nanoparticle to oscillate at a resonant plasmonic frequency, generating an enhanced local electric field. Efficient energy transfer can occur between metal nanoparticles and semiconductors if their plasmons are resonantly coupled, allowing light absorption and energy transfer.