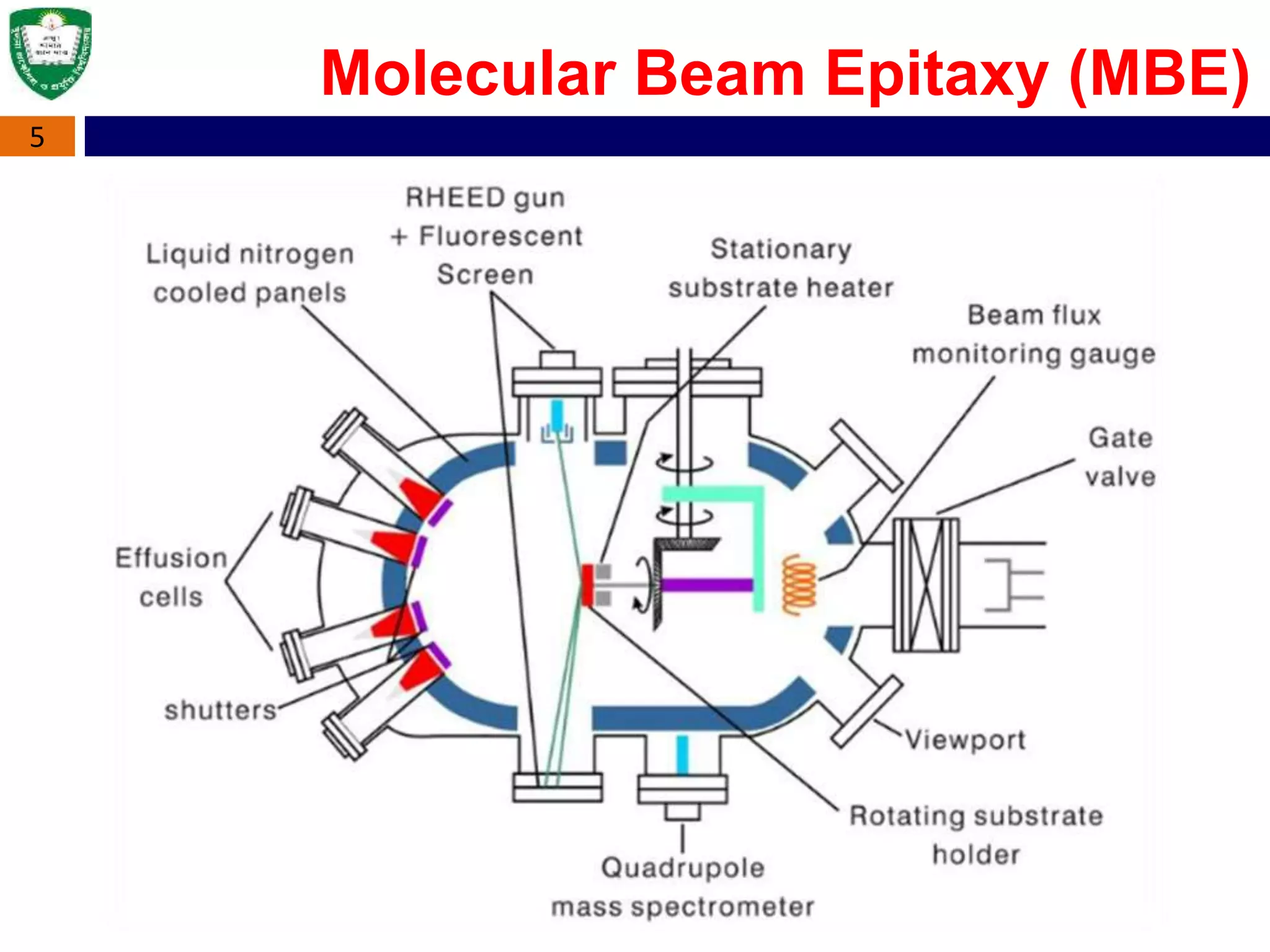
Molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) is a method for growing thin films one layer at a time under ultra-high vacuum conditions. It involves heating solid sources of material in effusion cells to create molecular beams that are deposited on a heated substrate. The absence of carrier gases and ultra-high vacuum environment result in films of the highest purity. MBE is widely used to manufacture semiconductor devices and is considered a fundamental tool for nanotechnology development due to its precise control over layer thickness down to a single atomic layer.