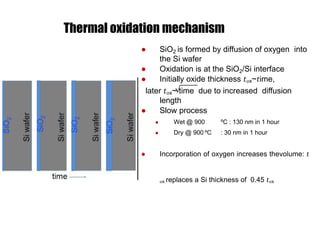
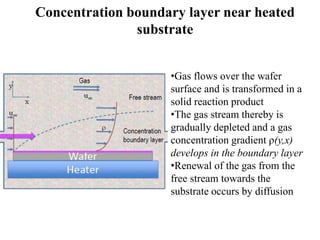
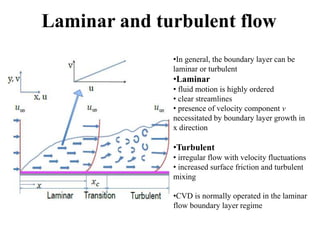
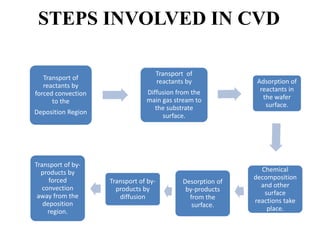
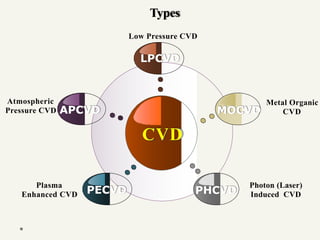
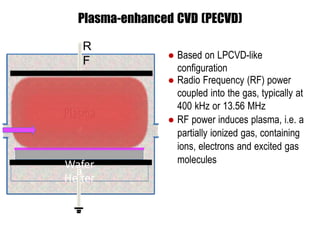
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a process for creating high-purity materials through chemical reactions of gaseous precursors on a substrate. Various types of CVD techniques exist, including low-pressure, atmospheric pressure, and plasma-enhanced CVD, each with different operational pressures and characteristics. CVD applications range from semiconductor manufacturing to coatings, providing benefits like conformal films, high purity, and economic efficiency in production.















![● Process is repeated generating a sequence of layers
● Technique to produce very thin, atomically specified conformal films
● Reaction is self-limiting, i.e. it stops once all reactive sites on the
surface of the wafer are occupied
● Example: trimethyl aluminium [Al(CH3)3] and H2O vapour exposure
sequences to form very thin and continuous Al2O3 dielectric films
Atomic layer CVD (ALCVD)
● Individual application of two
reactant gases A and B
allowing sequential
formation of layers
● Each of the
two
reaction steps is self-limiting
one molecular monolayer
deposition at a time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cvd-180511073216/85/Cvd-19-320.jpg)