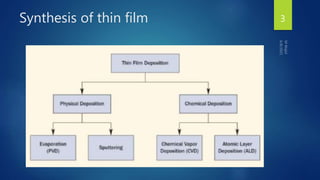
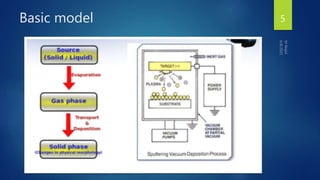
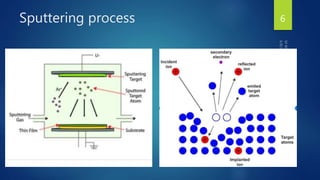
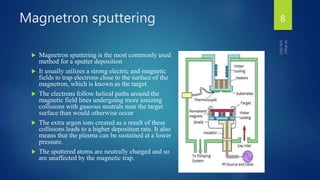
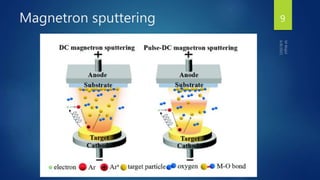
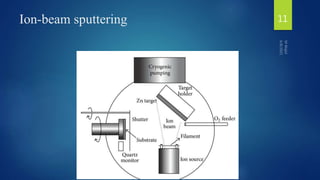
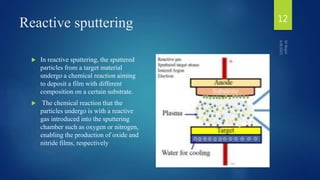
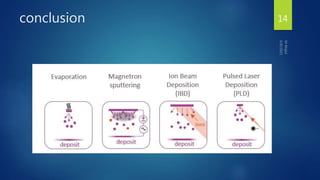
Muhammad Wajid and Muhammad Talha presented a report on sputtering process and its types to Dr. Shumaila Karmat. Sputtering is a process where atoms are ejected from a material's surface when struck by energetic particles, and it was first discovered in 1852. There are several types of sputtering including magnetron sputtering, ion-beam sputtering, and reactive sputtering. Magnetron sputtering traps electrons near the target using electric and magnetic fields to increase the deposition rate. Ion-beam sputtering uses a focused ion beam to sputter the target. Reactive sputtering introduces a reactive gas to deposit a film with a different composition than the target through a chemical reaction.