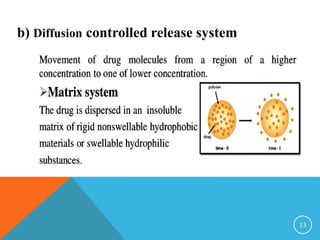
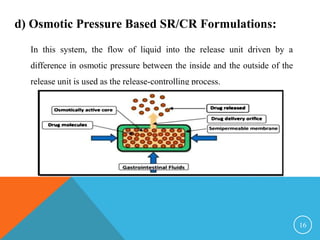
This document discusses sustained and controlled release drug delivery systems (SR and CRDDS). It defines SR and CRDDS and lists their advantages and disadvantages. It describes factors that influence the release rate from these systems, including physicochemical factors like solubility and biological factors like metabolism. The document outlines various physicochemical approaches to SR and CRDDS like matrix systems, reservoir systems, and ion exchange systems. It also discusses biological approaches using biopolymers and pulsatile release formulations. Finally, it briefly mentions applications and concludes with references.






![Physicochemical Factors
Aqueous solubility
Partition coefficient (K [O/W])
Drug pKa and ionization at physiological Ph
Drug stability
Molecular weight and diffusivity
Protein binding
Dose size.
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sustainedandcontrolledreleasedrugdeliverysystem-181206023131/85/Sustained-and-controlled-release-drug-delivery-system-8-320.jpg)