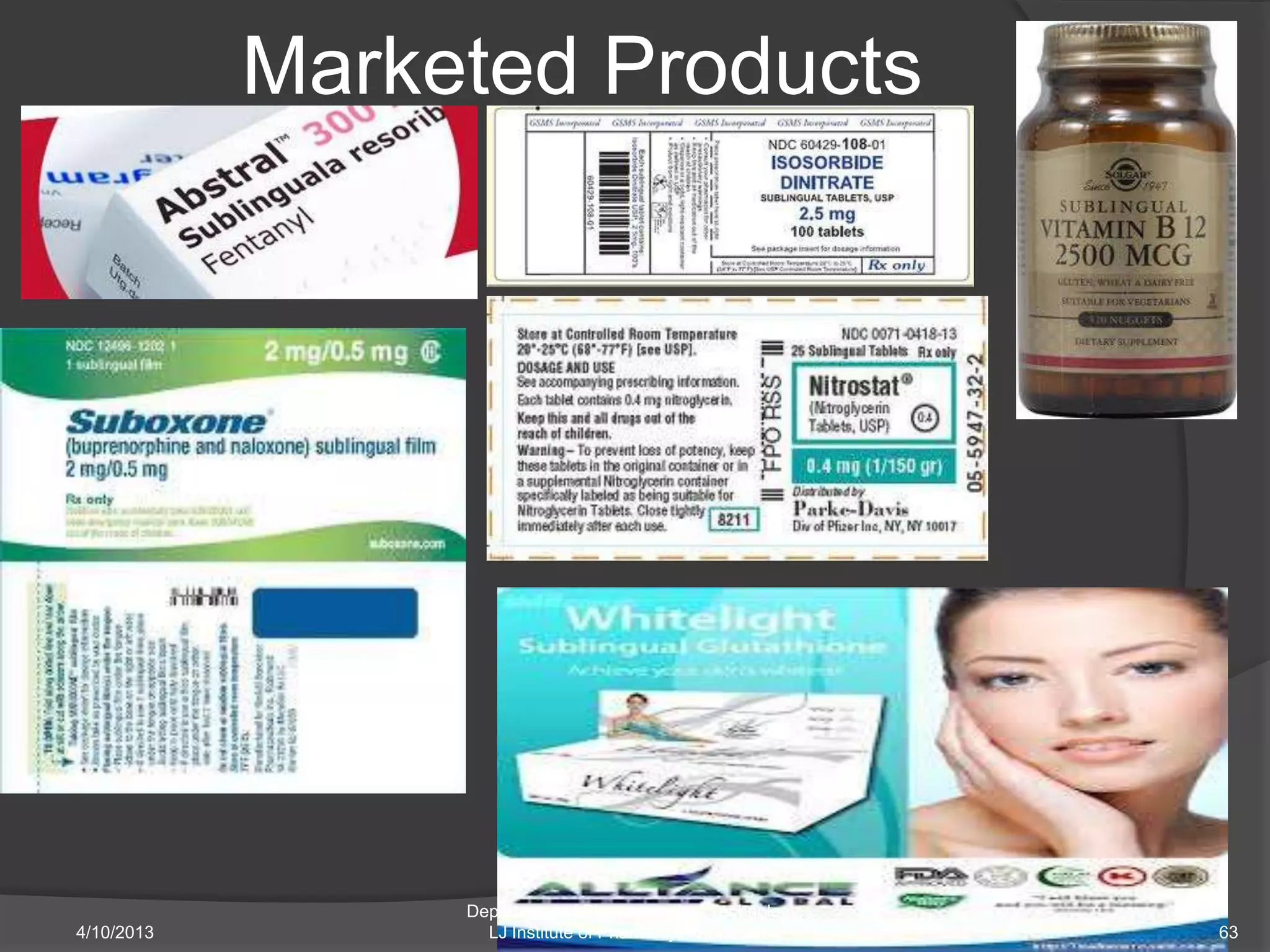
The document discusses Buccal Drug Delivery Systems (BDDS), focusing on their advantages such as avoiding first-pass metabolism and facilitating patient compliance, alongside disadvantages like suitability issues for certain patients and the challenges with drug stability. It describes the anatomy and physiology of the buccal cavity, the factors affecting drug delivery, mechanisms of bioadhesion, formulation components, and evaluates various dosage forms such as tablets and patches. Additionally, it outlines the selection criteria for drugs, types of mucoadhesive polymers, and the testing protocols for evaluating these delivery systems.