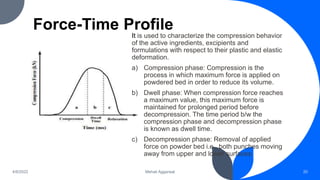
1) Tablet compression involves the application of force to reduce the volume of powder materials through three main processes: compression, compaction, and consolidation. Compression removes air, compaction rearranges particles, and consolidation increases strength through bonding.
2) Key forces involved in compression include inter-particulate and die wall friction, which can be reduced by adding glidants and lubricants, respectively. Distribution forces transmit pressure from the punches to the powder bed and die wall.
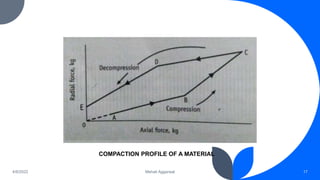
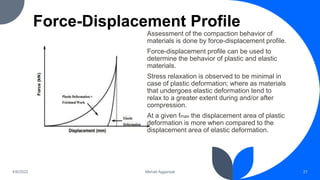
3) Compaction profiles examine the relationship between axial and radial pressure. They provide information on elastic versus plastic deformation and ejection forces.