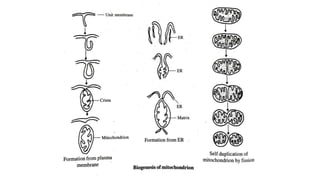
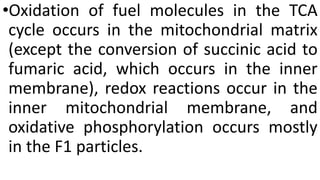
The document discusses three proposed mechanisms for the formation of mitochondria: self-duplication of existing mitochondria, de novo origin from cytoplasmic vesicles, and transformation from non-mitochondrial systems like the plasma membrane or ER. It states that the self-duplication hypothesis through fission of existing mitochondria is now most widely accepted. The endosymbiont hypothesis that mitochondria evolved from prokaryotes engulfed by early eukaryotic cells over a billion years ago is also described. Mitochondria's key functions like ATP production through oxidative phosphorylation are summarized.