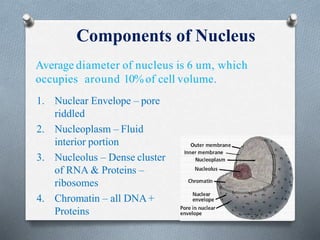
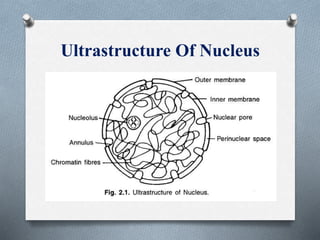
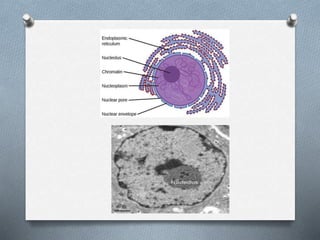
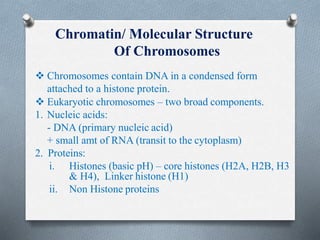
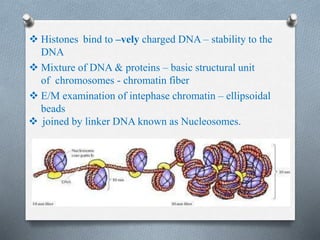
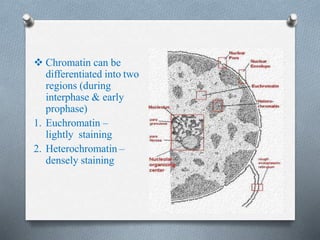
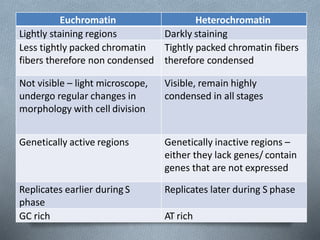
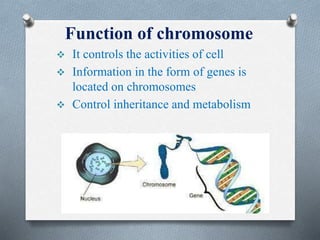
The nucleus is the control center of eukaryotic cells that contains DNA and directs protein synthesis and cell regulation. It is enclosed by a double membrane and contains nucleoplasm, nucleoli, and chromatin. Chromatin contains DNA and histone proteins that package DNA into chromosomes. The nuclear envelope separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm while nuclear pores allow transport of molecules. The nucleolus produces ribosomes and rRNA. The nucleus controls DNA replication, protein production, and cell processes through gene expression and protein synthesis.