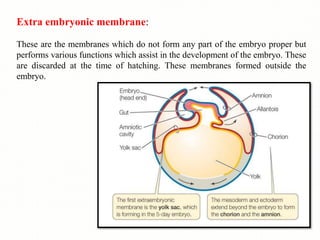
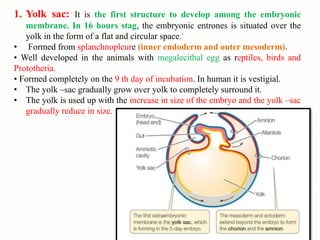
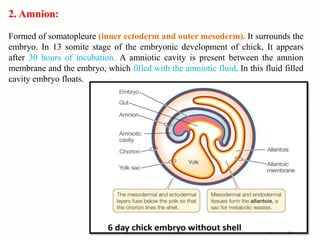
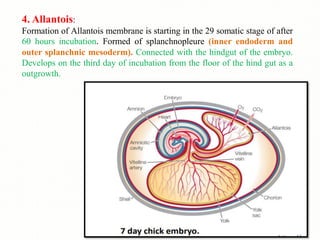
The document discusses the four main types of extra-embryonic membranes that develop in birds during embryonic development - the yolk sac, amnion, chorion, and allantois. Each membrane has a distinct structure and function. The yolk sac surrounds and digests the yolk. The amnion forms a fluid-filled cavity that protects the embryo. The chorion forms the outermost layer where gas exchange occurs. The allantois acts as a respiratory organ and aids in waste removal. Together these membranes provide protection, nutrition, respiration and excretion to support the developing embryo.