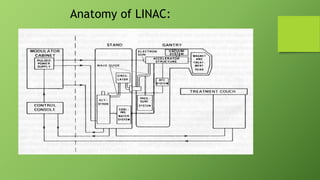
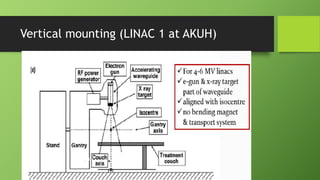
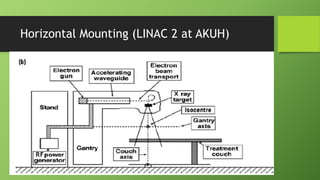
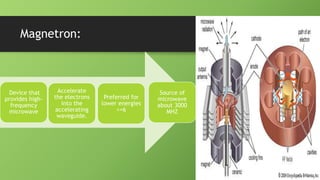
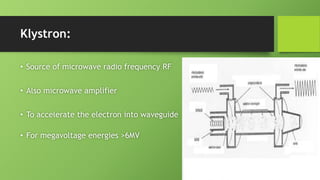
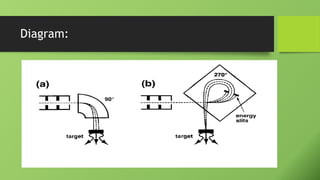
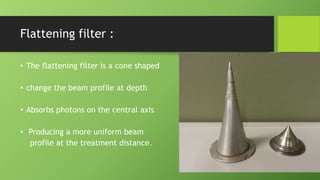
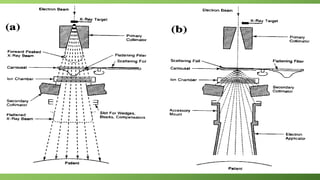
A linear accelerator is a machine that accelerates charged particles along a linear path to deliver radiation therapy for cancer treatment. It consists of an electron gun that produces electrons, an accelerator structure that accelerates the electrons using microwaves, and a treatment head that shapes and monitors the x-ray beam. Key components include the gantry that directs the beam, flattening filters and collimators that shape the beam, and ionization chambers that monitor the dose. The linear accelerator accelerates electrons to produce x-rays that are precisely aimed at the tumor to destroy cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue.