This document summarizes the expectations and key learnings from a linear accelerator acceptance, commissioning, and annual QA training that occurred from September to November 2008. The training covered:
1. Fundamental concepts of linear accelerators, beam production, safety features, and the acceptance testing process.
2. Techniques for collecting beam data needed for commissioning, including measurements and data definitions.
3. Procedures for linear accelerator QA and other treatment machine QA on an annual basis.
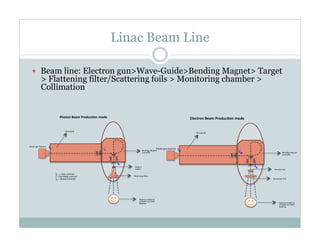
Key topics included the beamline components that produce photon and electron beams, characteristics of linear accelerator beams, the importance of acceptance testing and commissioning the machine properly, and techniques for annual QA tests.