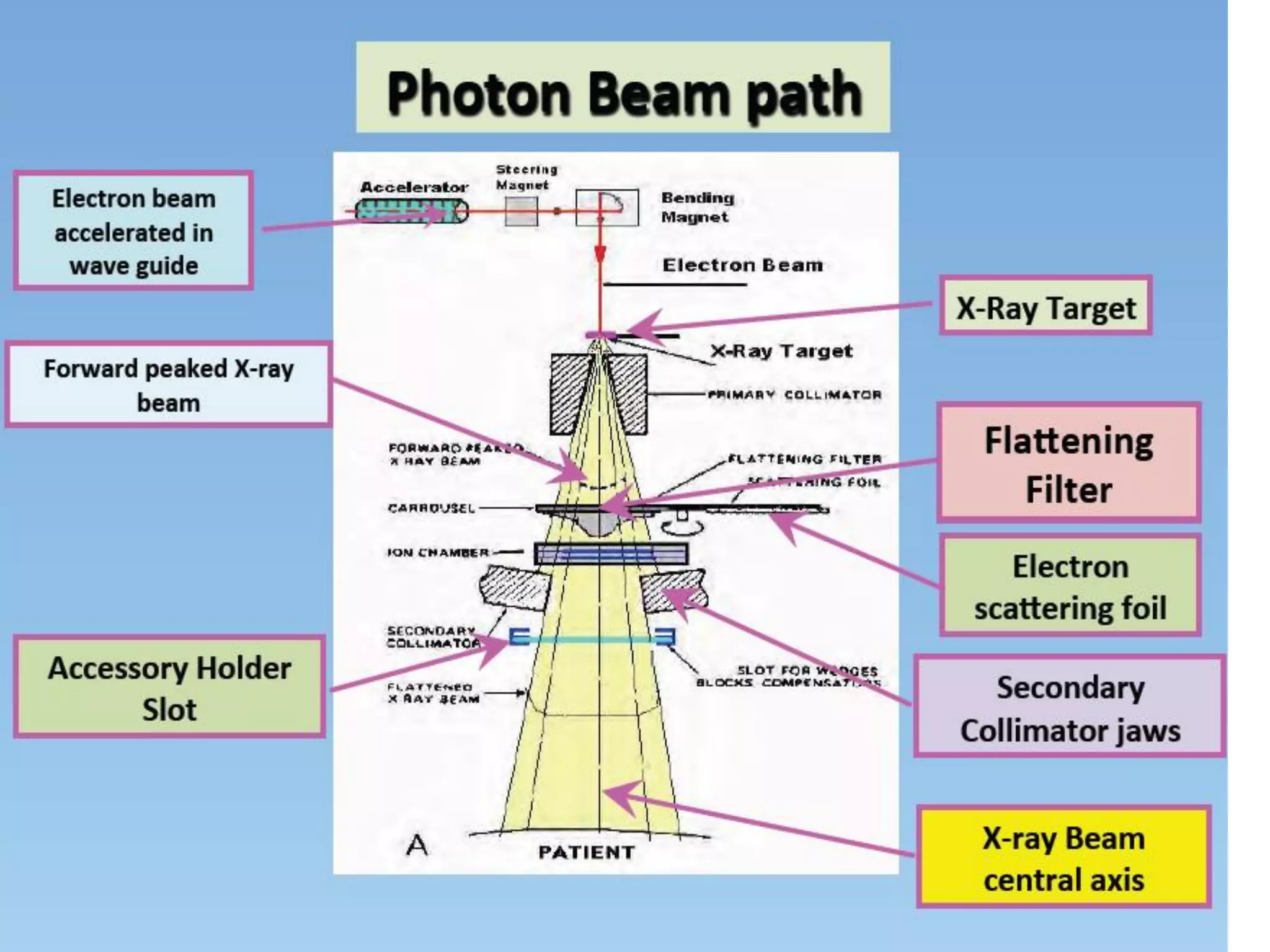
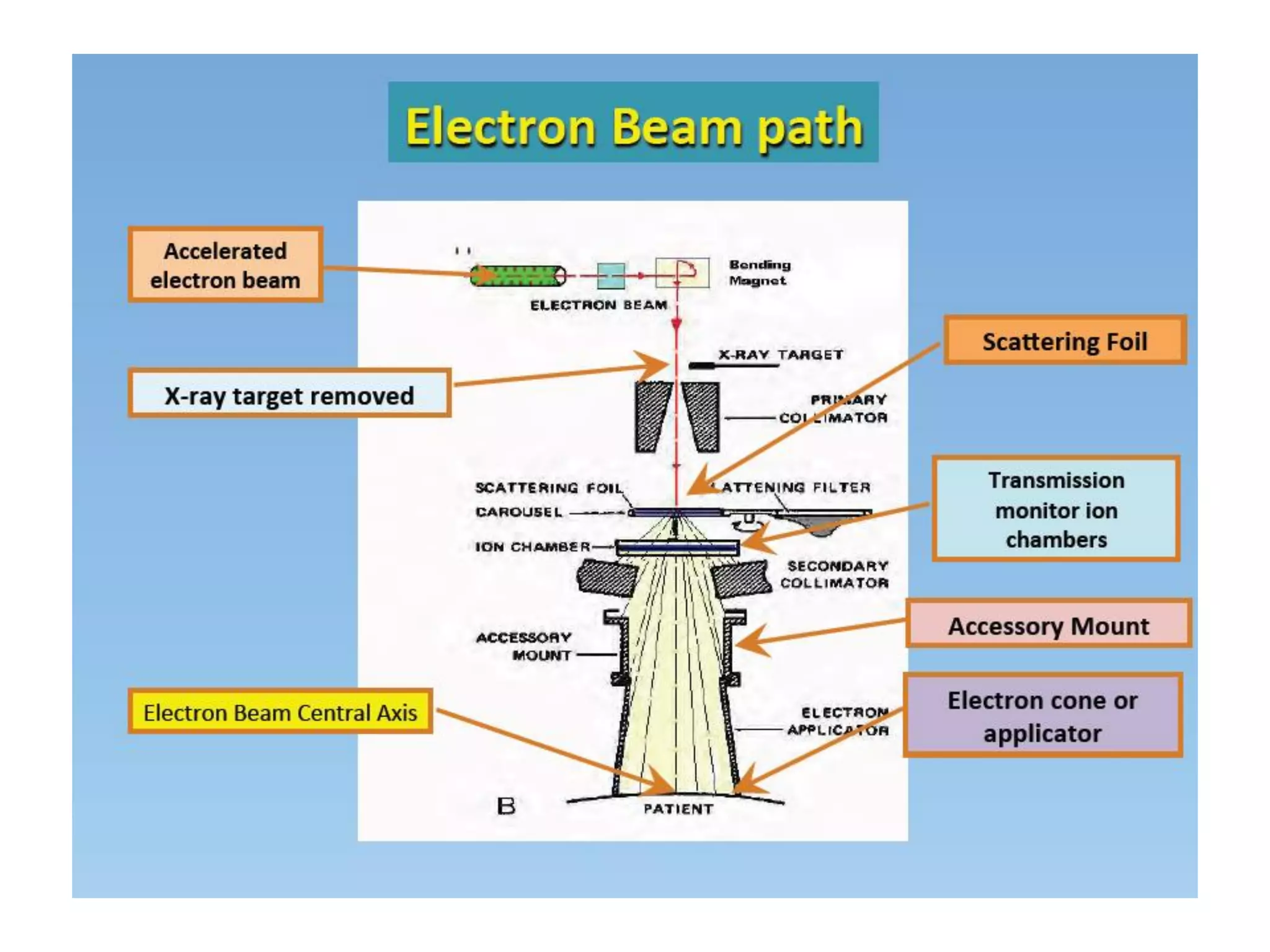
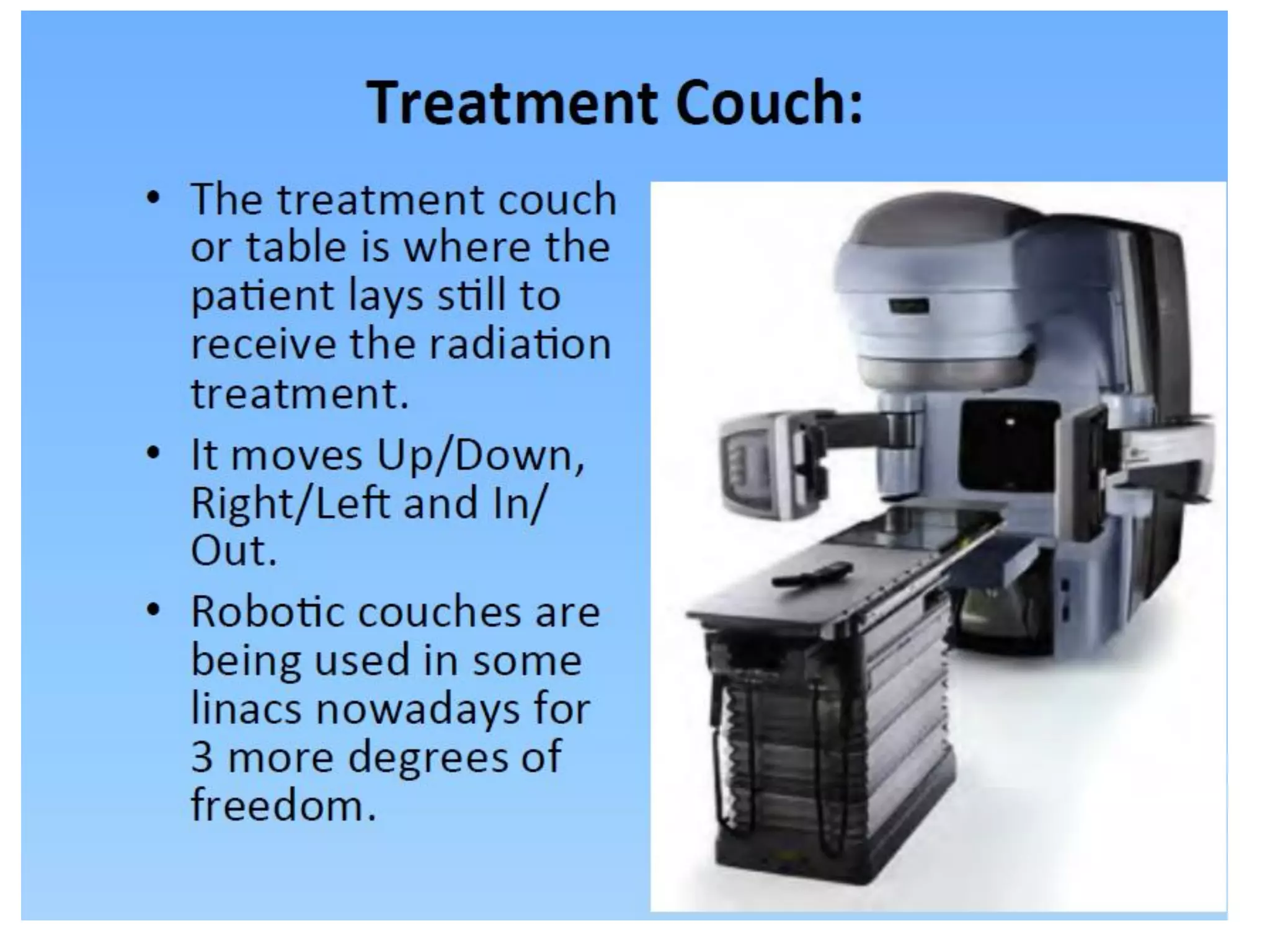
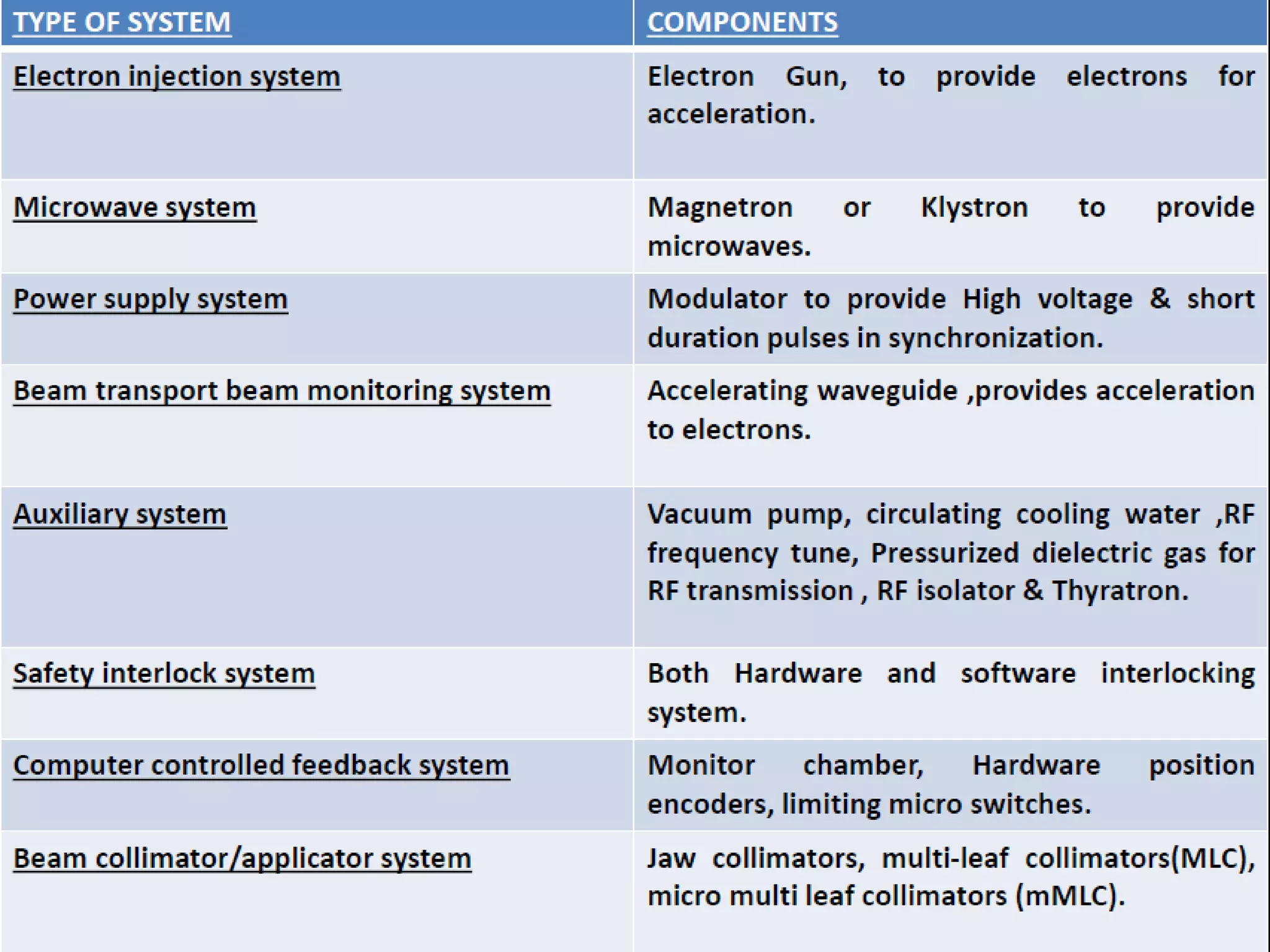
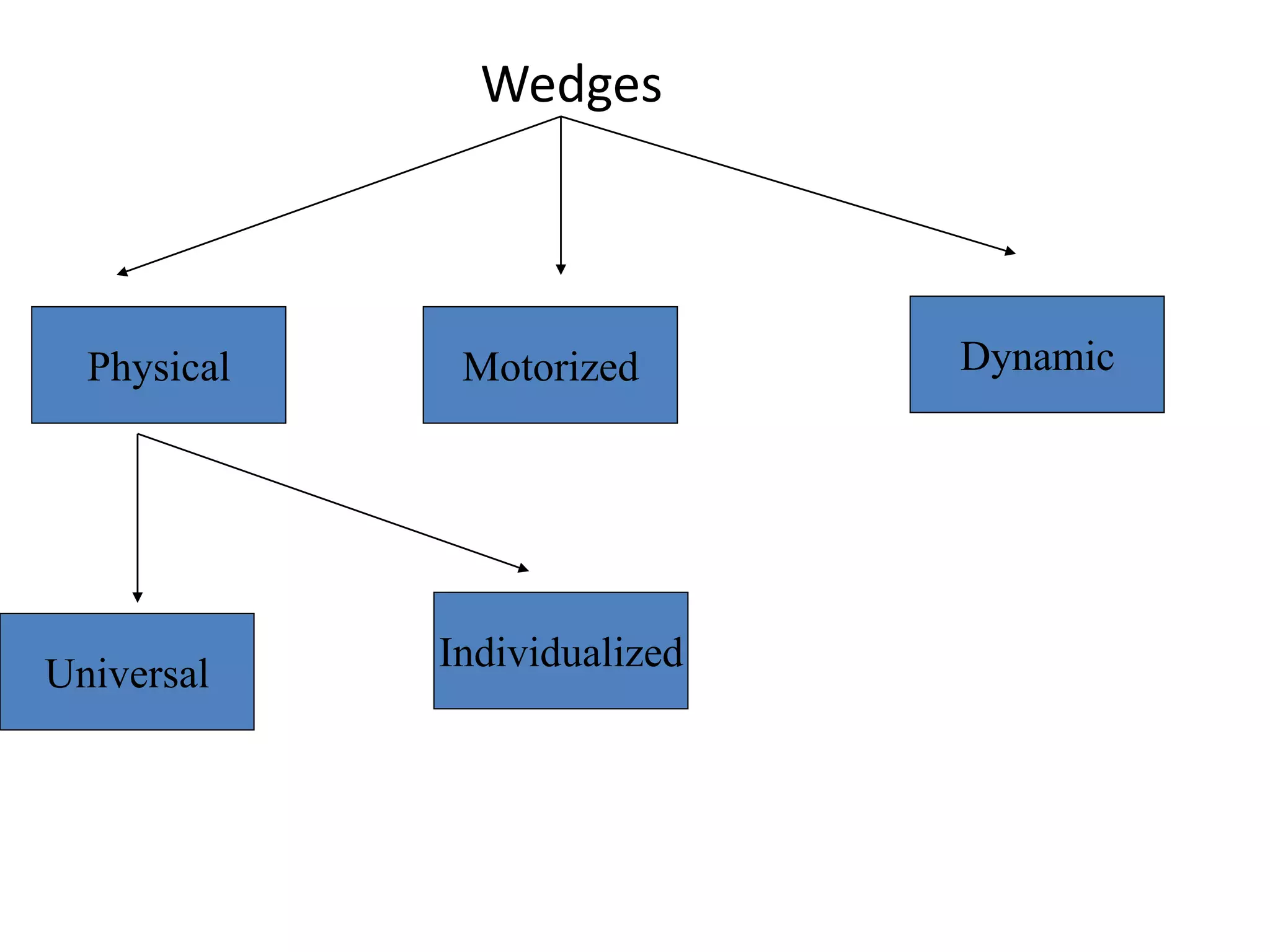
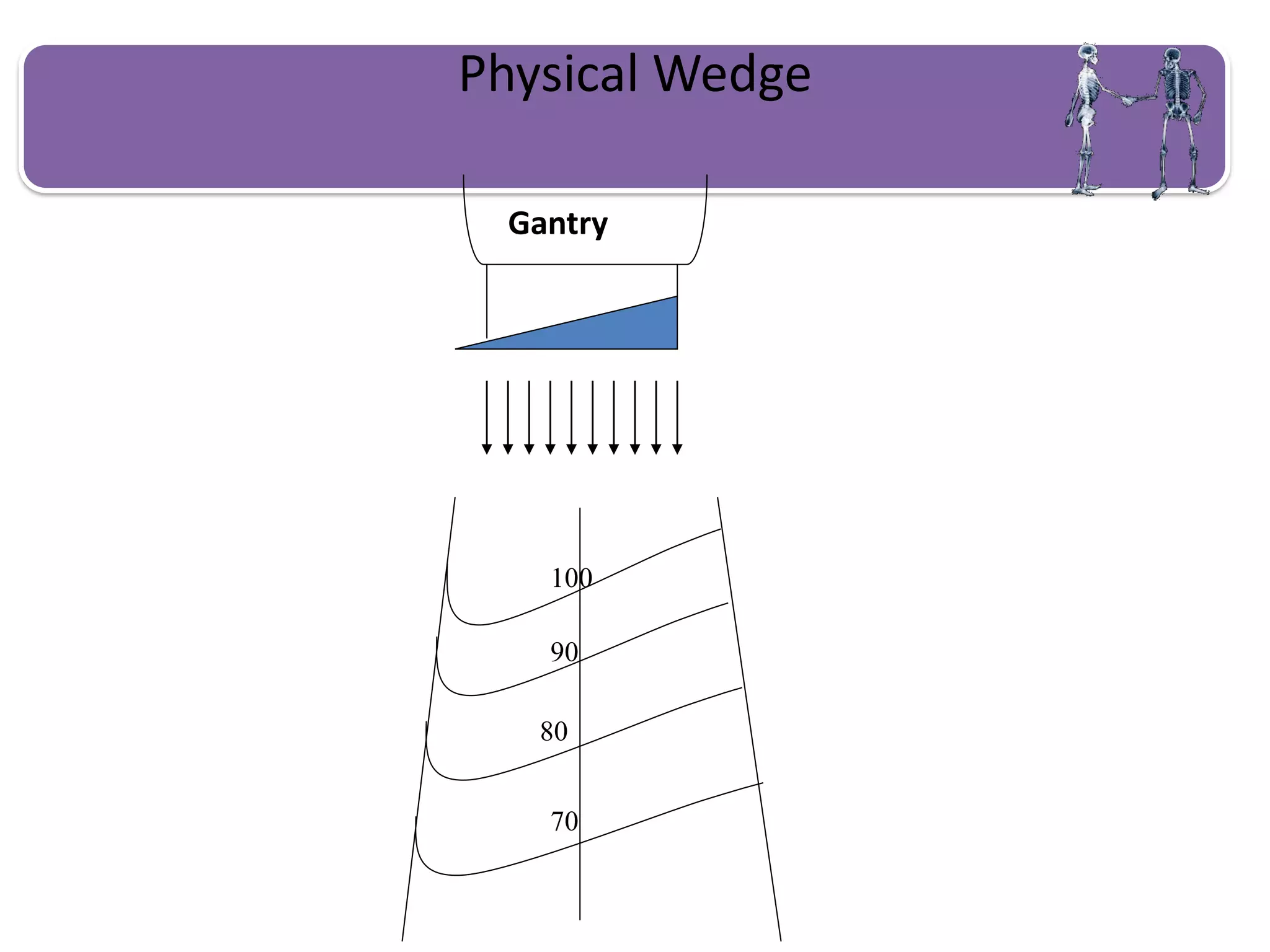
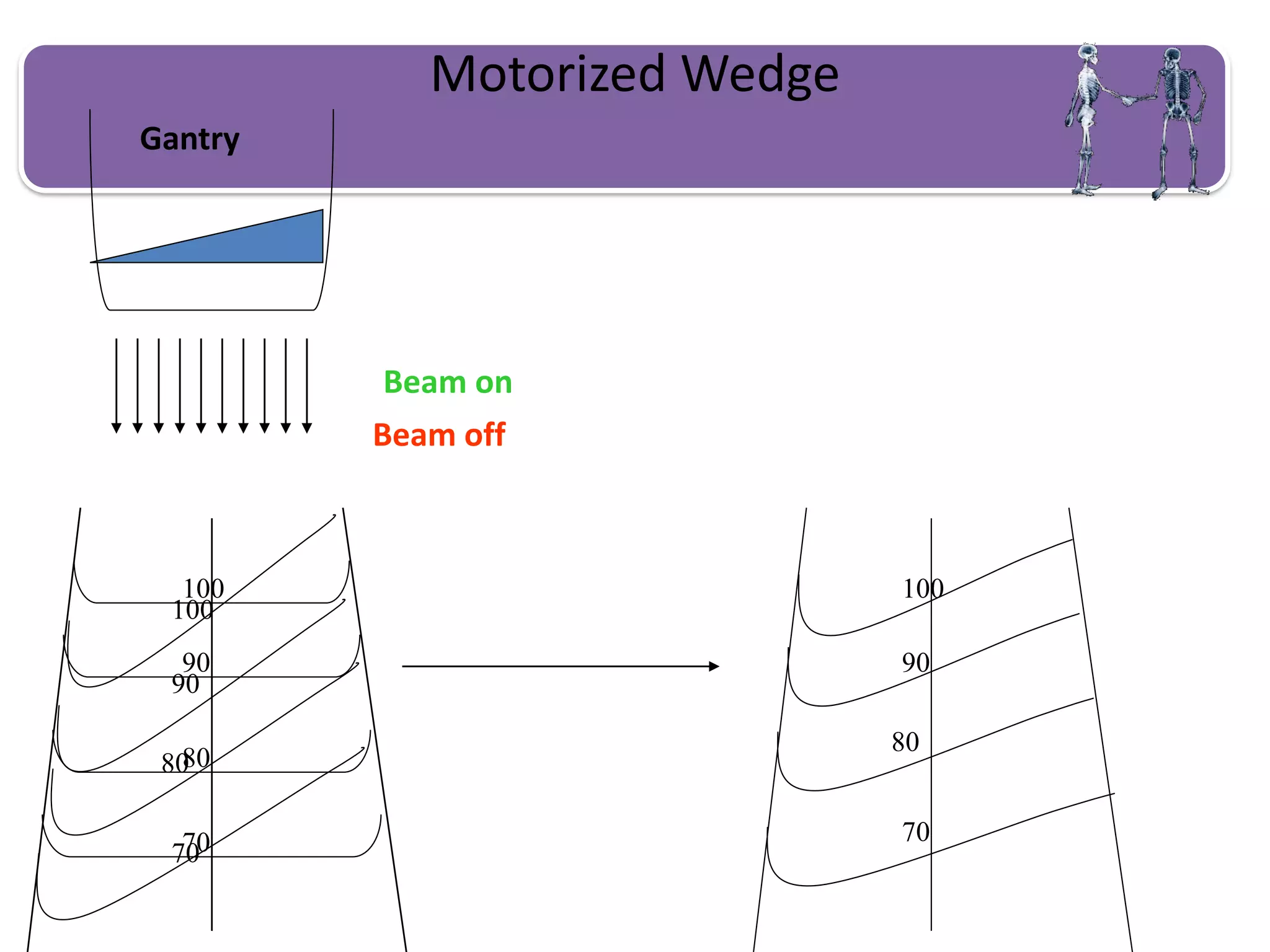
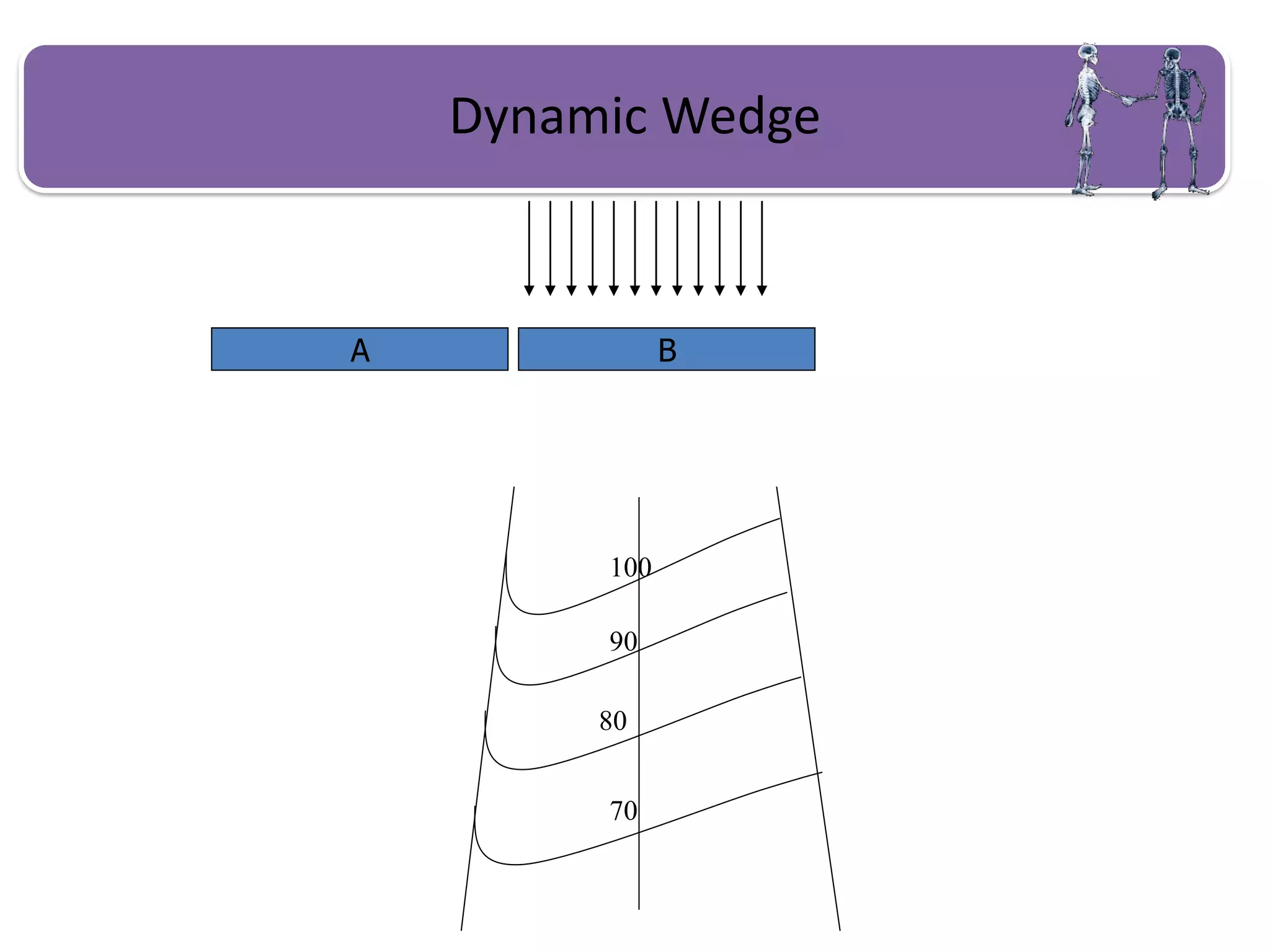
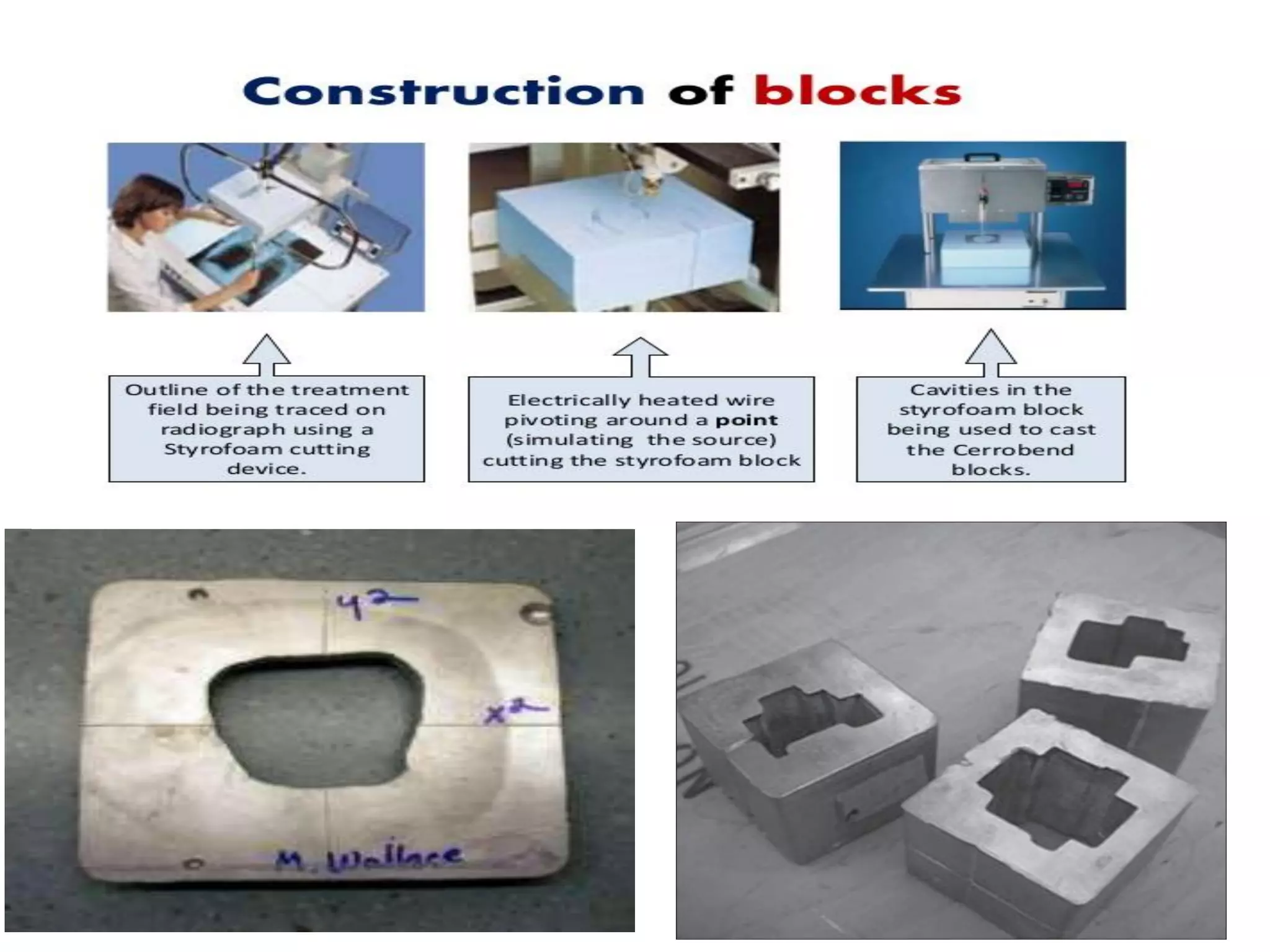
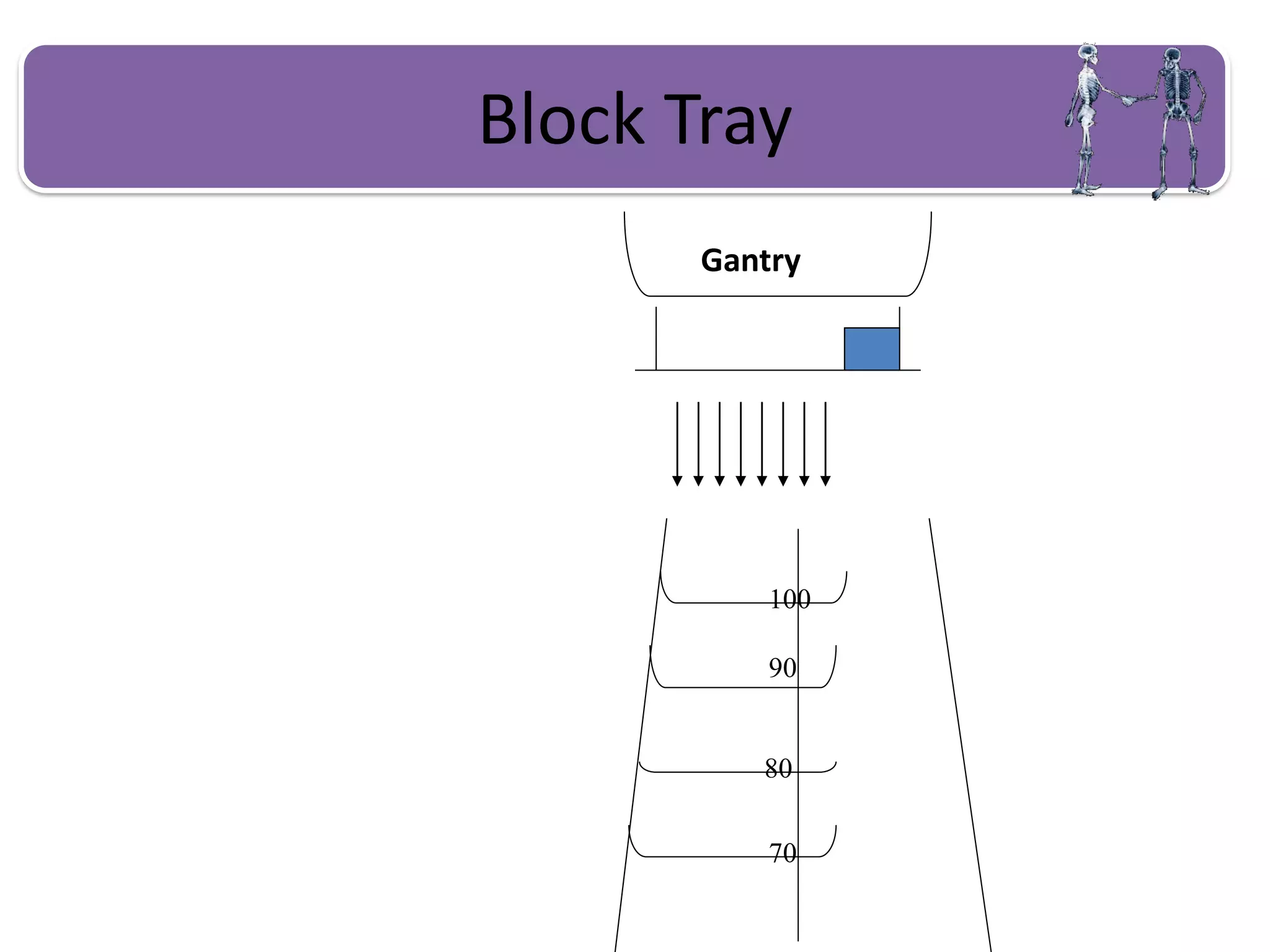
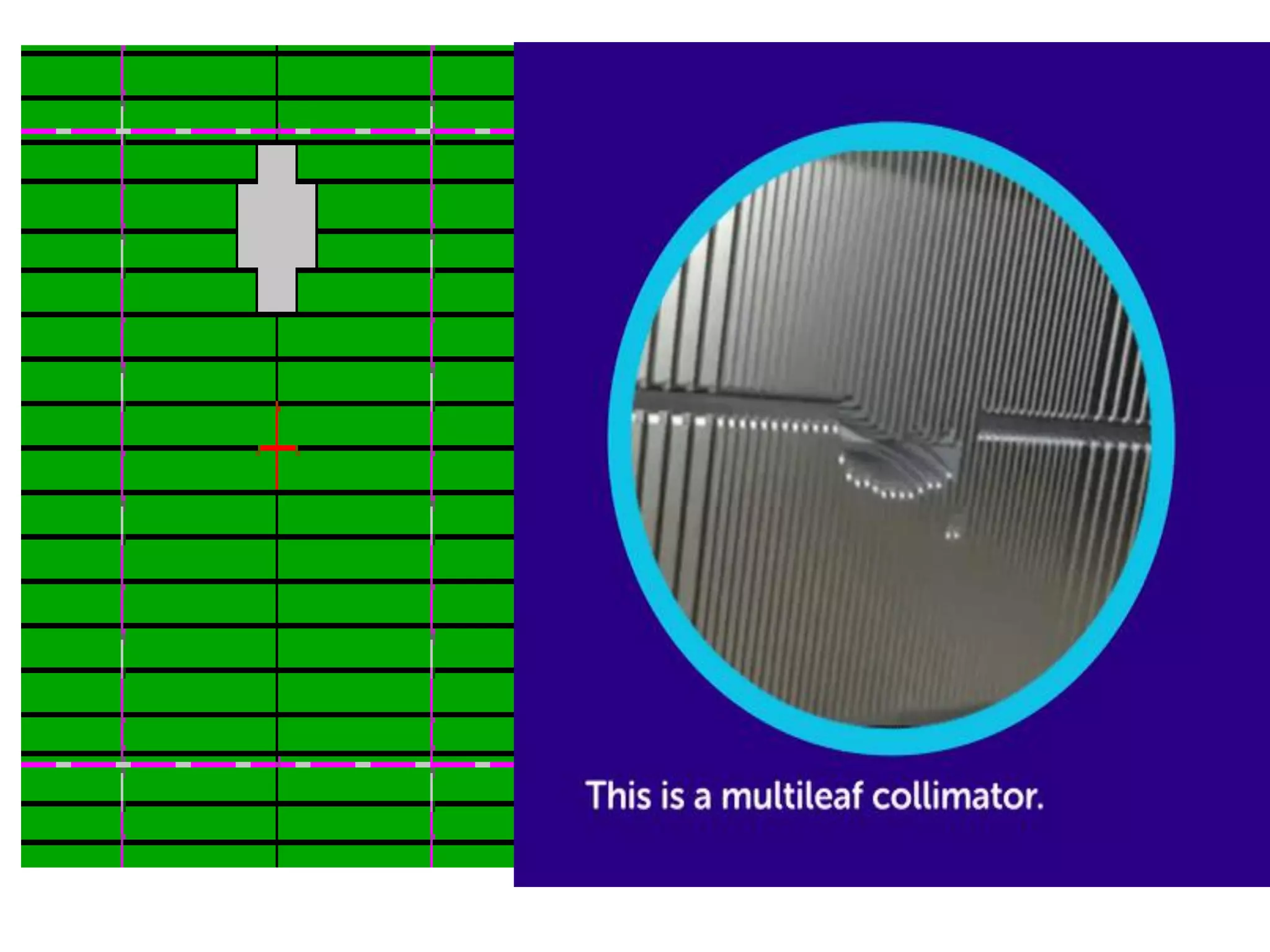
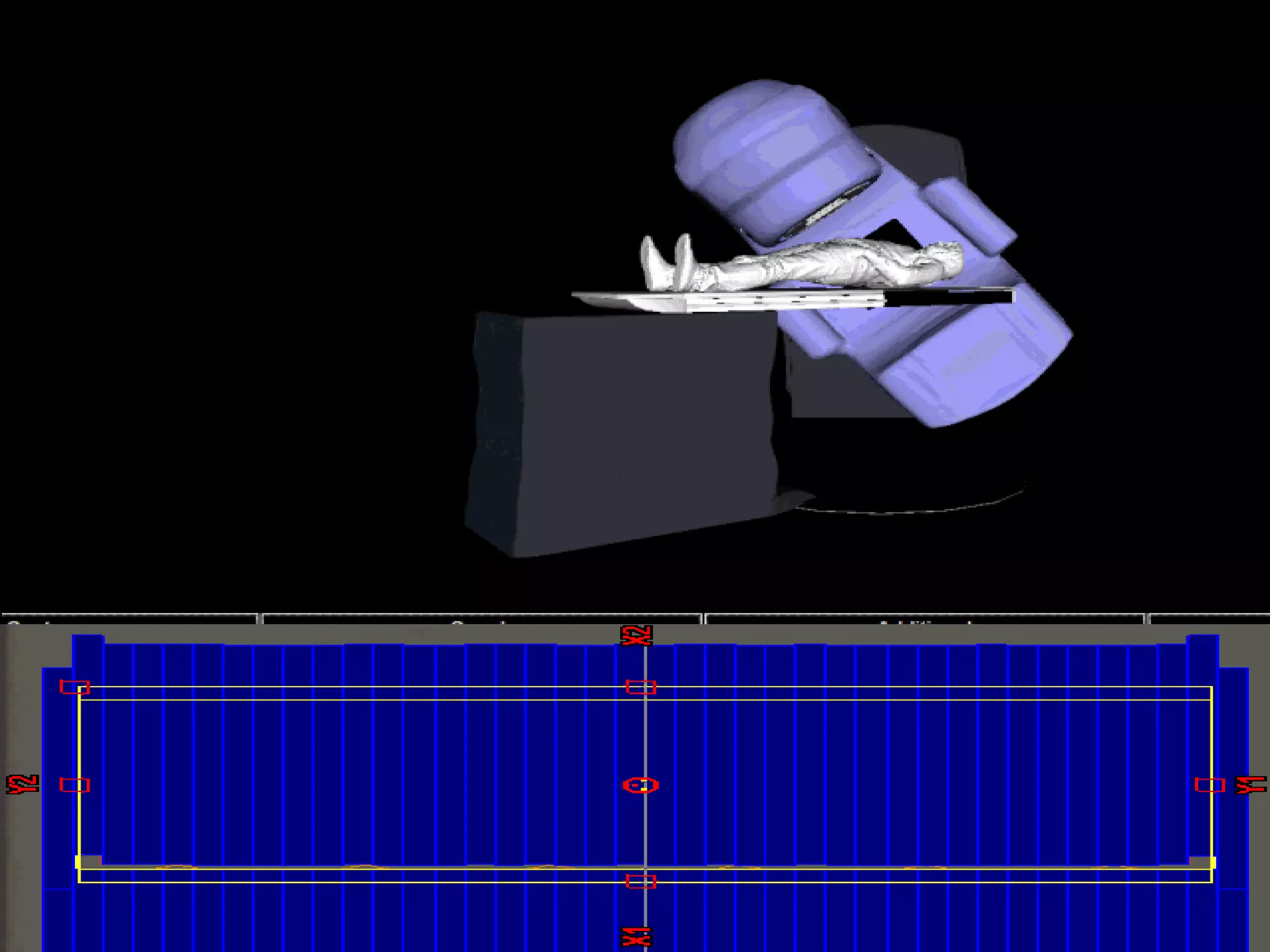
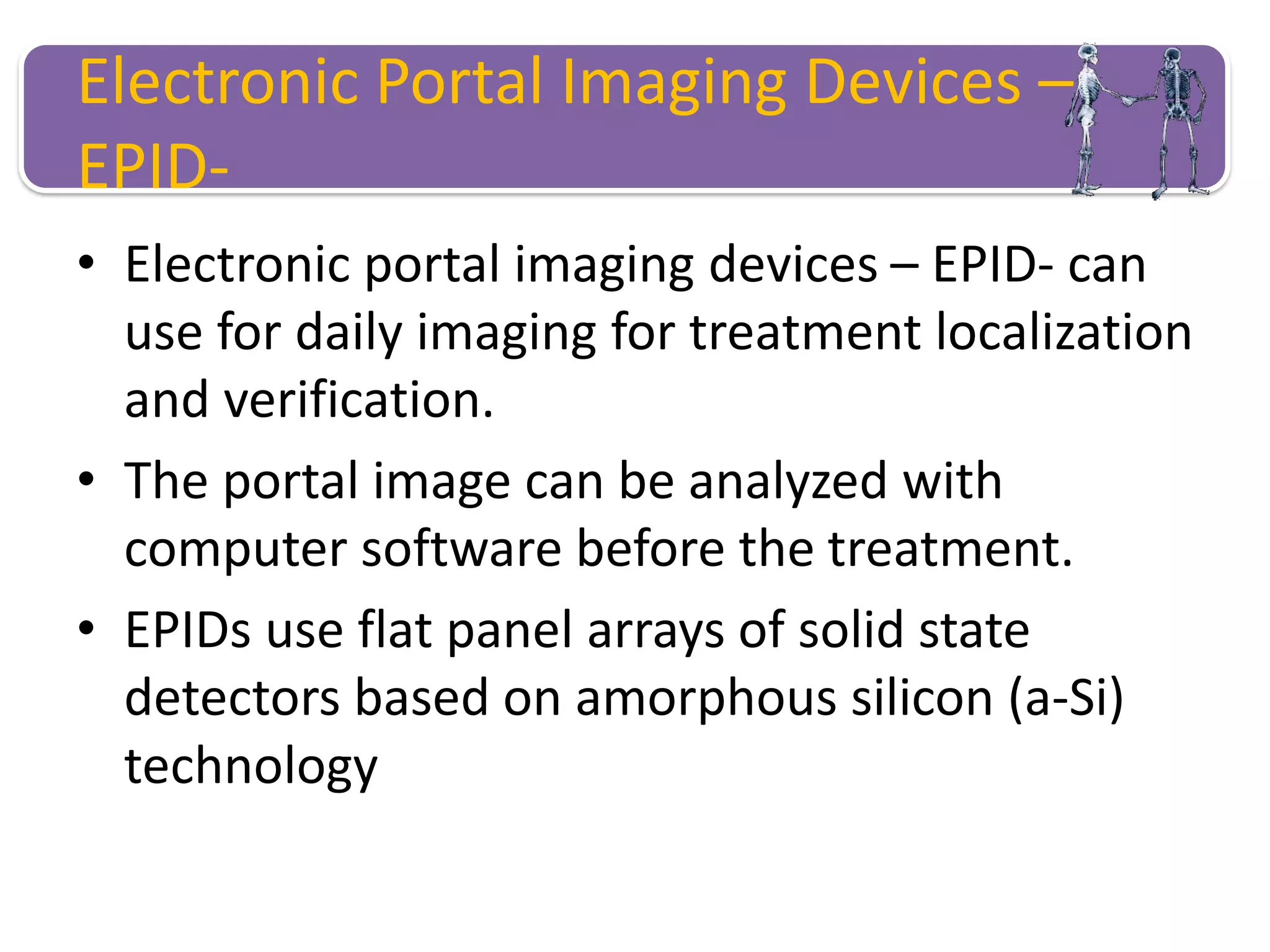
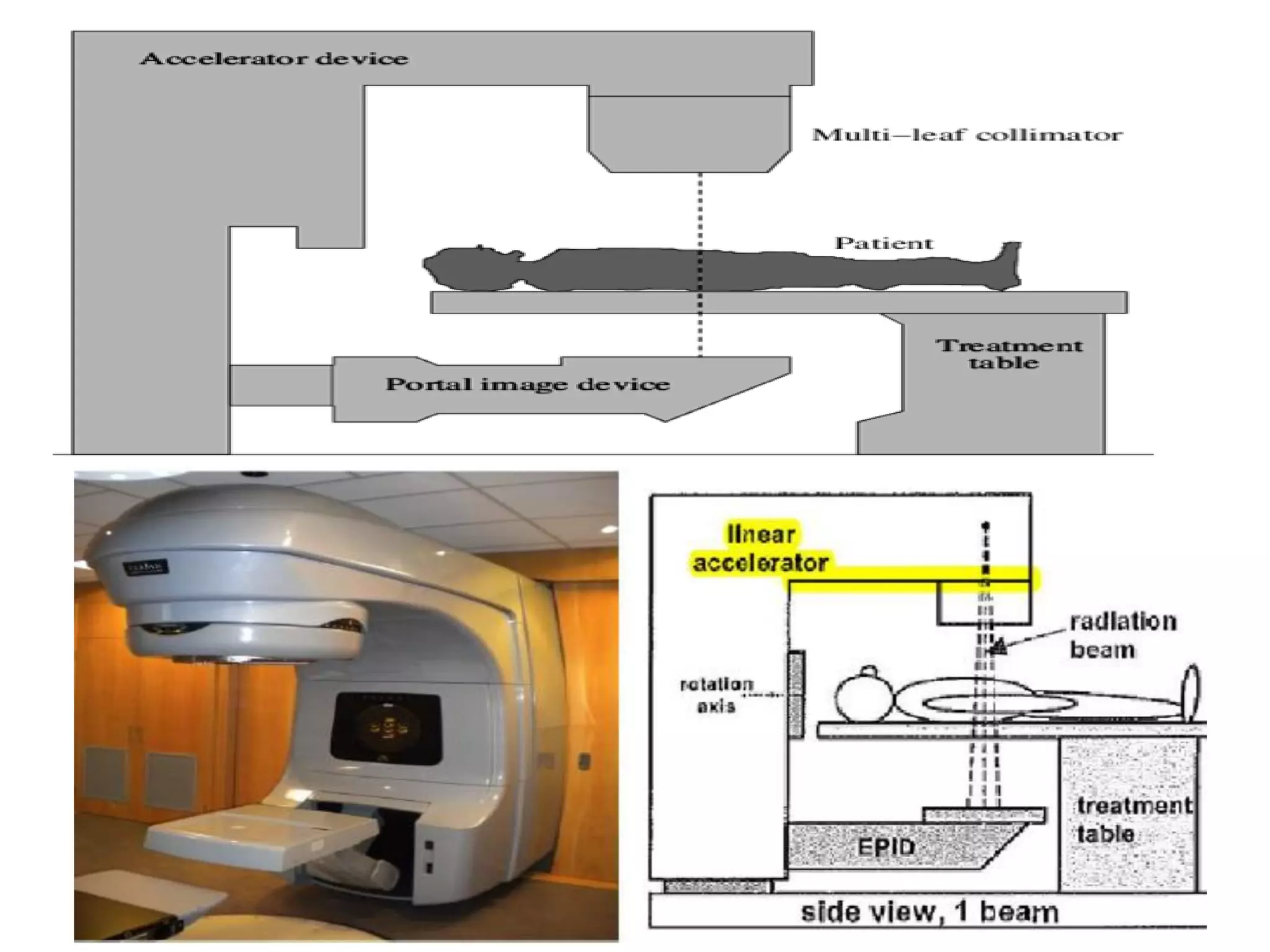
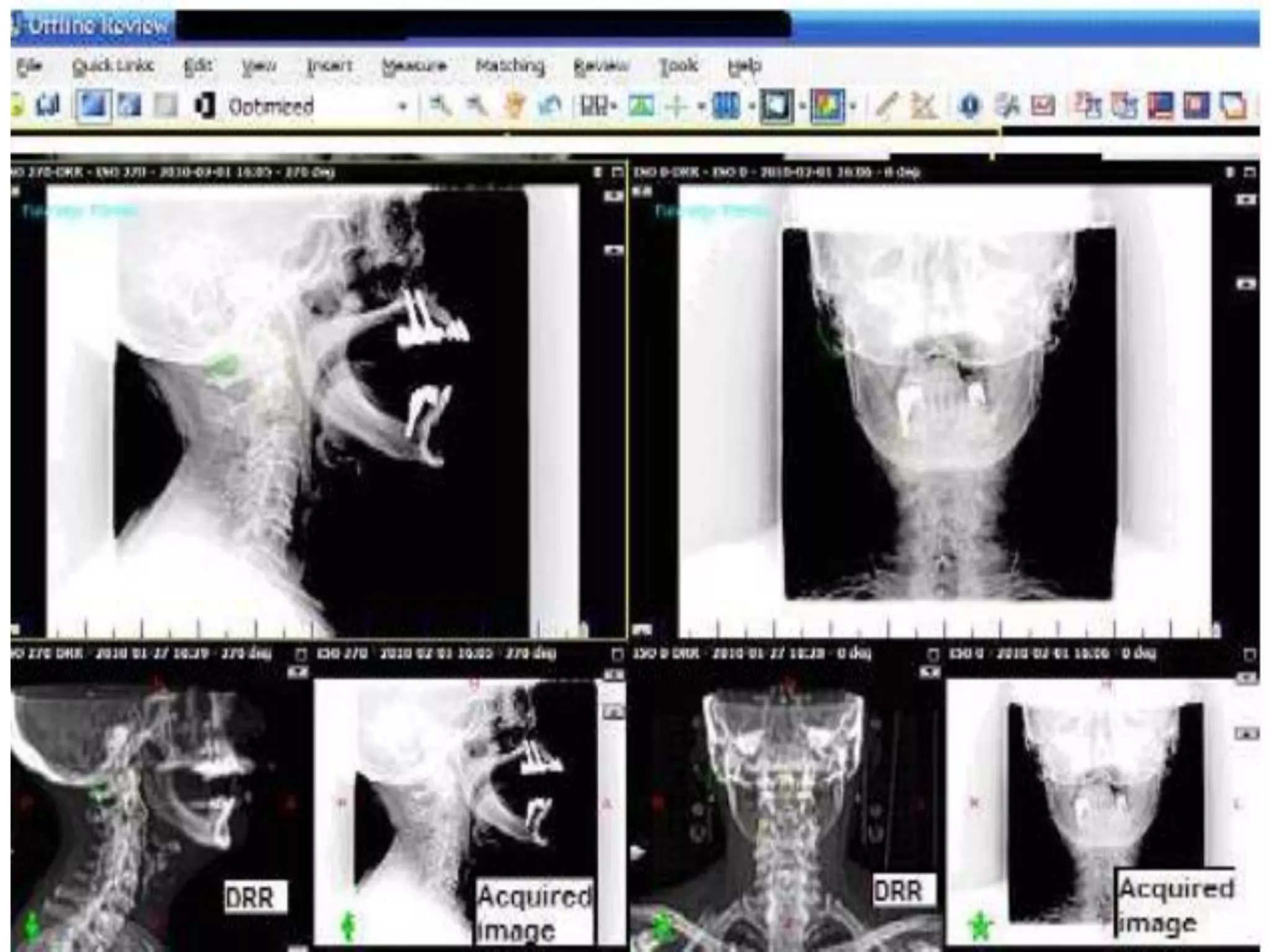
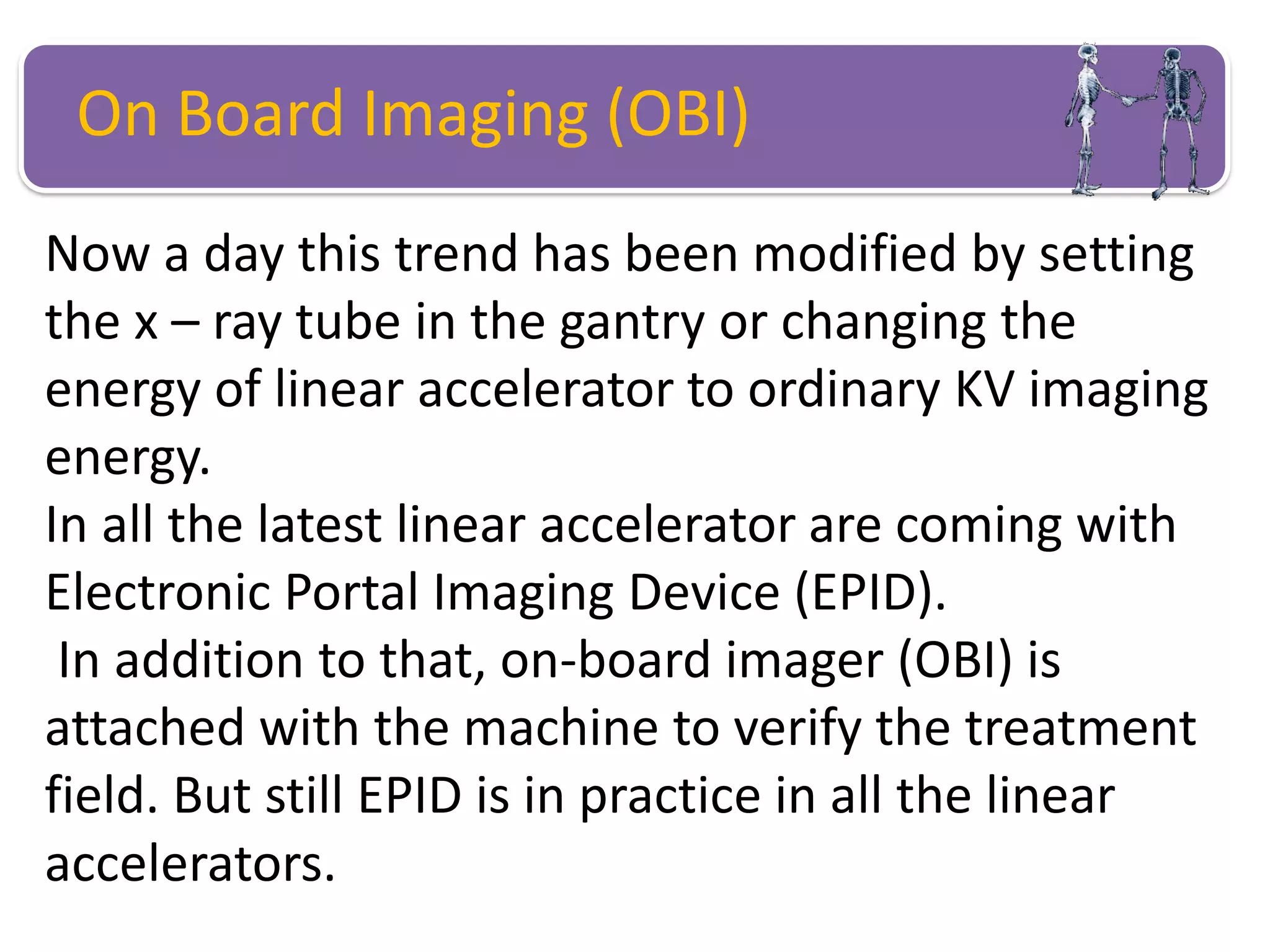
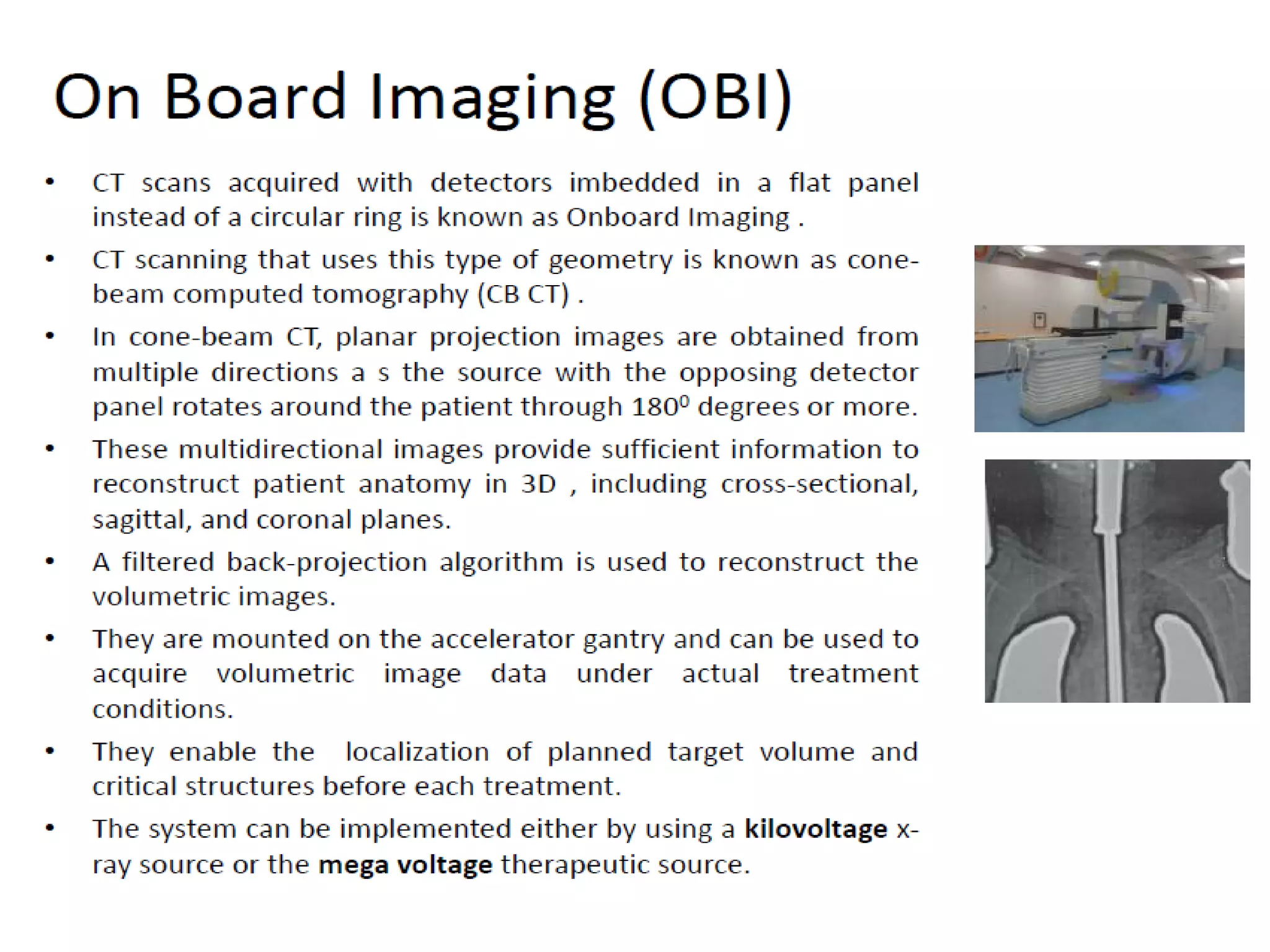
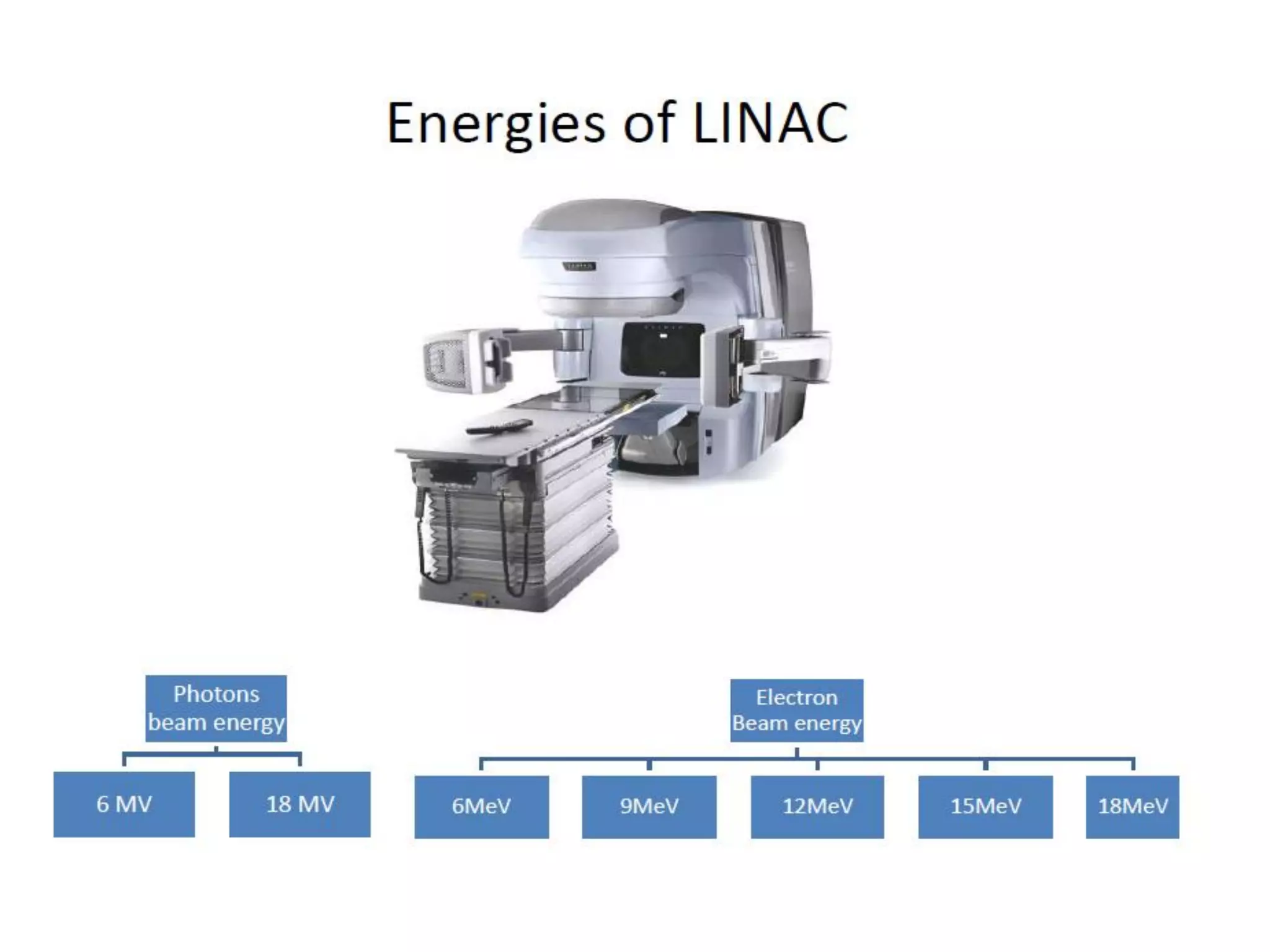
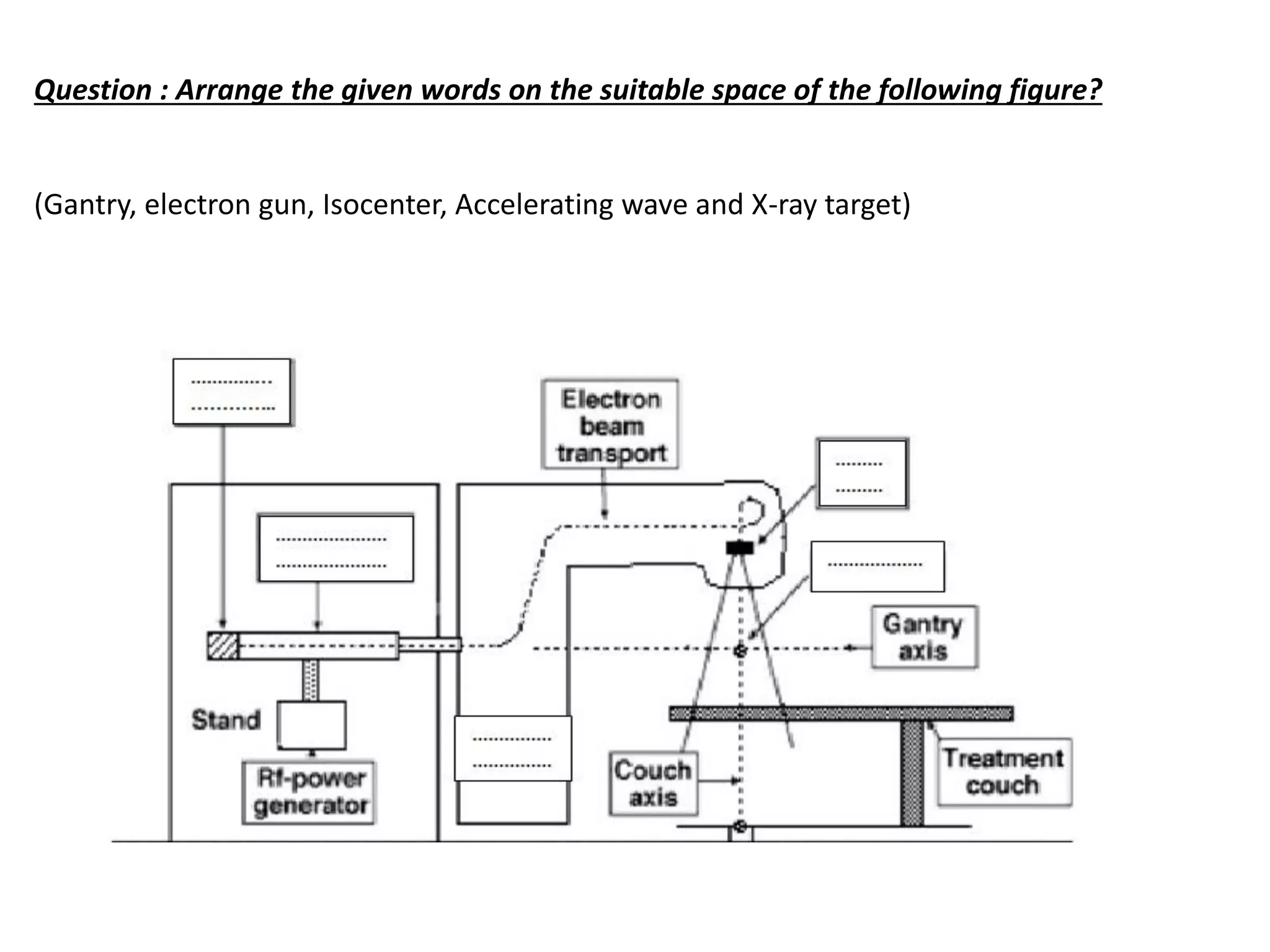
This document provides information about external beam therapy and linear accelerators used for radiation therapy. It discusses various components of linear accelerators including the electron injection system, microwave system, and beam collimation/applicator system. It also describes accessories used with linear accelerators like wedges (physical, motorized, dynamic), blocks, and multi-leaf collimators. Portal imaging devices are discussed as well as on-board imaging capabilities. Console control and safety features are also summarized. Key linear accelerator concepts like isocenter, treatment head, and beam flattening filters are defined.