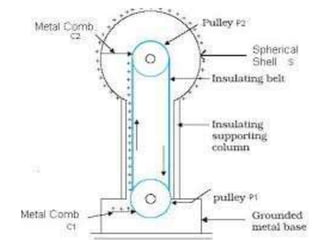
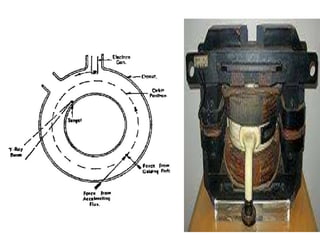
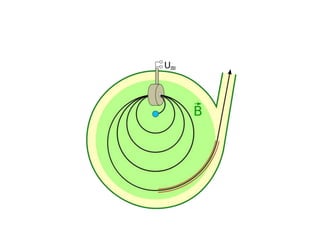
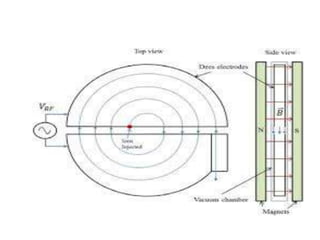
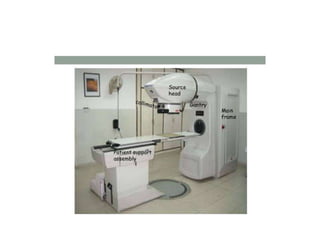
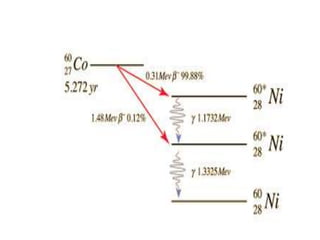
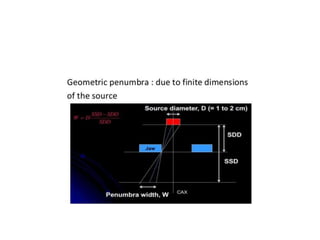
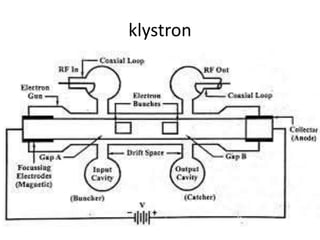
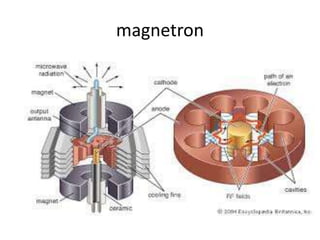
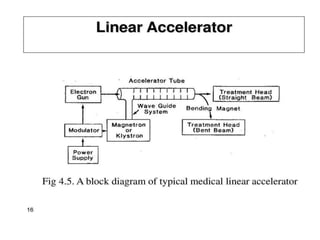
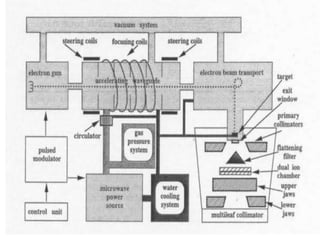
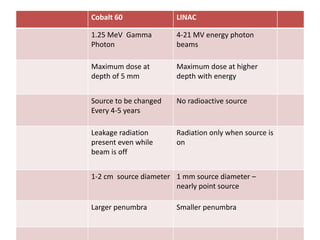
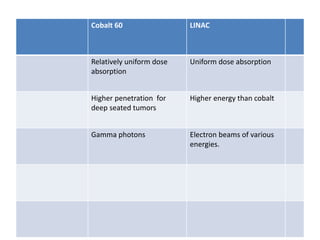
Teletherapy equipment and sources can use either cobalt-60 or linear accelerators (LINACs) to deliver radiation therapy. Cobalt-60 units contain a radioactive cobalt-60 source that produces high-energy gamma photons. LINACs use microwave cavities and magnetic fields to accelerate electrons, which then produce x-ray beams when striking a target. Both systems include a gantry that rotates a radiation head around the patient, and the head houses components like collimators, flattening filters, and targets/sources to shape and deliver the beam.