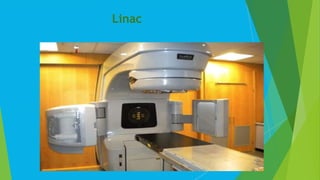
The document discusses linear accelerators (linacs) used in cancer treatment, detailing their development from bulky early models to advanced third-generation machines that offer improved precision and capability. Linacs generate high-energy x-rays to target tumors while sparing healthy tissue, utilizing microwave technology to accelerate electrons. Despite their effectiveness, operating costs are high, with initial investments ranging from one to three million dollars and annual operating expenses around $900,000.