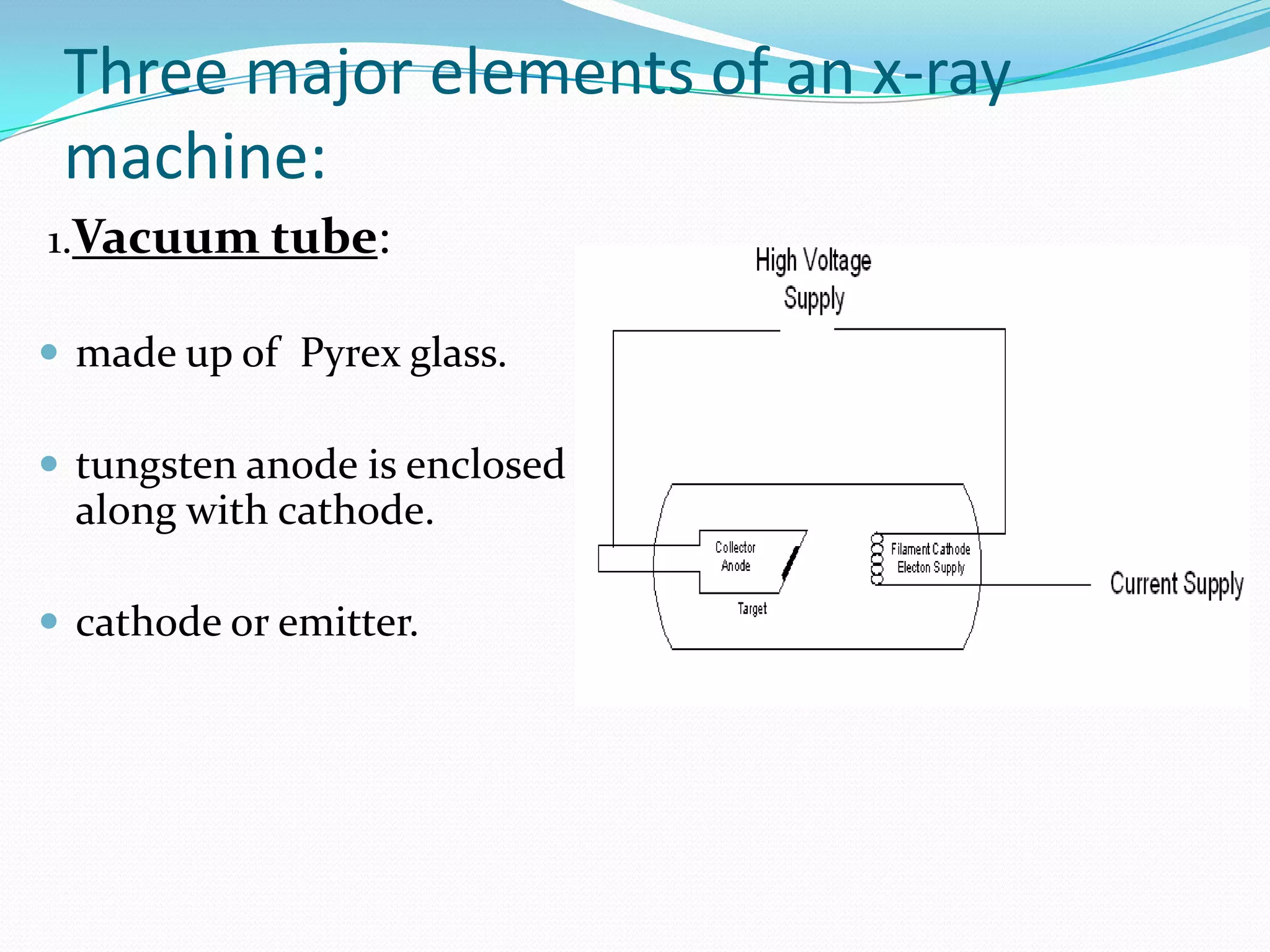
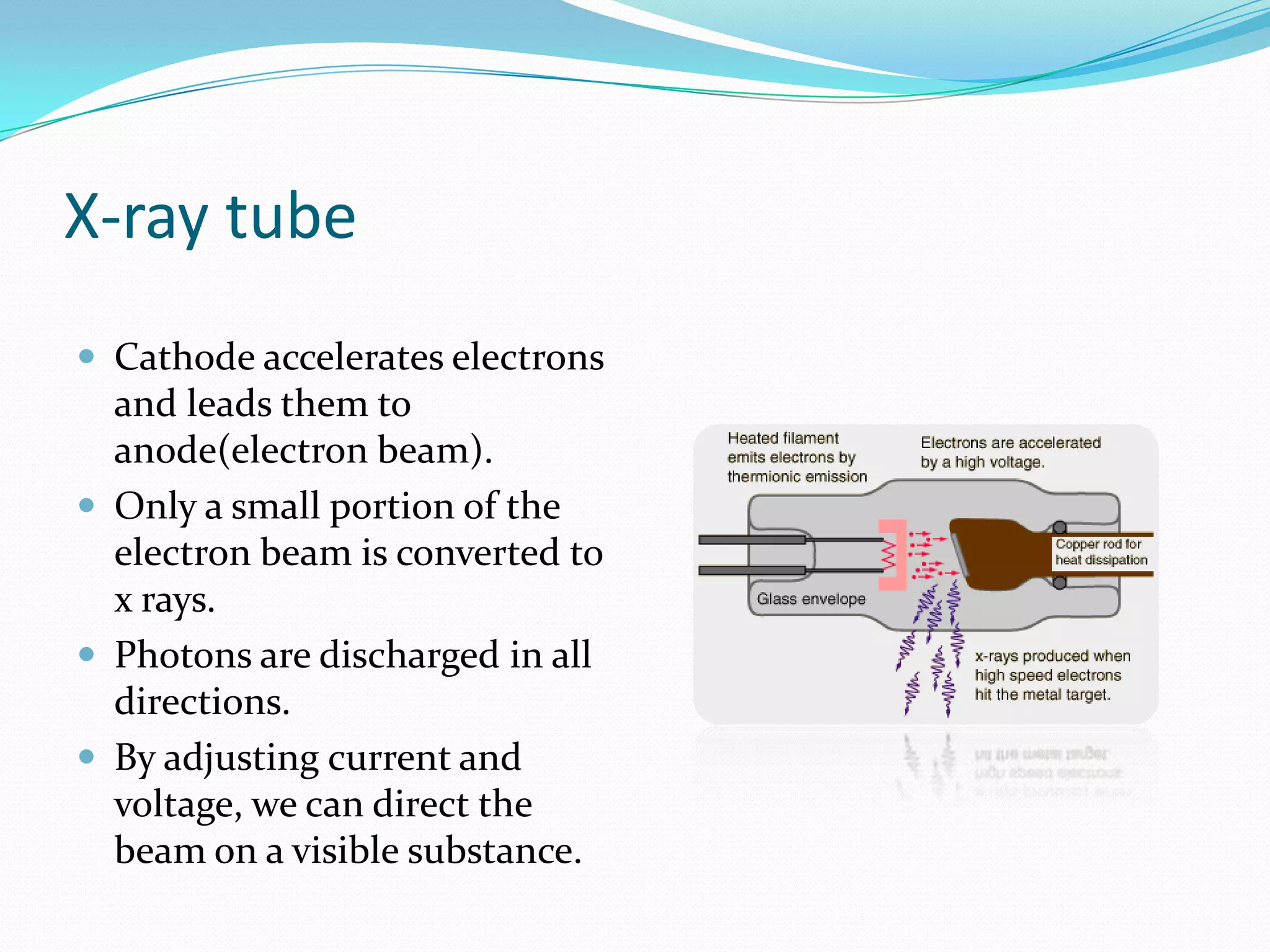
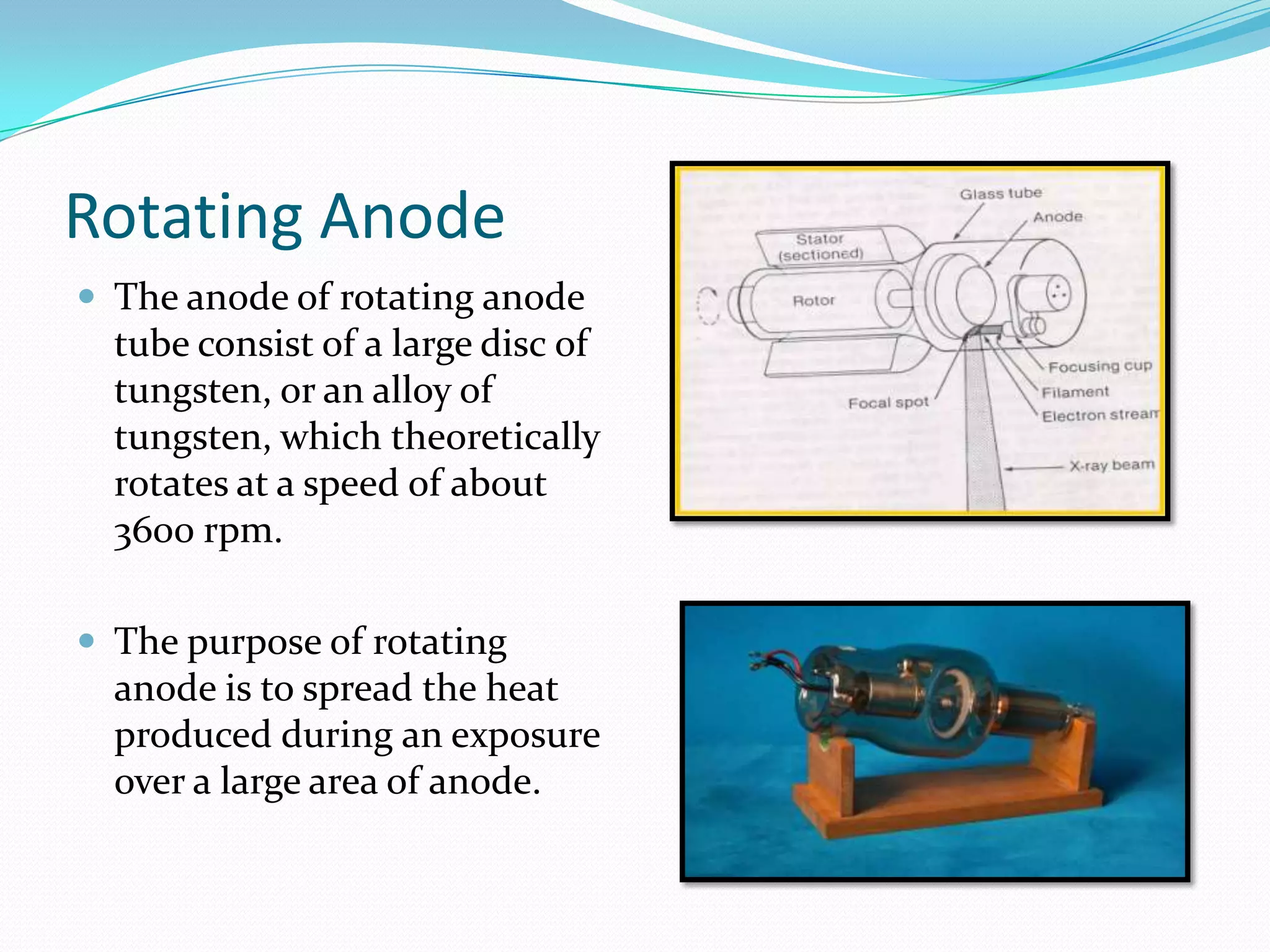
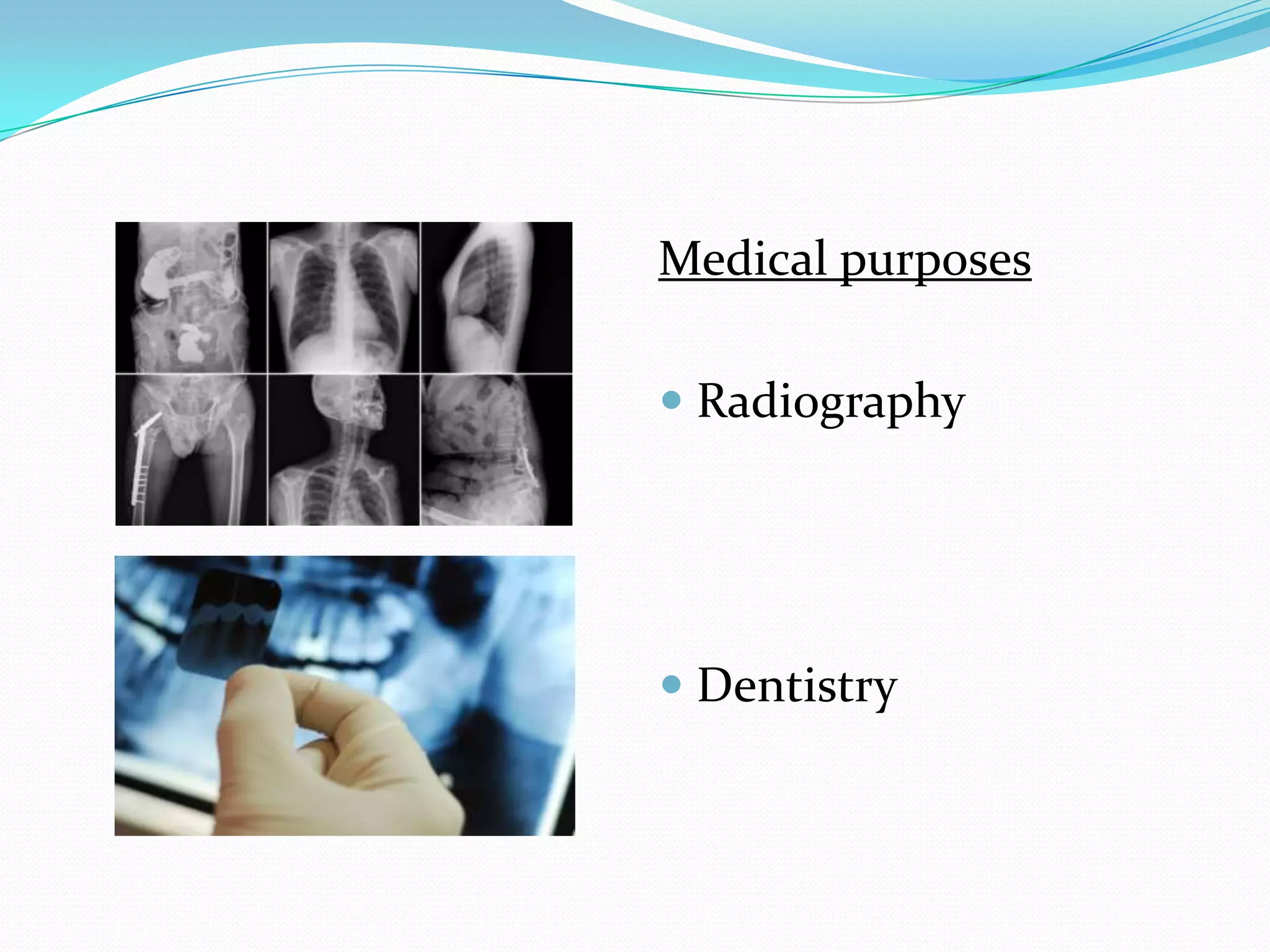
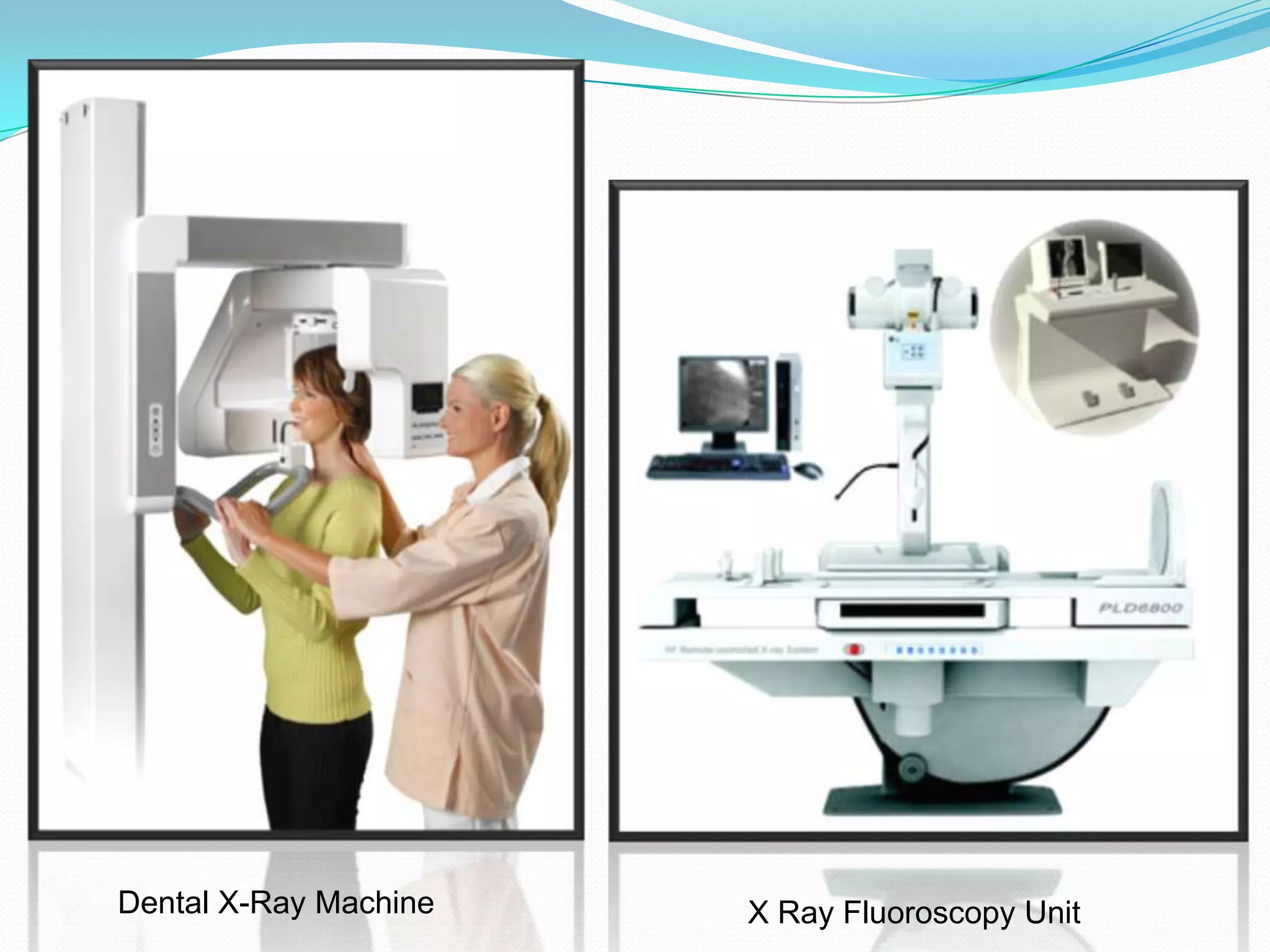
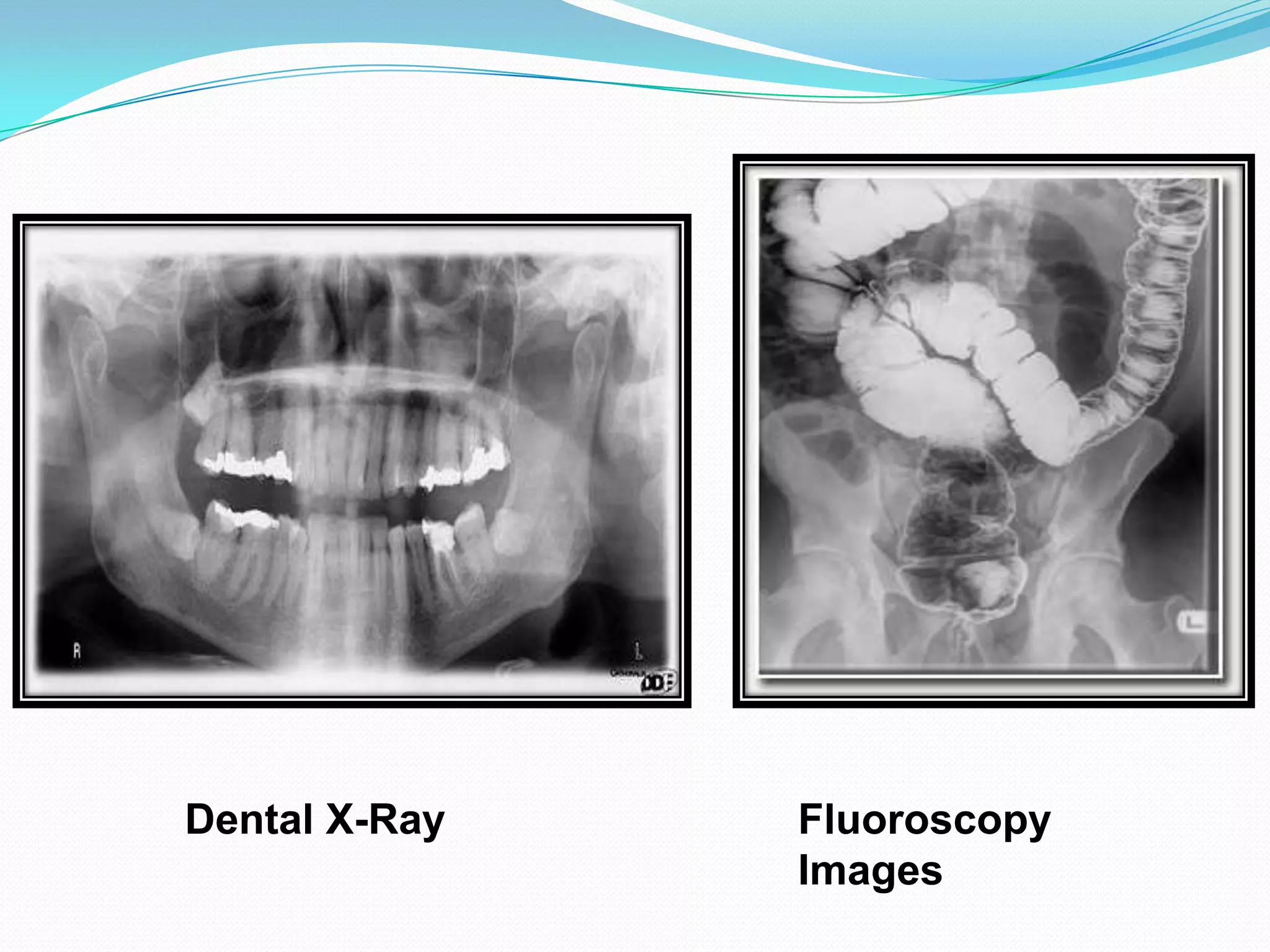
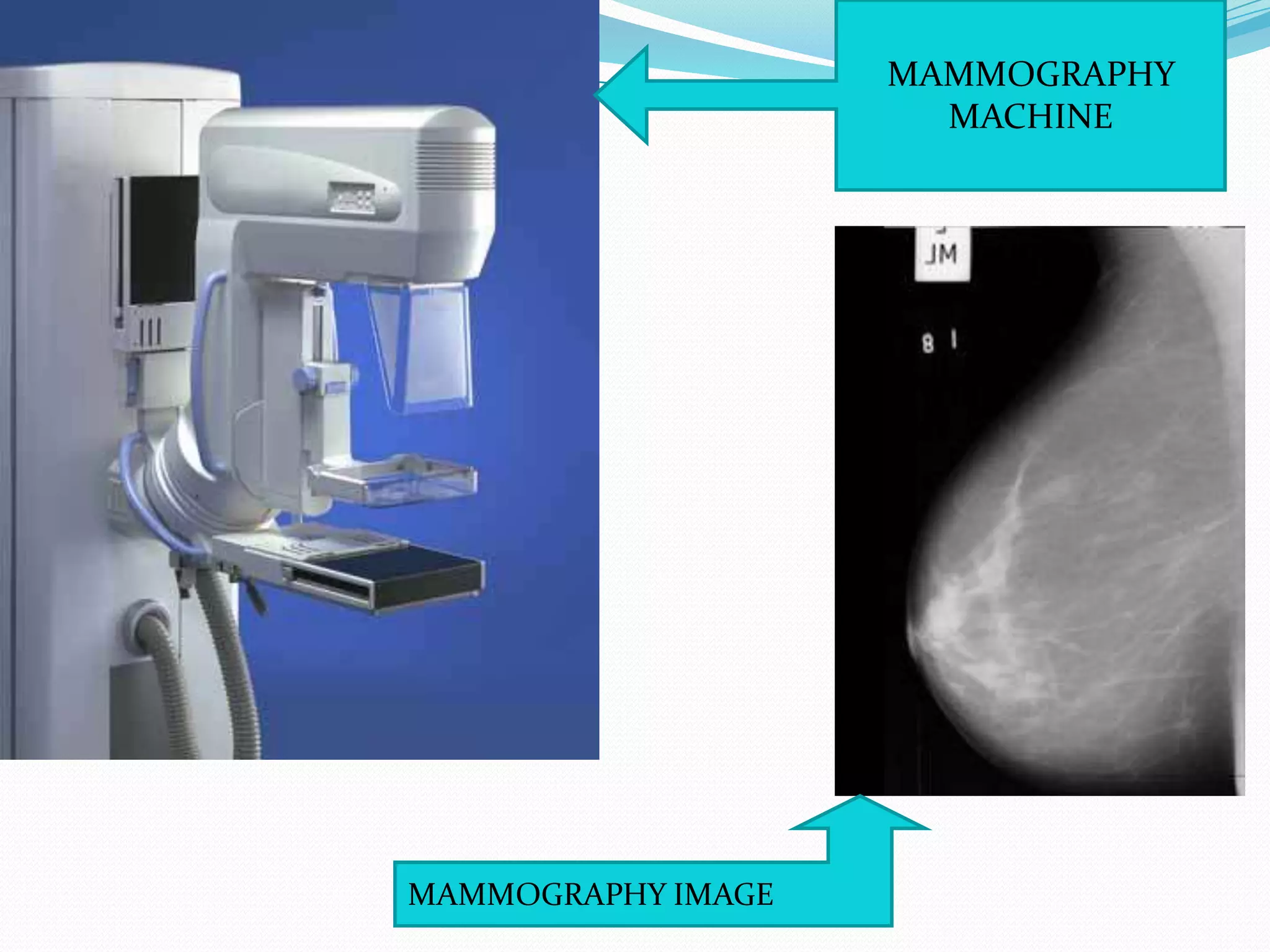
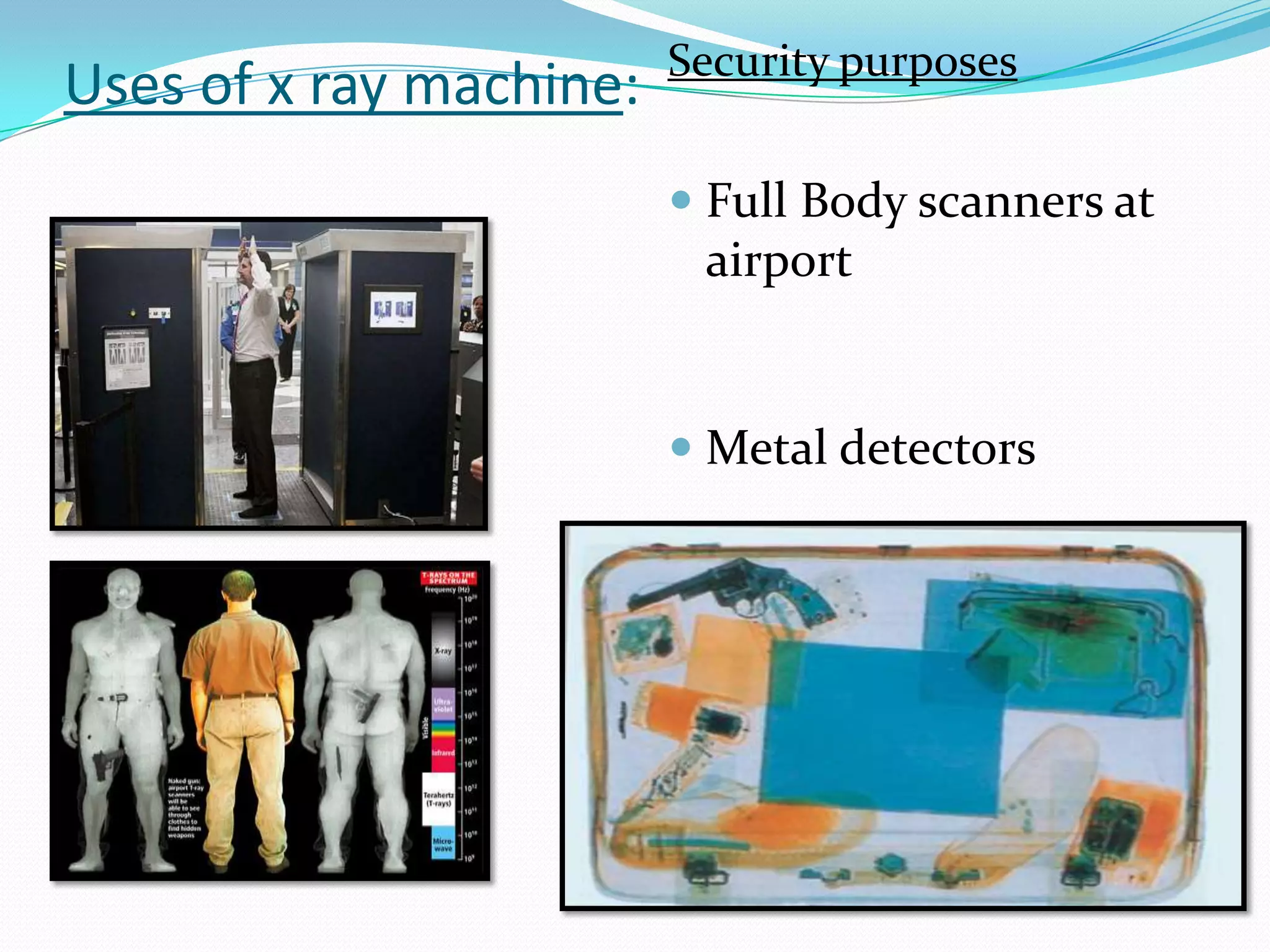
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between 0.01 to 10 nanometers that can penetrate some materials like soft tissue. The three main components of an x-ray machine are the vacuum tube, high voltage power source, and operating console. X-rays are produced when electrons are accelerated toward a metal target in the vacuum tube. They are used medically for diagnostic imaging like radiography and mammograms due to their non-invasive nature, though overexposure can increase cancer risk.