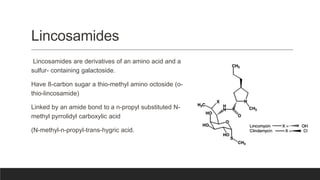
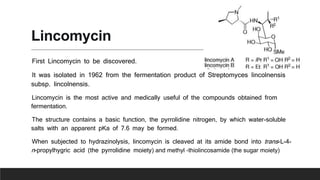
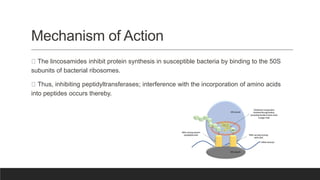
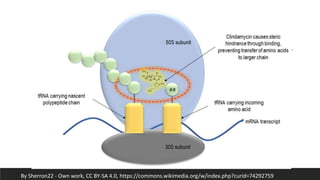
Lincosamides are a class of antibiotics that include lincomycin, clindamycin, and pirlimycin. They are derived from the fermentation of Streptomyces bacteria and contain a sugar moiety linked to a pyrrolidine carboxylic acid. Clindamycin is a semi-synthetic derivative of lincomycin created by replacing the 7-hydroxy group with chlorine. Lincosamides inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit. They are primarily effective against Gram-positive bacteria and anaerobes but not most Gram-negatives.