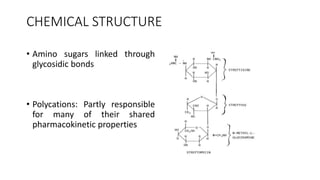
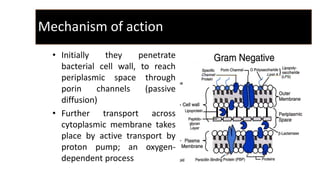
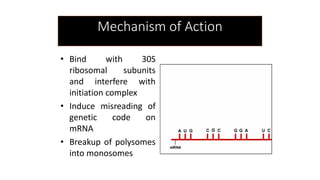
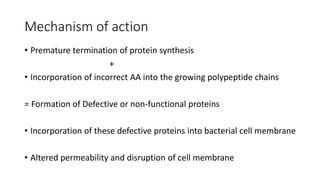
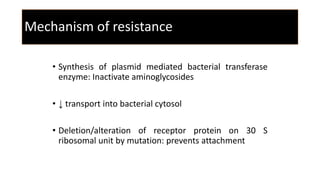
Aminoglycoside antibiotics consist of amino sugars linked by glycosidic bonds. This class includes drugs like streptomycin, gentamicin, and amikacin. They act by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, interfering with protein synthesis and causing defective or non-functional proteins. Their use requires monitoring due to risks of ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. They are effective against aerobic gram-negative bacteria and are used to treat infections like pneumonia, UTIs, and tuberculosis. Individual drugs have varying spectrums of activity, with gentamicin and tobramycin being effective against pseudomonas.