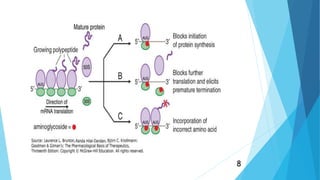
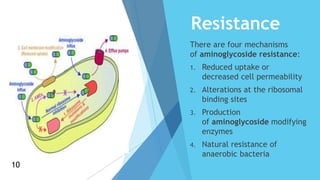
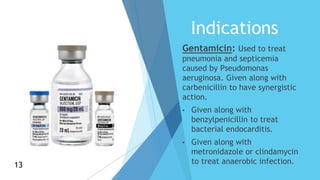
Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics that consist of amino sugars attached to a hexose ring. They are bactericidal and used to treat infections caused by aerobic gram-negative bacteria. Aminoglycosides work by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit and inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. They are not absorbed orally and are administered via injection or topically. Common adverse effects include ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and neuromuscular blockade. Aminoglycosides require monitoring due to their toxicity profile.