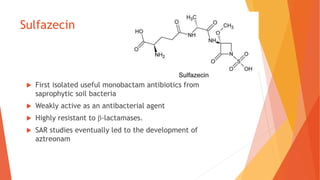
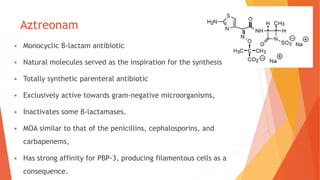
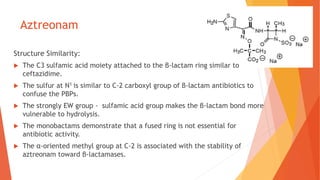
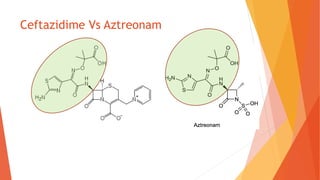
The document discusses monobactam antibiotics, focusing on sulfazecin and aztreonam, detailing the structural characteristics that affect their antibacterial activity and stability against β-lactamases. It highlights the development of tigemonam, an orally active monobactam with a spectrum of activity similar to aztreonam, particularly effective against gram-negative bacteria. The document emphasizes the importance of specific chemical groups in enhancing antibacterial potency and resistance to enzymes.