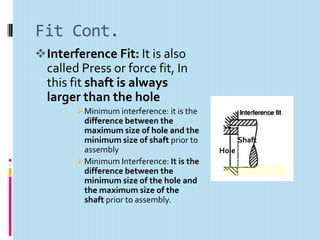
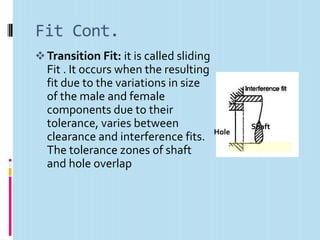
This document discusses interchangeable manufacture, terminology for limits and fits. It defines interchangeable manufacture as parts that are identical enough to be mutually interchangeable in any device of the same type. It provides examples like bottle caps, rims, tires. The advantages are easy replacement, assembly, repair by minimizing time and cost.
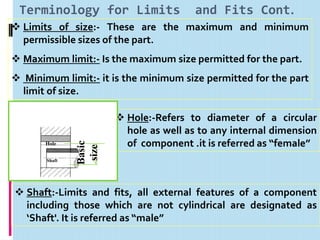
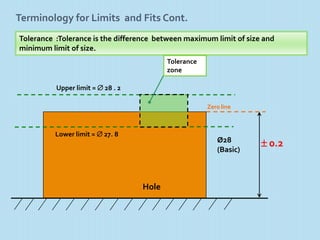
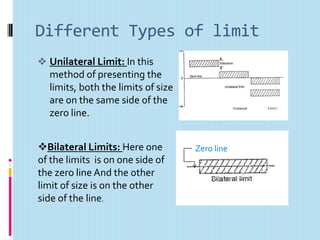
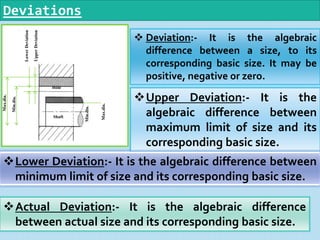
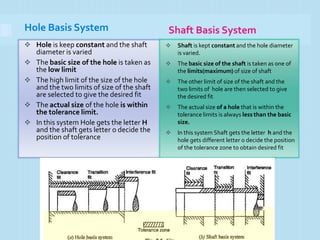
It then defines terminology for limits and fits, including basic size, tolerance, allowance, deviations, fits. It explains hole basis and shaft basis systems for defining limits and fits between holes and shafts to achieve clearances, interference or transition fits.