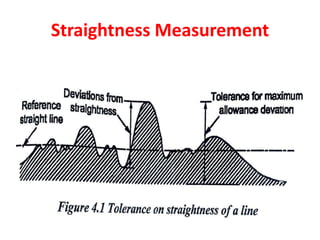
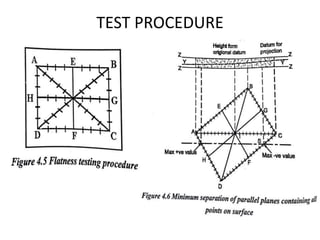
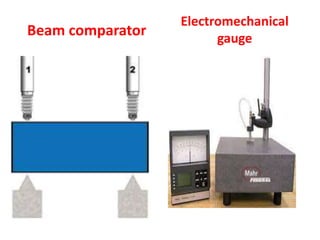
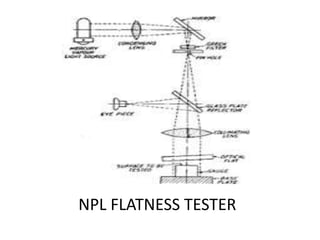
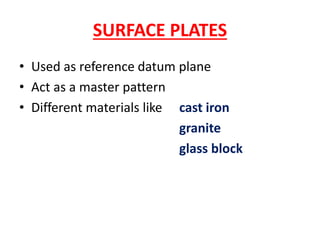
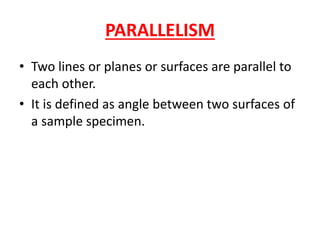
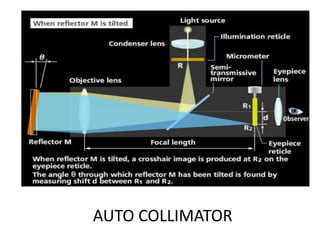
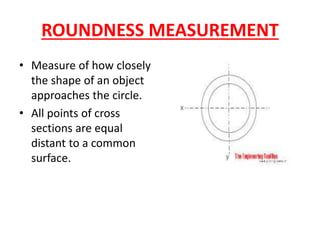
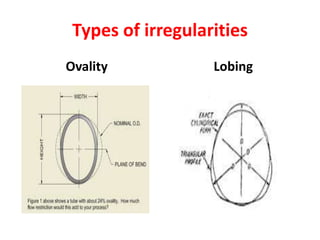
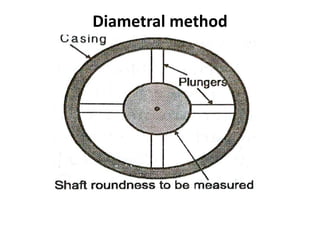
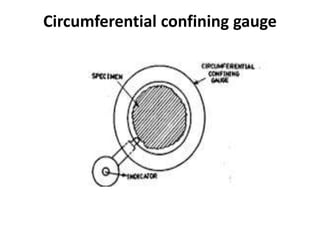
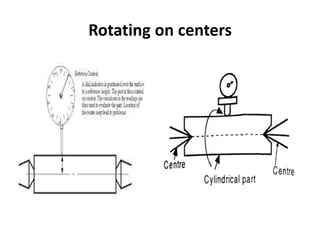
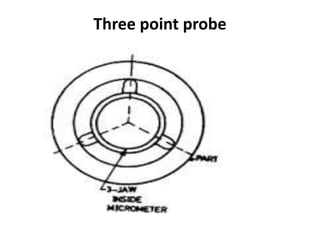
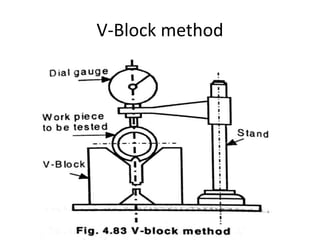
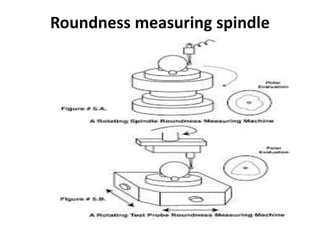
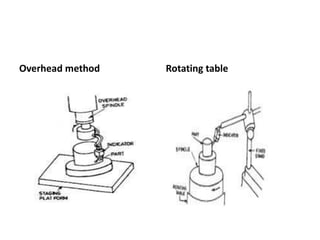
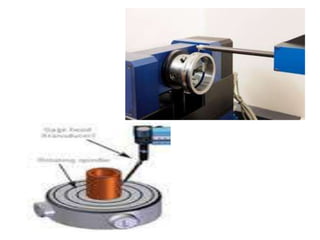
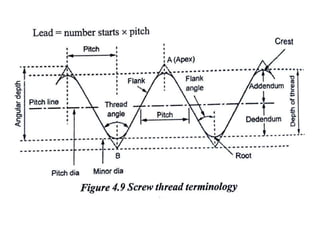
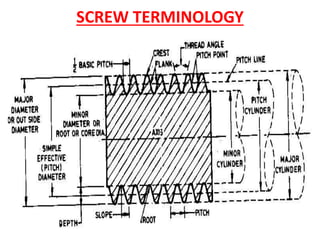
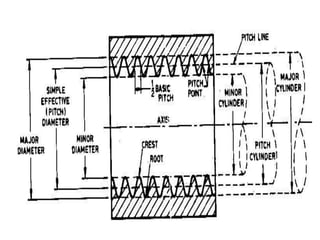
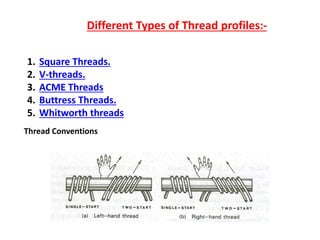
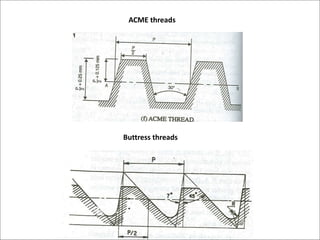
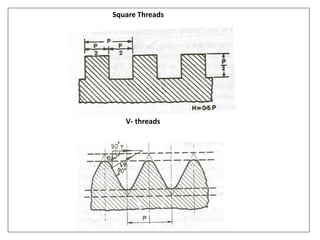
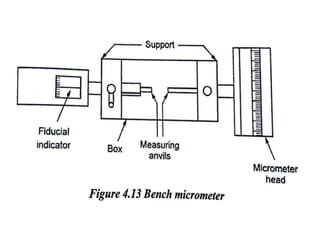
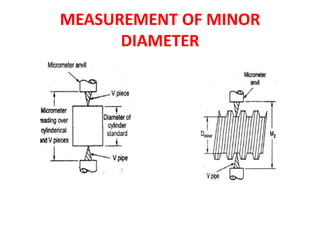
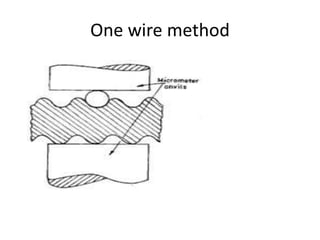
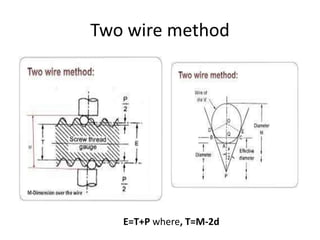
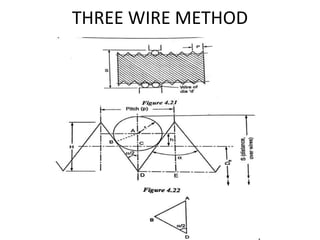
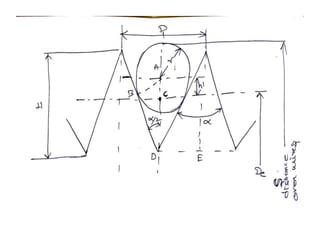
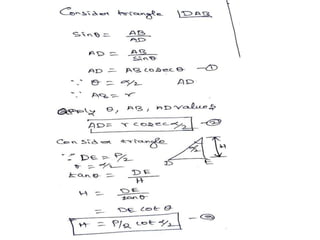
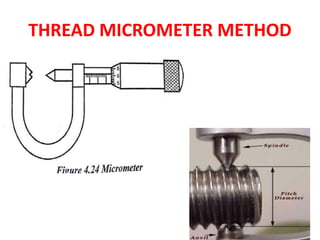
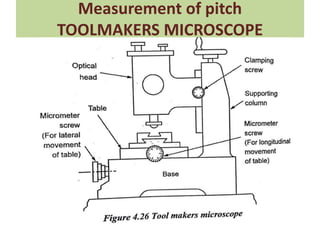
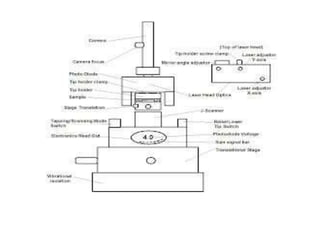
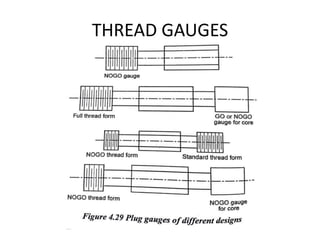
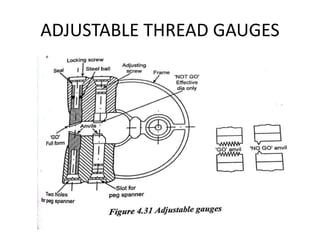
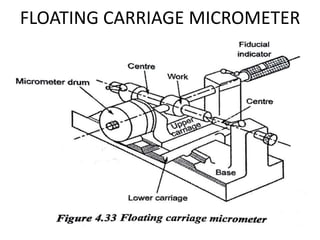
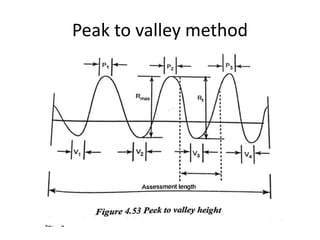
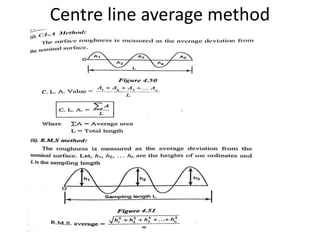
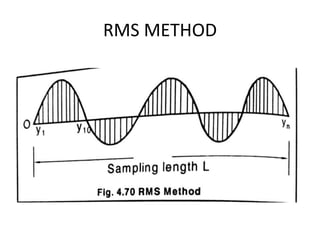
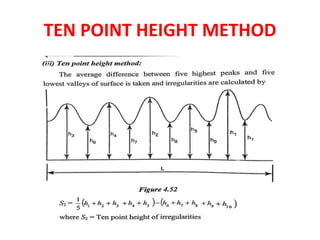
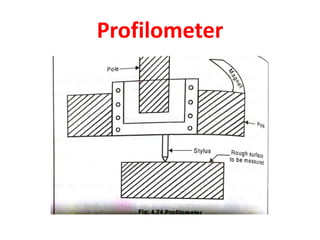
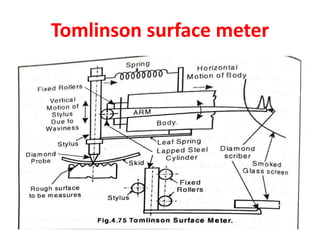
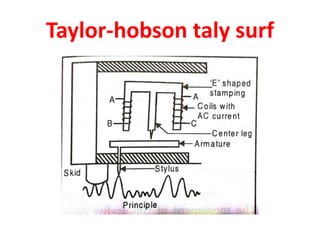
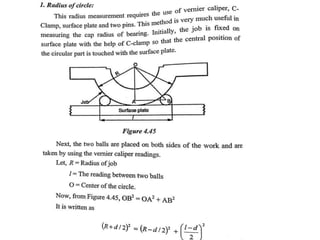
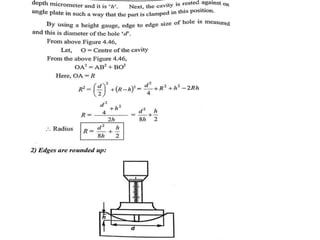
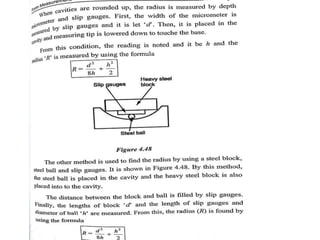
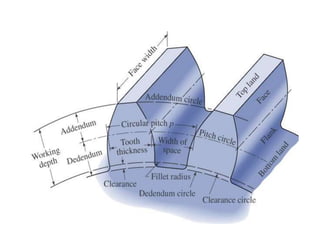
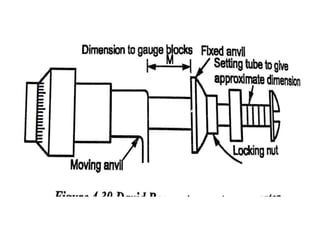
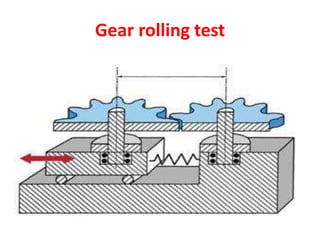
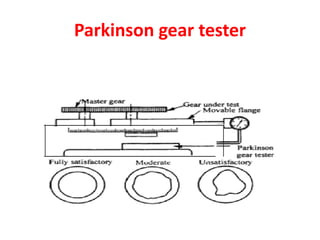
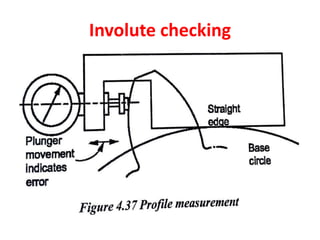
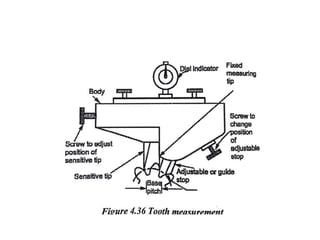
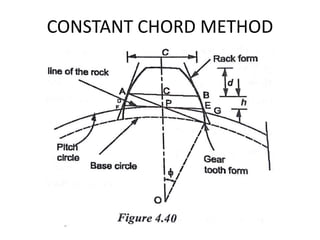
This document discusses various form measurement principles and methods, including straightness, flatness, thread, gear, and surface finish measurement. It describes key concepts like straightness, flatness, and parallelism. Methods for measuring straightness include spirit levels, straight edges, and laser systems. Flatness can be measured using beam comparators, interferometry, and electromechanical gauges. Thread measurement involves assessing elements like major diameter, minor diameter, pitch, and form using tools like micrometers, thread gauges, and microscopes. Surface roughness is analyzed using methods like peak-to-valley, average roughness, and RMS. Gear measurement techniques include using vernier calipers, the base tangent method, and invol