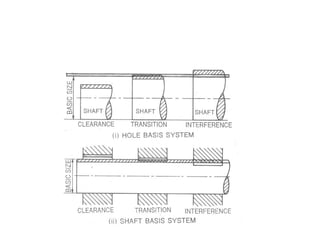
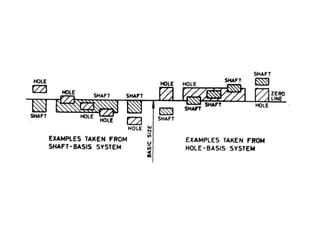
This document discusses different systems of fit for shafts and holes, types of gauges, and gauge tolerances. It describes two systems - the hole basis system where the hole size is fixed and the shaft is varied, and the shaft basis system where the shaft is fixed and the hole is varied. It also outlines different types of gauges like standard, limit, workshop, and inspection gauges. Limit gauges in particular have two ends, one for maximum and one for minimum limits. The document concludes by noting that gauges have tolerances to account for manufacturing imperfections, and that unilateral tolerances are preferred.