Embed presentation
Downloaded 74 times


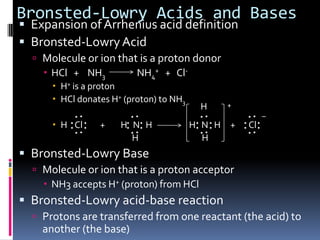
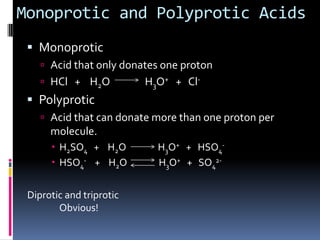
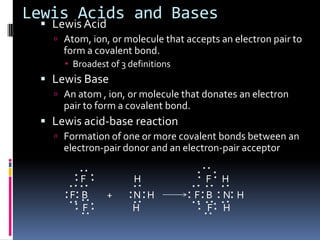
The document discusses acid-base theories including Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases, Lewis acids and bases, and monoprotic and polyprotic acids. Under the Bronsted-Lowry definition, an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor in a proton transfer reaction. A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor that forms a covalent bond, while a Lewis base is an electron pair donor. Monoprotic acids donate one proton, while polyprotic acids like sulfuric acid can donate multiple protons in successive reactions.




