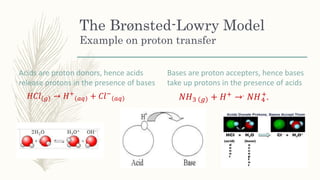
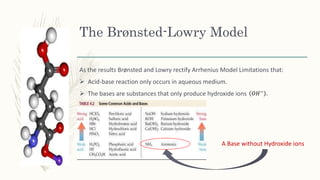
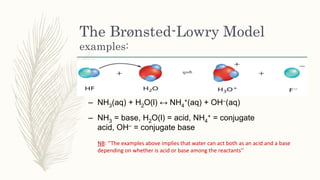
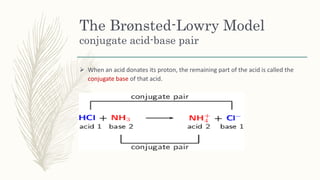
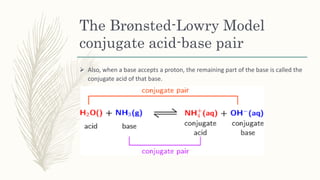
The document outlines the Brønsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases, stating that acids are hydrogen ion donors while bases are hydrogen ion acceptors. It explains proton transfer through chemical equations and identifies conjugate acid-base pairs formed during these reactions. Additionally, it highlights the limitations of the Arrhenius model and provides exercises for practical understanding of the concepts discussed.