Embed presentation
Download to read offline






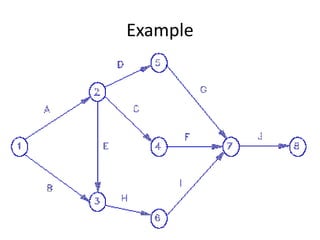
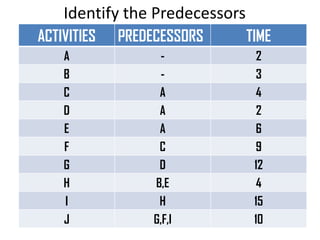
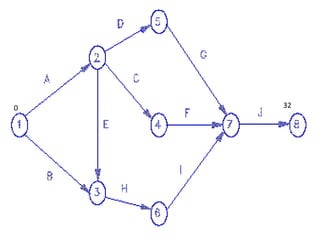
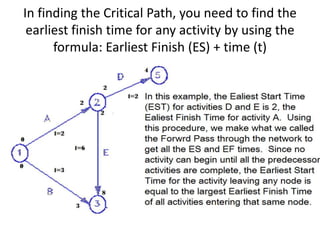
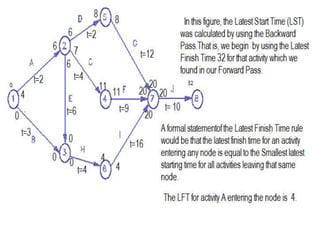



This document discusses critical path method (CPM) and critical path analysis (CPA) for project management. It defines CPM and CPA, explains that CPM is used to determine the critical path or longest sequence of dependent activities, and notes that CPA is important for management to make decisions. The document provides instructions on how to identify activity predecessors and durations, compute earliest and latest finish times, and identify the critical path. Managers are advised to take action if delays occur on the critical path. An example CPM network is given and students are assigned to create their own CPM, identify the critical path, and suggest management solutions.












