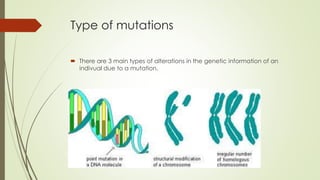
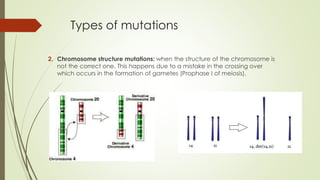
Mutations are caused by mistakes during DNA replication or cell division that produce a new DNA sequence. There are three main types of mutations: gene mutations which create new gene alleles, chromosome structure mutations from errors during crossing over, and numerical mutations resulting from alterations in chromosome number such as trisomies and monosomies. Mutations can have consequences like genetic disorders but also contribute to genetic variability in populations.