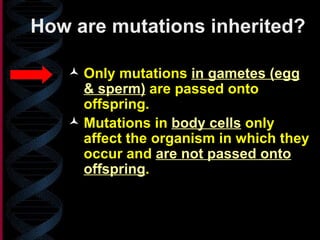
A gene mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that results from alterations like a substitution, insertion, or deletion of nucleotide bases. Substitution mutations, which replace one base for another, typically have minimal effects, while insertions and deletions cause frameshift mutations that strongly impact protein production. These frameshift mutations can lead to genetic disorders like Huntington's disease. Mutations originate from natural errors or environmental mutagens like radiation and chemicals. They are inherited if present in gametes but only affect the individual if in somatic cells.