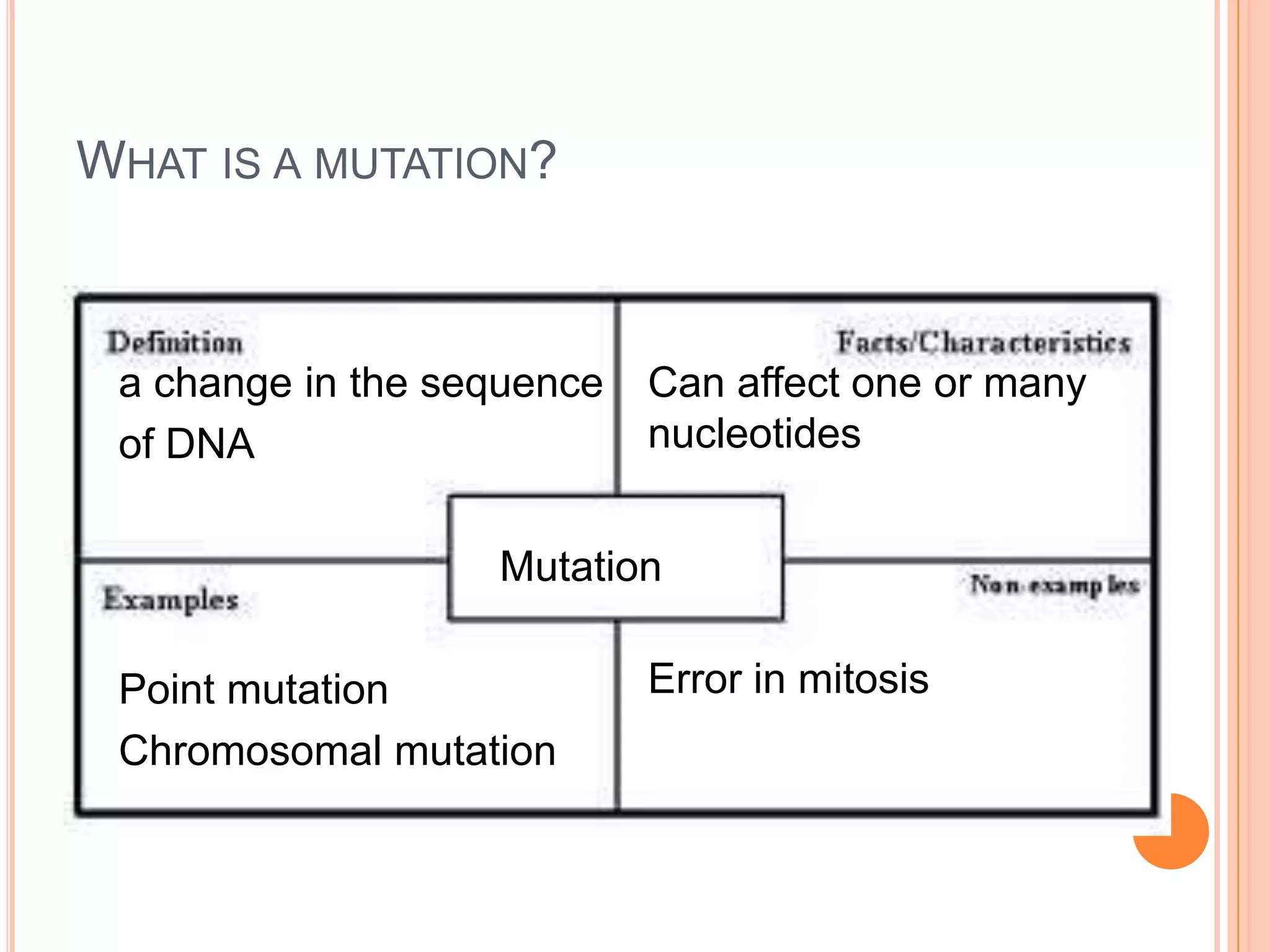
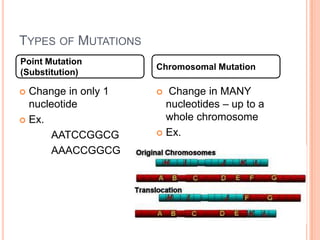
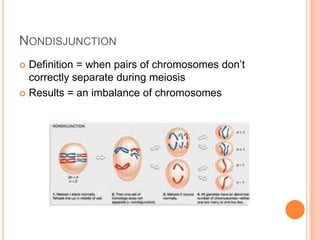
A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that can affect one or many nucleotides. There are two main types of mutations: point mutations, which change a single nucleotide, and chromosomal mutations, which change many nucleotides or an entire chromosome. Point mutations include substitutions, deletions, and insertions. Chromosomal mutations result from errors in mitosis or nondisjunction during meiosis, which leads to an imbalance of chromosomes.