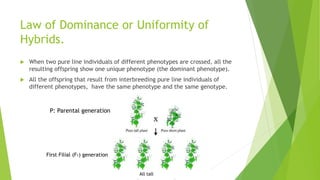
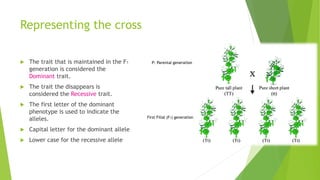
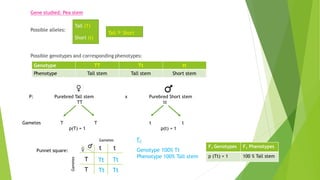
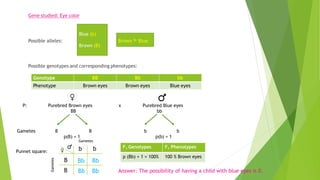
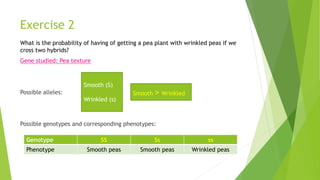
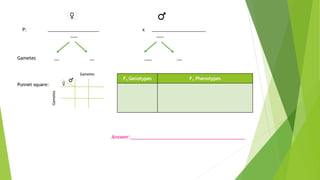
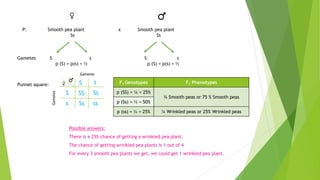
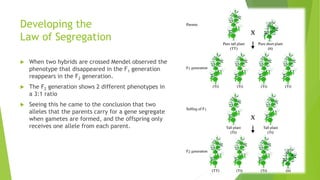
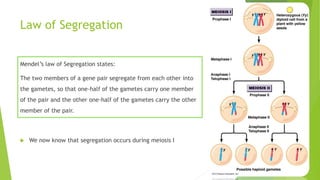
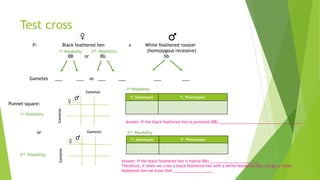
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants in the 1850s and 1860s. Through his experiments, he discovered the basic principles of heredity and inheritance. He found that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units called genes, and that these genes segregate and assort independently during the formation of gametes. Mendel's work established the fundamental laws of inheritance and provided the foundation for the modern science of genetics.