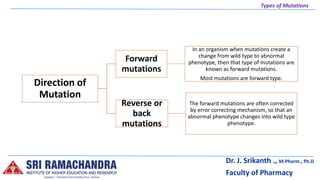
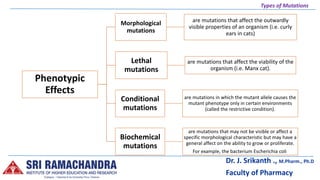
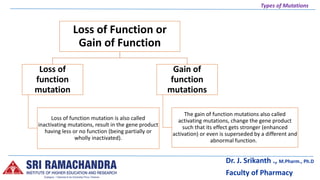
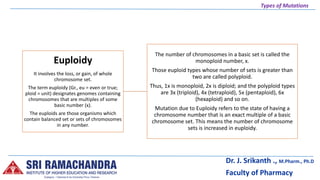
There are several types of mutations including gene mutations, chromosome mutations, point mutations, deletions, insertions, frameshifts, substitutions, translocations, and inversions. Mutations can occur in somatic or germ cells and can arise spontaneously or be induced. They are classified based on factors like the type of cell involved, origin, direction, size, phenotypic effects, magnitude of effects, loss or gain of function, and type of chromosome. Chromosomal mutations include changes in number, like aneuploidy, or structural changes such as duplications, inversions, and translocations. [/SUMMARY]