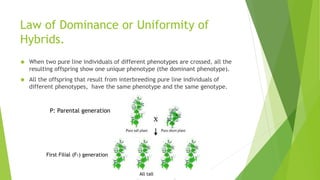
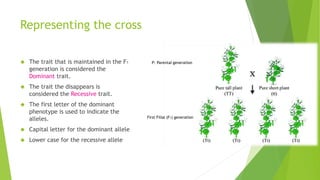
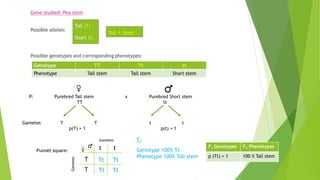
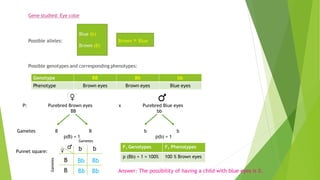
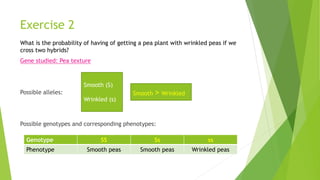
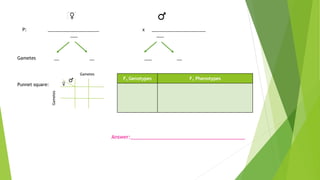
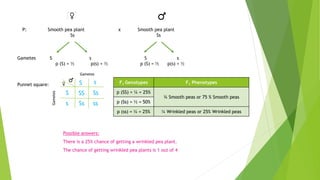
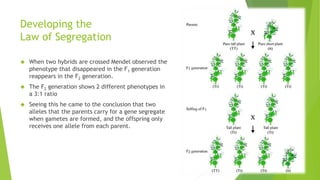
This document provides information about Gregor Mendel and his experiments with pea plants that formed the basis of modern genetics. It discusses how Mendel:
- Studied inherited traits in pea plants like seed texture, color, flower color and plant size.
- Developed the concept of inherited factors (now called genes) that are transmitted from parents to offspring.
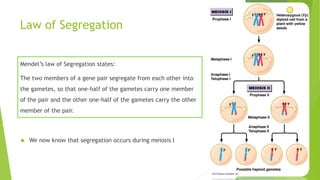
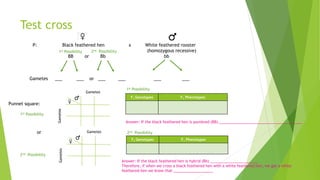
- Formulated Mendel's laws of inheritance, including the law of dominance and the law of segregation, based on his experimental results showing dominant and recessive traits separating and recombining in offspring over generations.