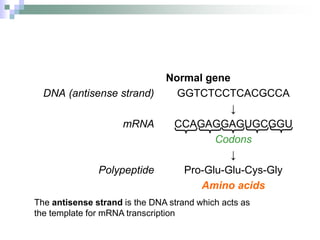
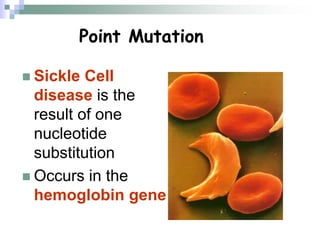
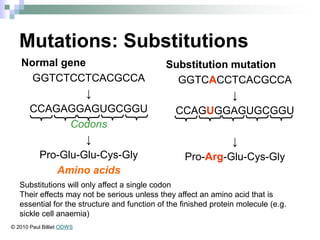
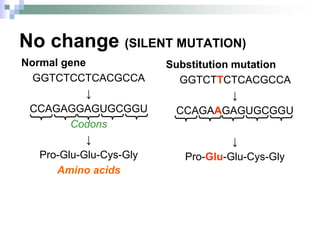
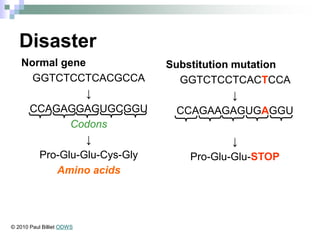
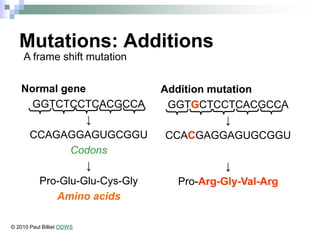
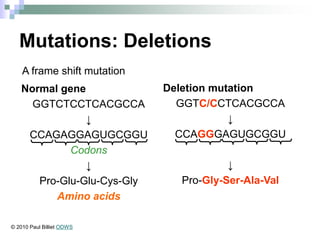
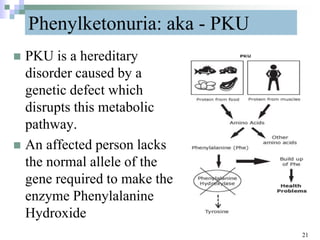
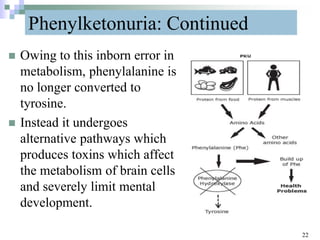
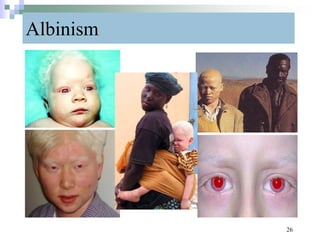
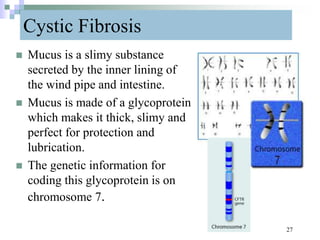
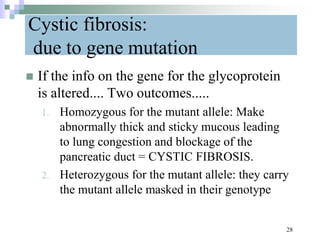
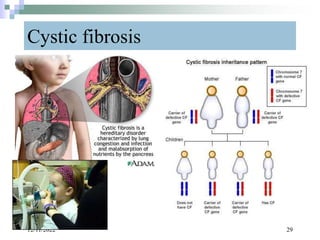
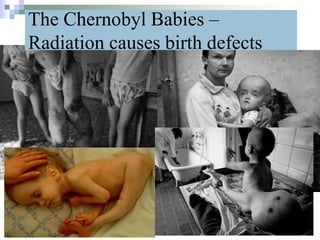
This document discusses mutations, which are changes in DNA that affect genetic information. It defines mutations as changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA that can occur in somatic or germ cells. Most mutations are neutral, but some can be beneficial or harmful. Mutations can be inherited from parents or acquired through environmental damage or DNA copying mistakes. Different types of mutations are described, including point mutations like substitutions, insertions, and deletions, as well as frameshift, chromosome, and gene mutations. Examples of genetic disorders caused by mutations, like sickle cell anemia, phenylketonuria, albinism, and cystic fibrosis are provided. Mutagens that can increase the mutation rate such as chemicals, radiation, and ultraviolet