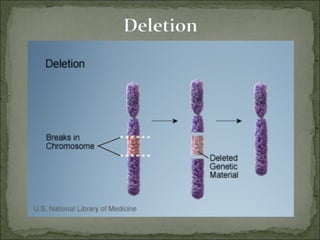
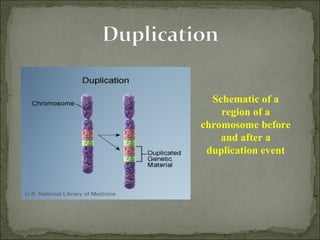
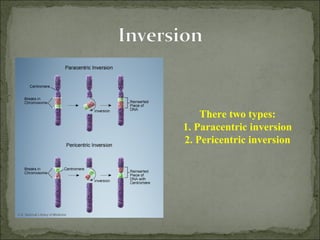
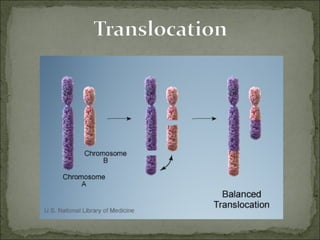
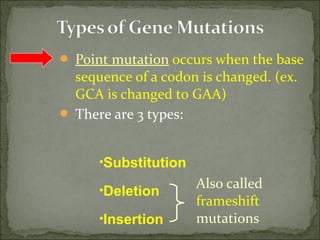
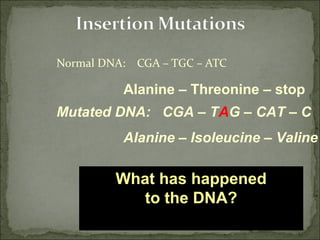
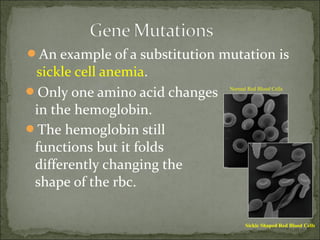
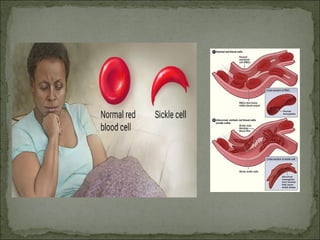
Mutations are changes in genetic material that can result from errors during DNA replication or damage to DNA. There are two main types of mutations: chromosomal mutations and genetic mutations. Chromosomal mutations include deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations that involve changes in chromosome structure. Genetic mutations are changes in DNA sequence, such as point mutations involving substitutions, insertions, or deletions of nucleotide bases. Insertion and deletion mutations tend to have the largest effects as they can alter multiple amino acids and proteins, while substitution mutations often have the smallest effects since only a single amino acid may change. Examples of diseases caused by mutations include sickle cell anemia from a substitution and Huntington's disease from an expansion insertion.