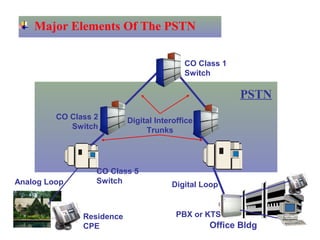
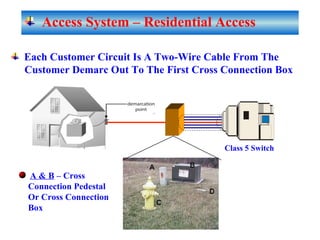
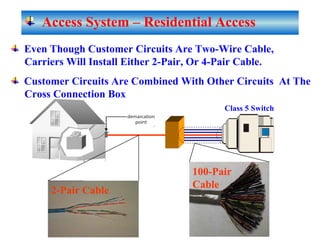
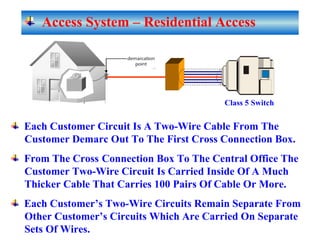
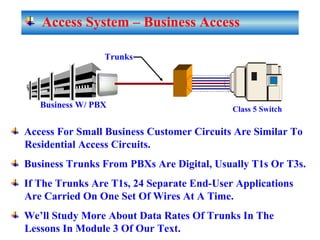
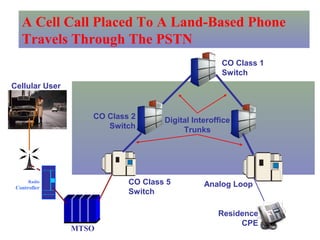
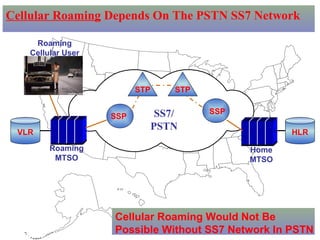
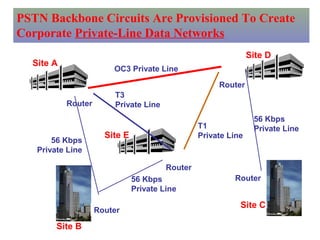
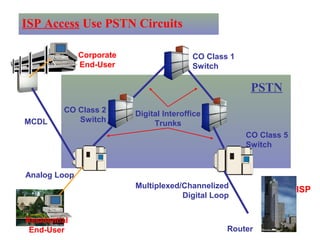
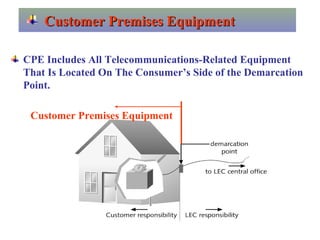
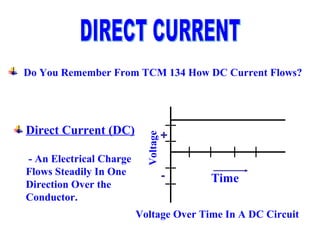
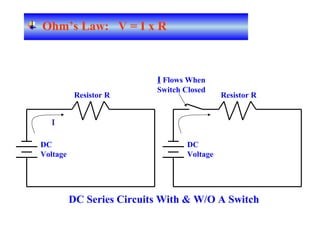
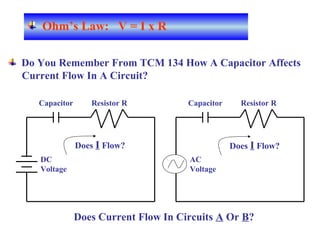
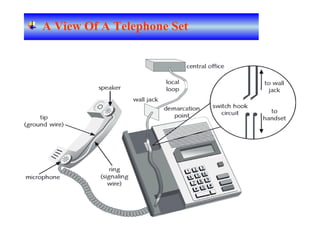
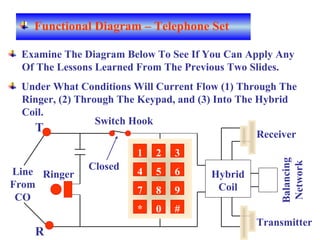
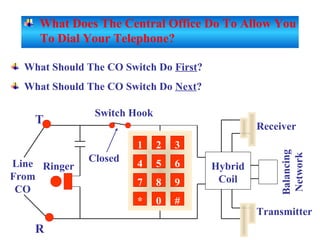
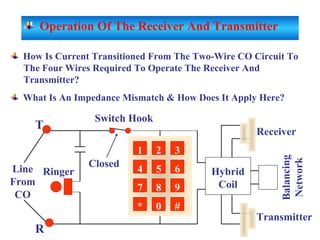
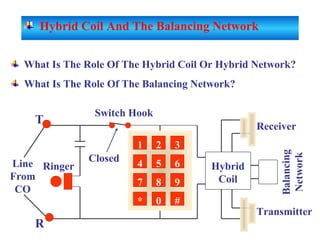
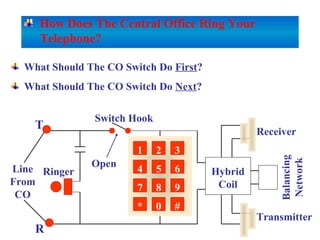
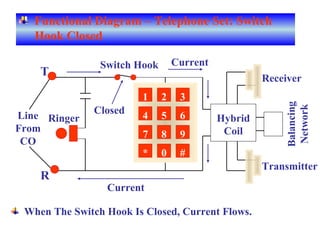
The document provides an overview of topics to be covered in Lesson 1, including the Public Switch Telephone Network (PSTN), its role, and an example of how customer premises equipment (CPE), specifically telephones, work. It will discuss the PSTN's original design for voice services and how it has evolved to support modern data and video. It will also explain the major elements of the PSTN - CPE, access systems, transport networks, and signaling - using telephones as an example CPE to illustrate how one piece of equipment interfaces with the PSTN. The lesson objectives are to understand the PSTN and learn how telephones connect to and utilize the network.