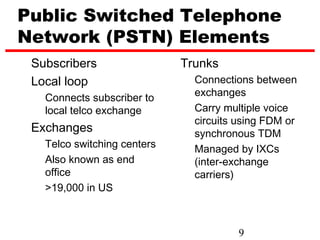
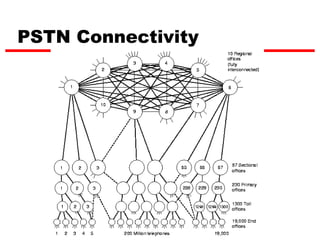
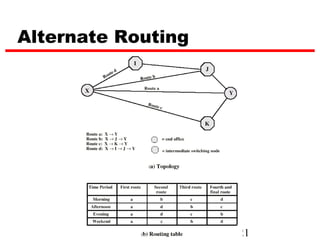
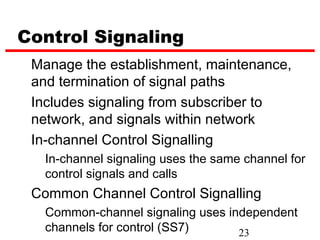
Circuit switching is the oldest networking technology, establishing a dedicated communication path between devices through intermediate nodes. It works by setting up connections between parties before data transmission and dedicating the path for the duration of the call. While well-suited for analog voice, circuit switching is inefficient for data due to wasted bandwidth when connections are idle. Examples of circuit-switched networks include the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and private branch exchanges (PBX).