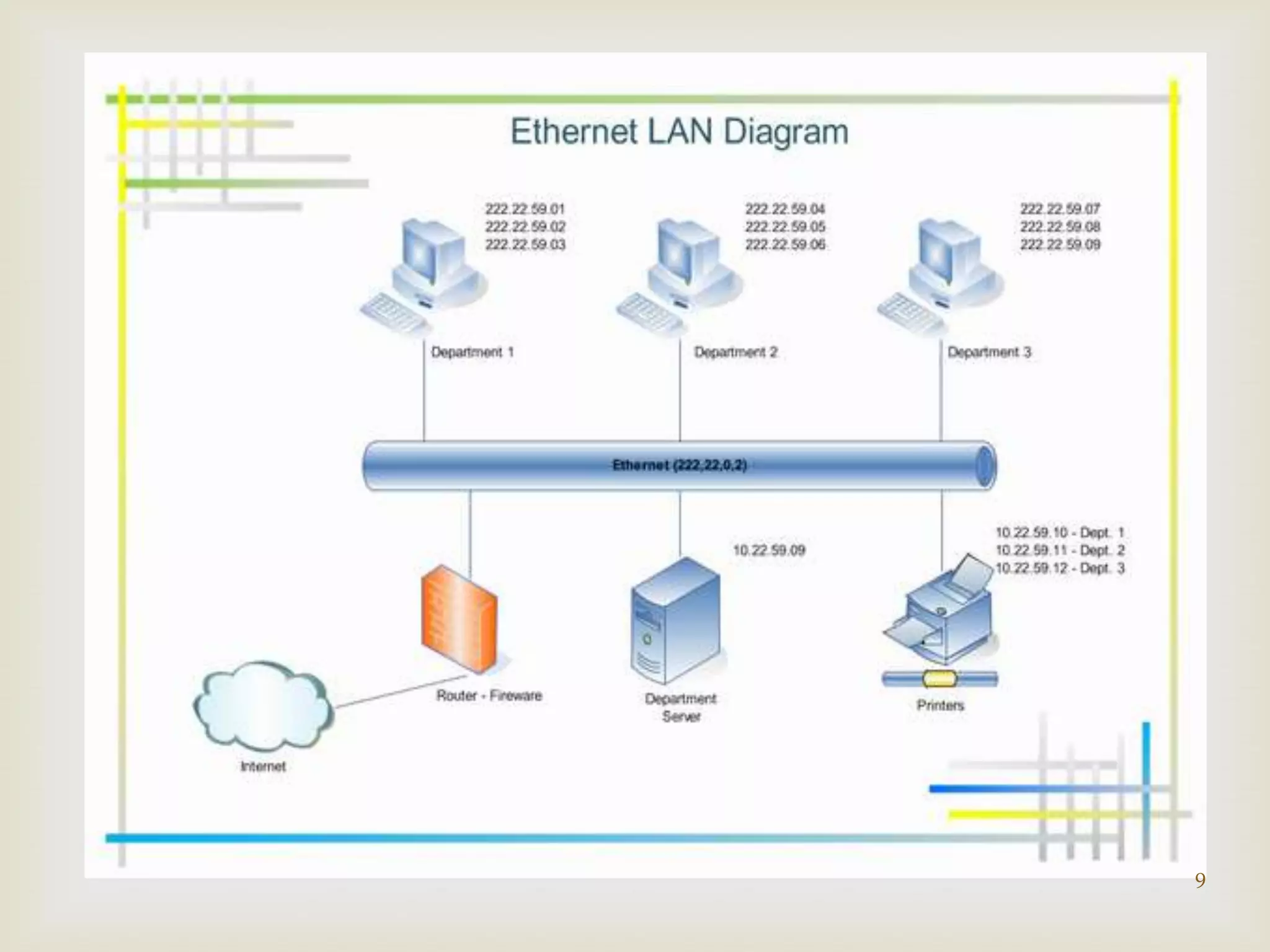
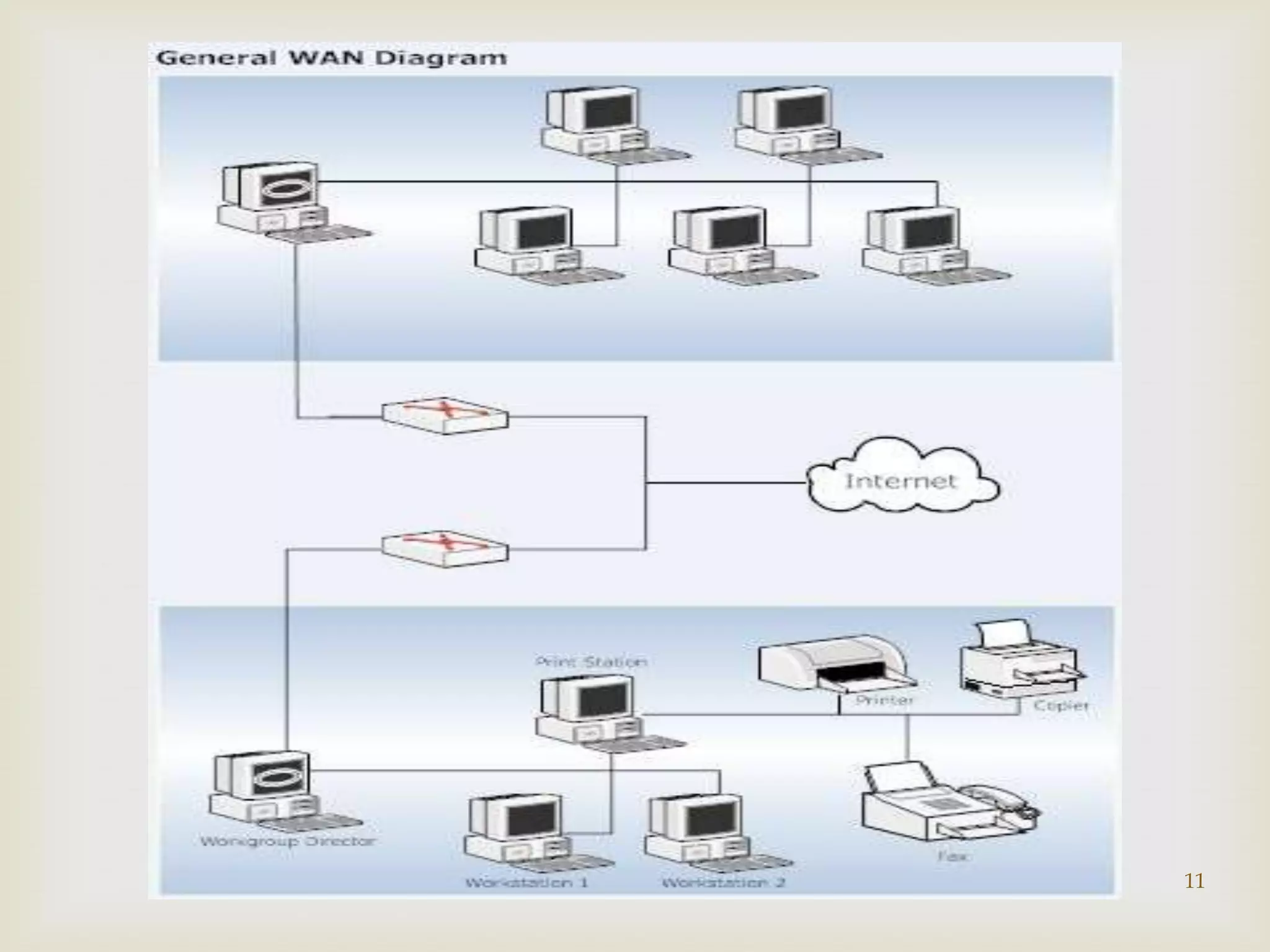
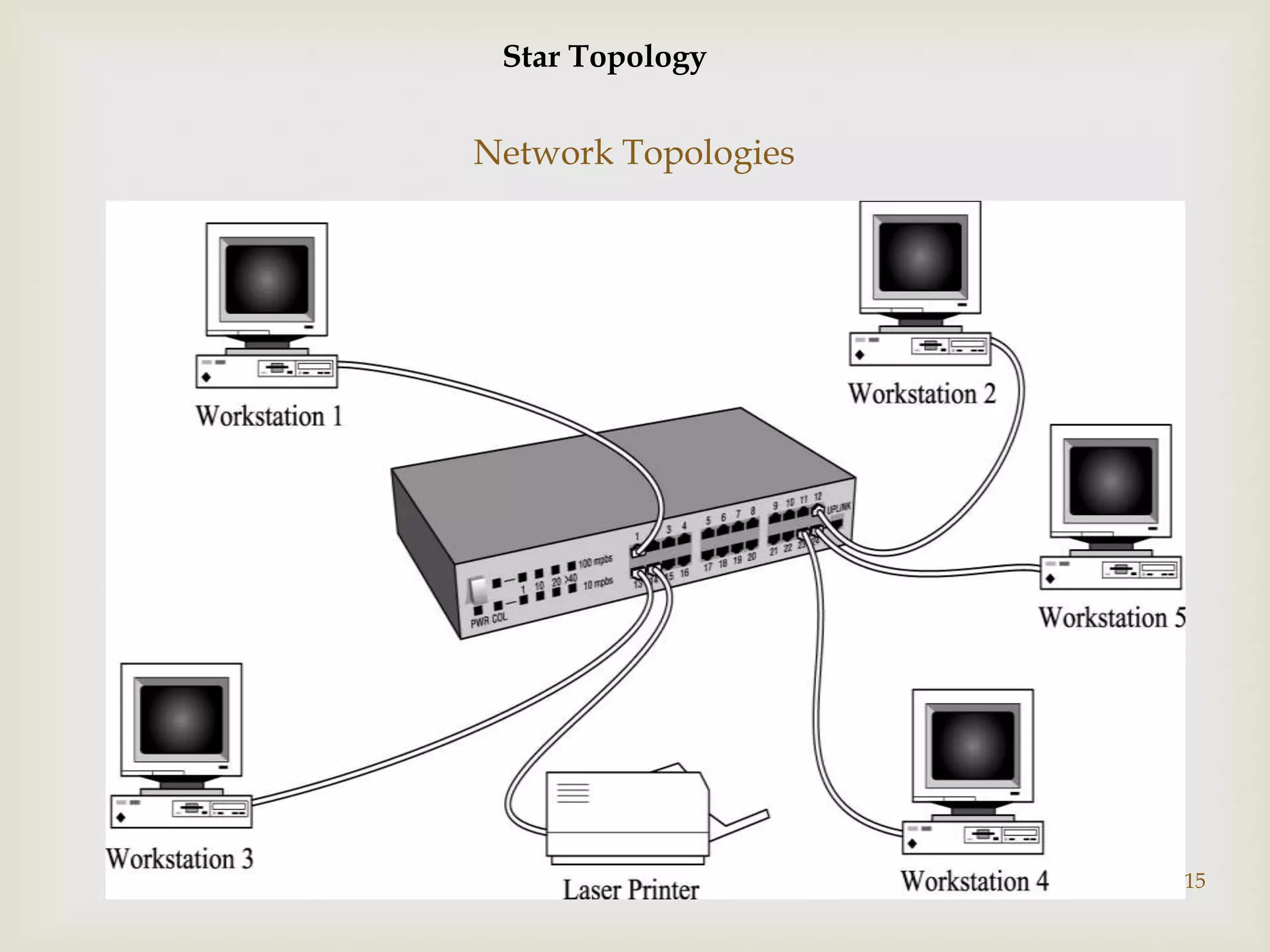
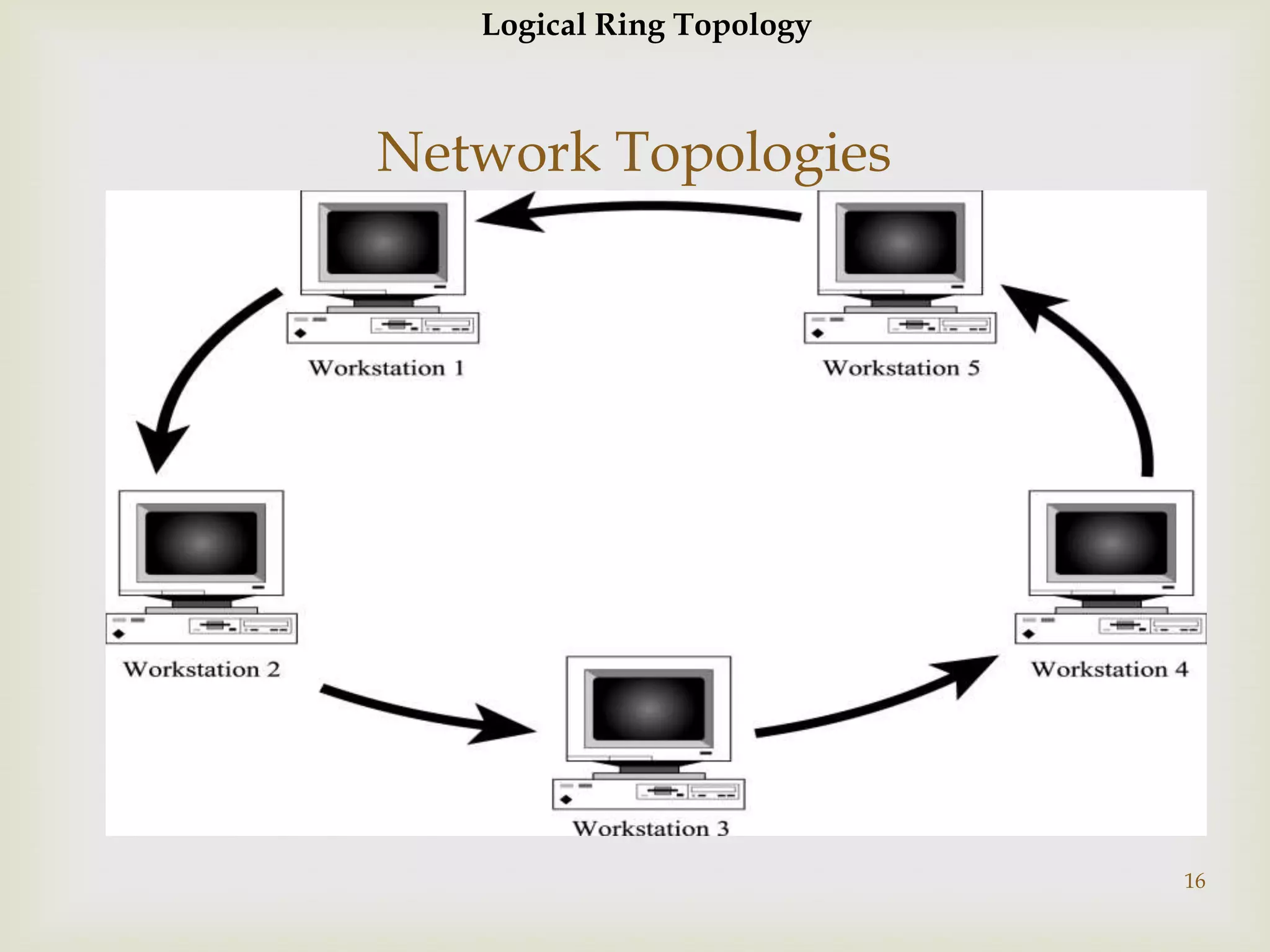
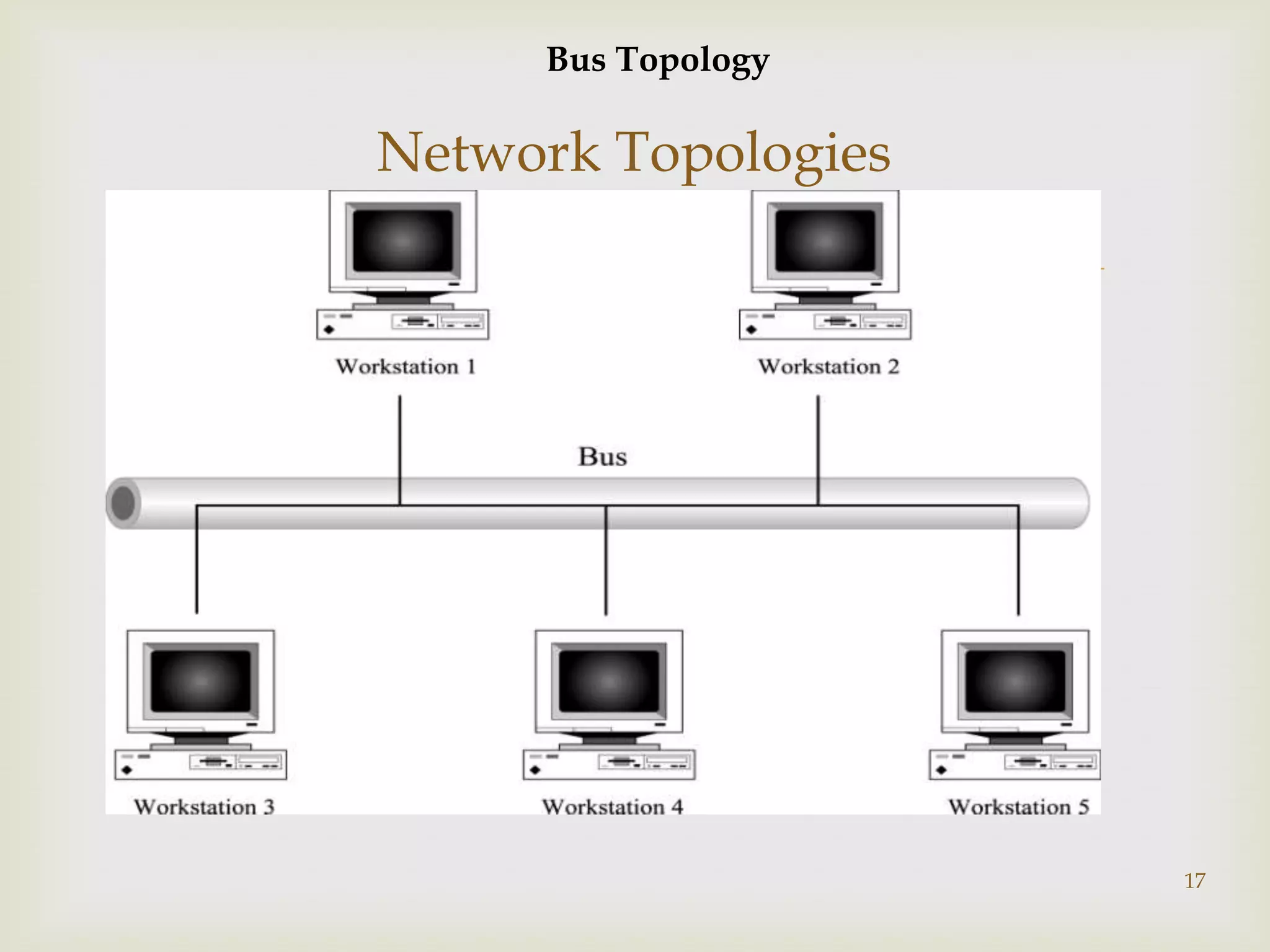
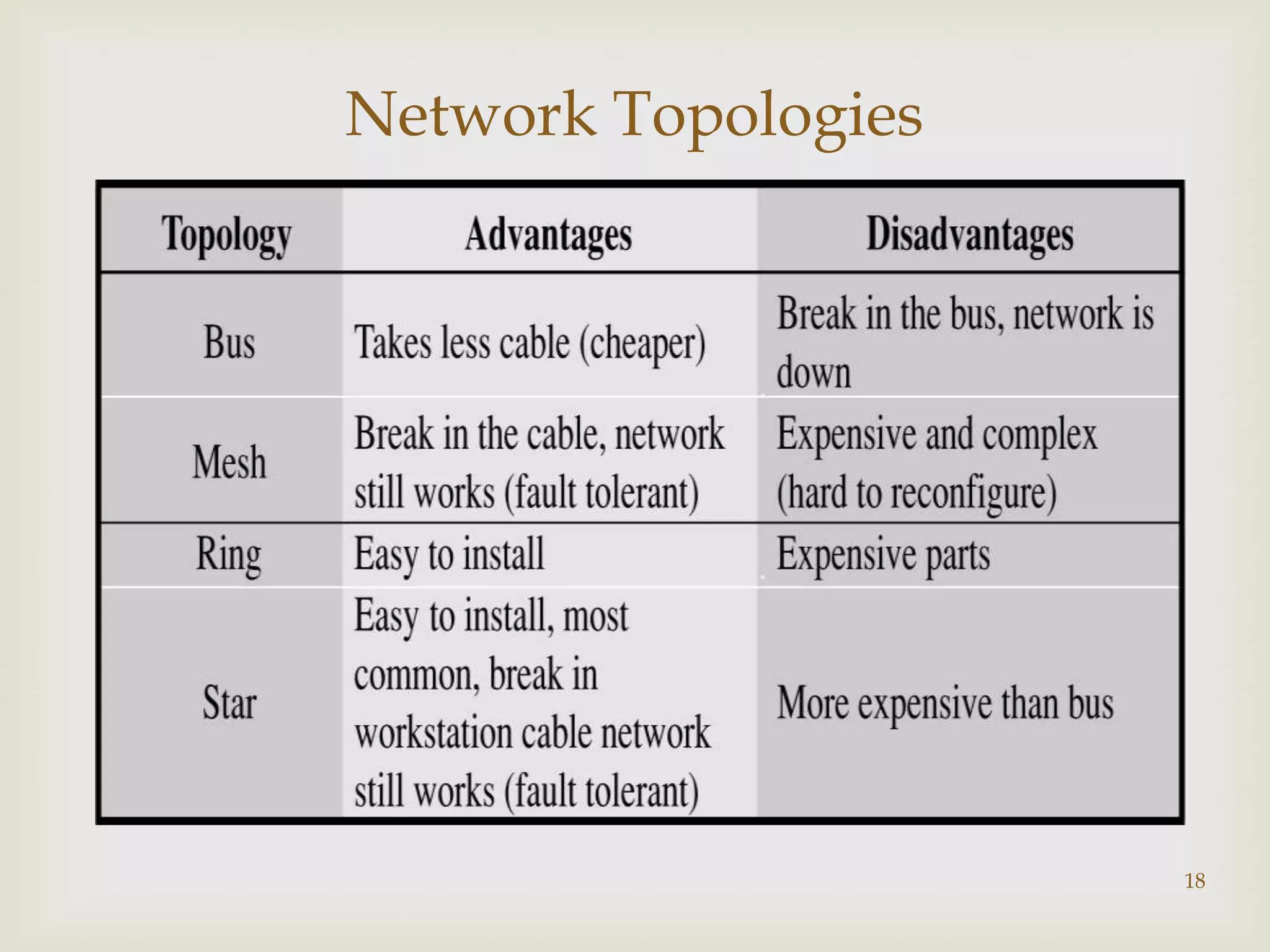
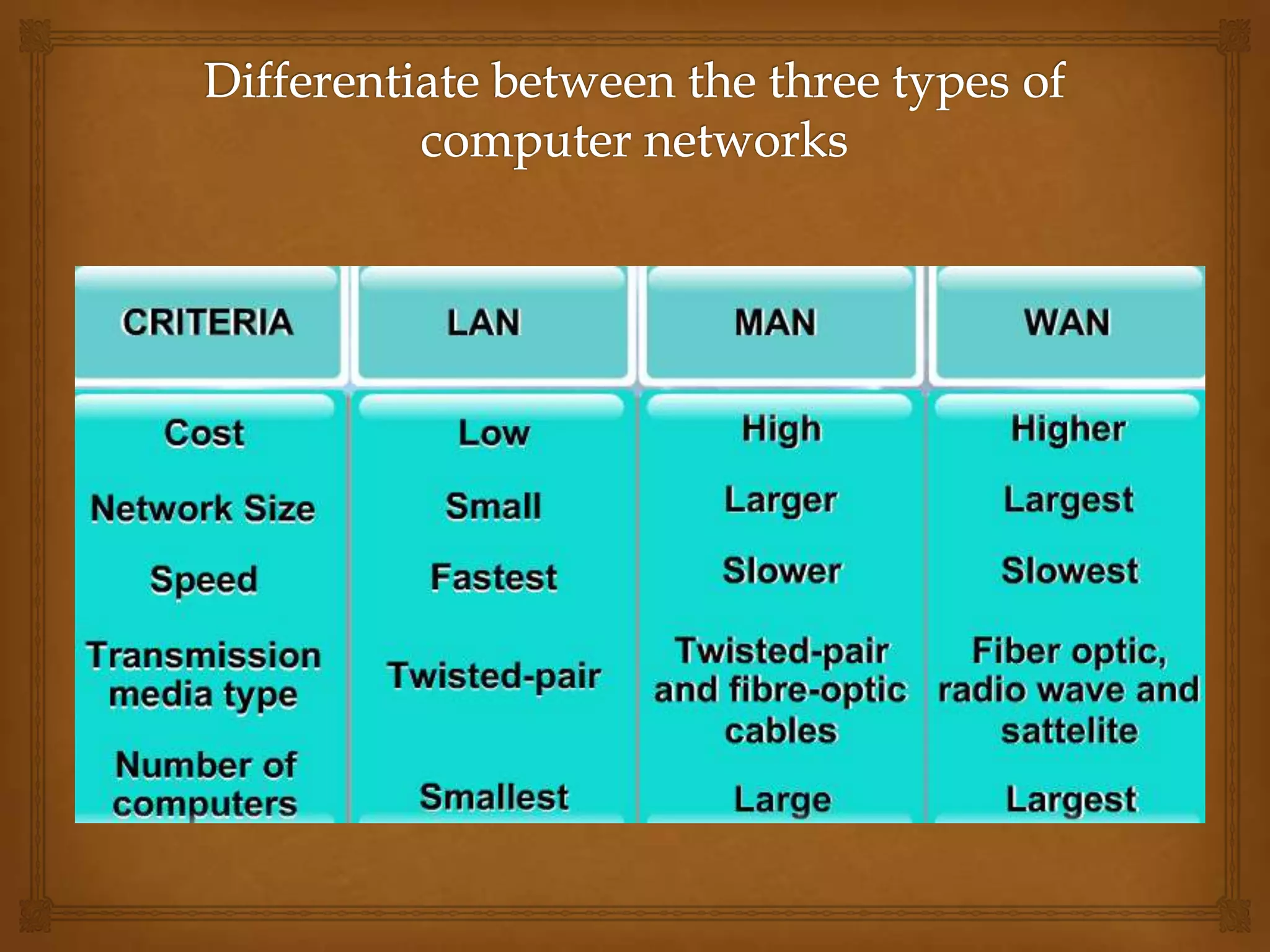
This document contains information about computer networks presented by Darshit Narechania. It defines a computer network as two or more connected computers that share resources and exchange files. The need for networks is described as file sharing, resource sharing, communication, remote access, and data protection. Common connection devices include routers, gateways, repeaters, bridges, hubs, and modems. The main types of networks covered are local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and metropolitan area networks (MANs). LANs connect computers in a small local area like a home or office, while WANs connect LANs over a larger area like a college campus or between cities. MANs interconnect