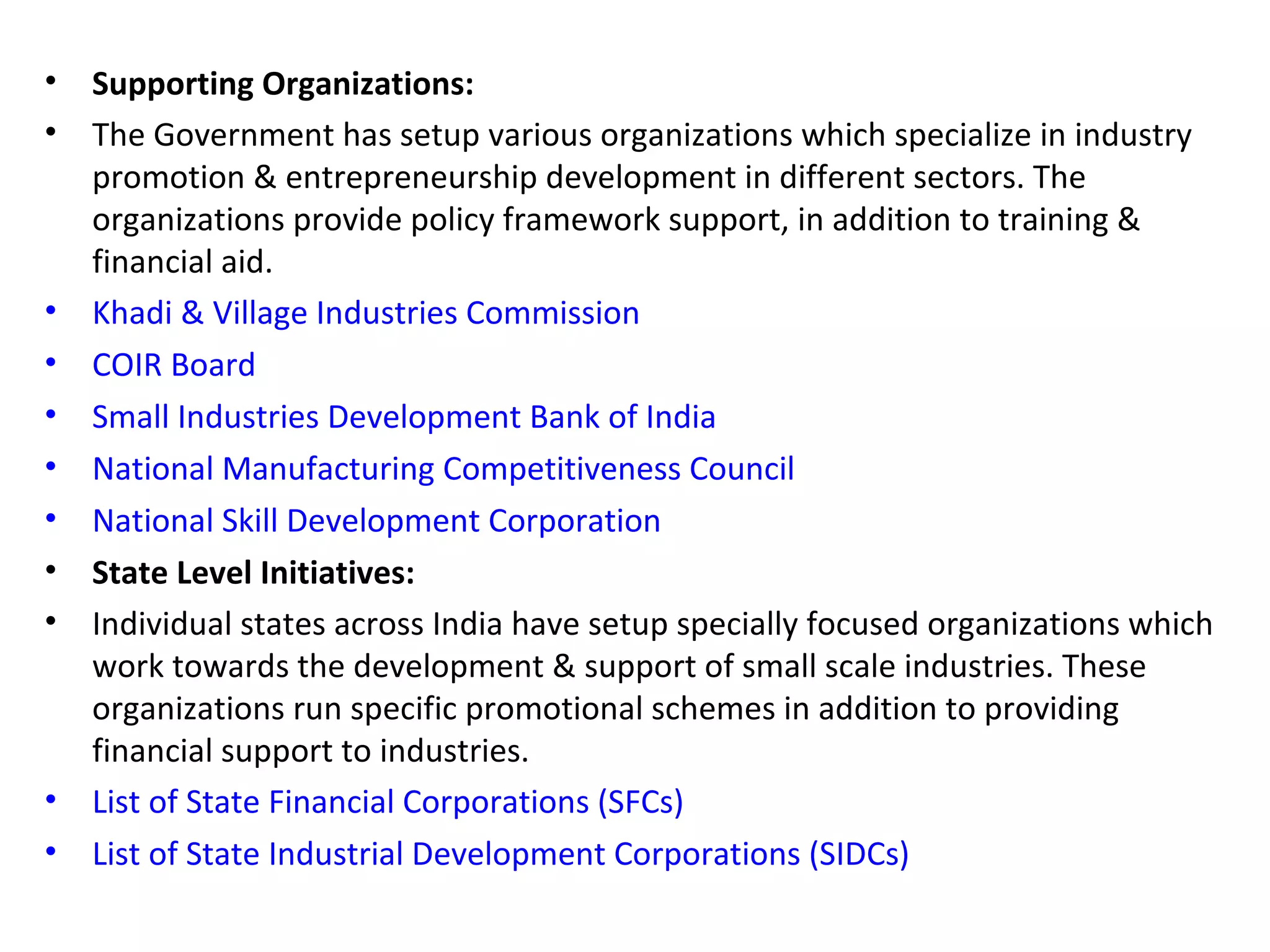
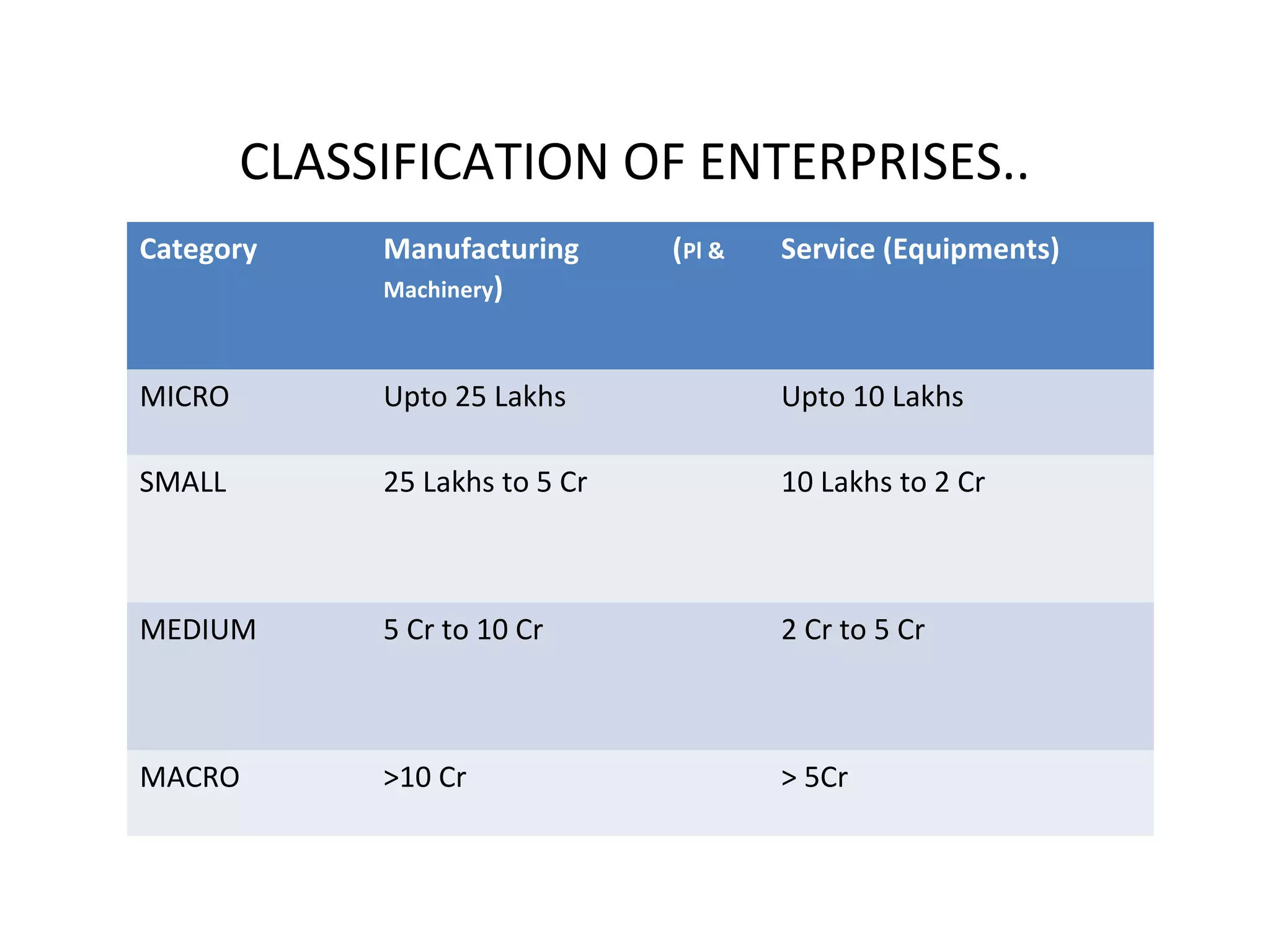
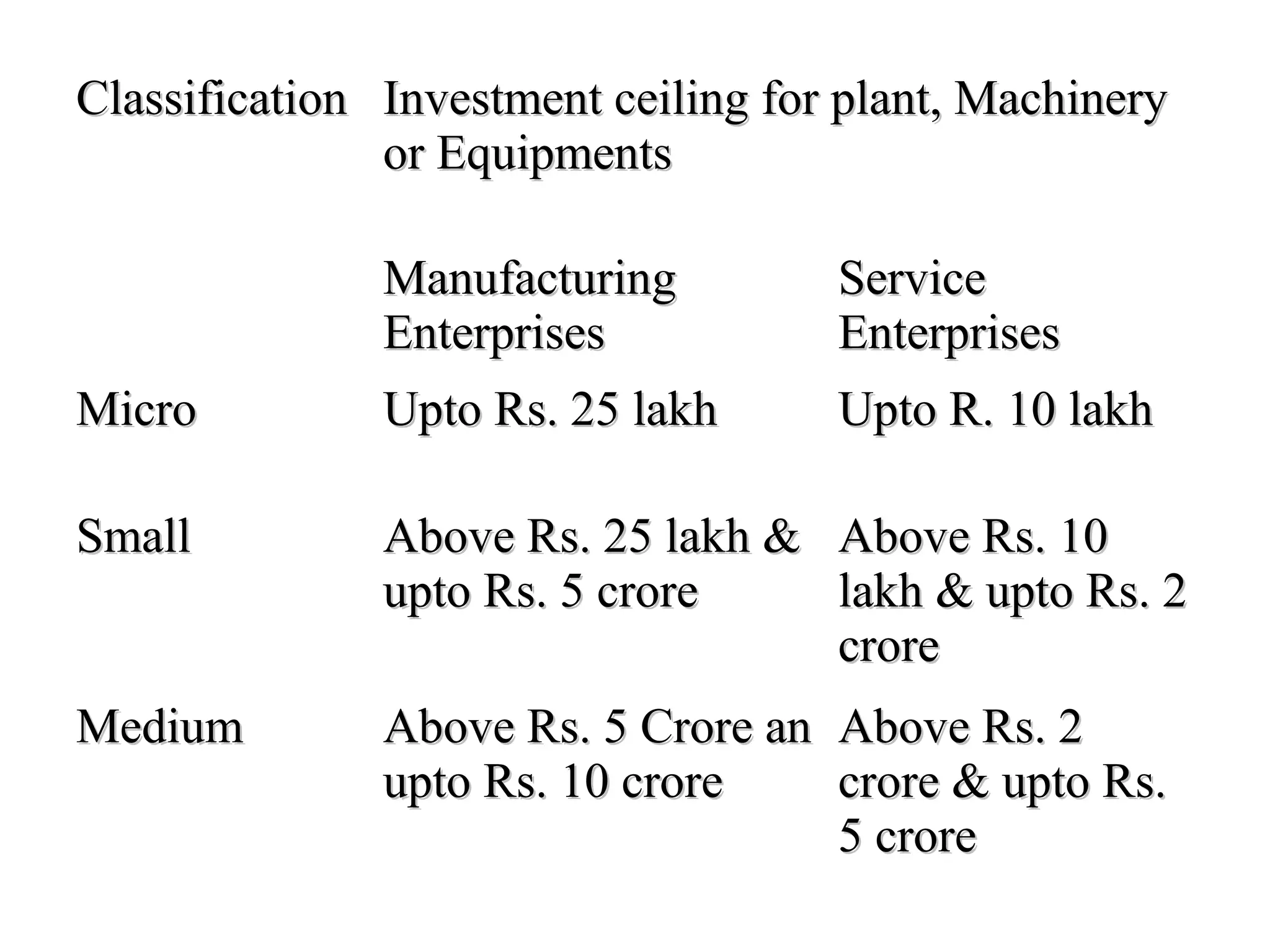
The document discusses entrepreneurship in India, noting there are ample small business opportunities but support is needed from the government and society. It outlines various government organizations that promote industries and entrepreneurship through training and funding. These include groups at the national, state, and local levels. The document also discusses industry associations that help entrepreneurs and steer policy, as well as development organizations that provide training and support for new businesses. It concludes that increasing entrepreneurship is key to fighting unemployment and poverty in India.