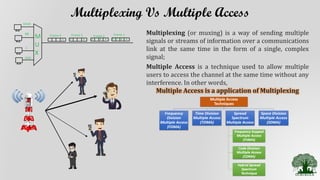
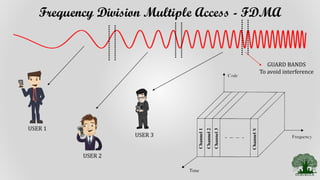
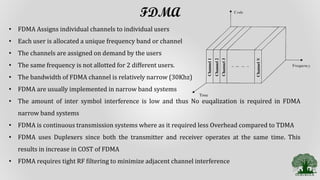
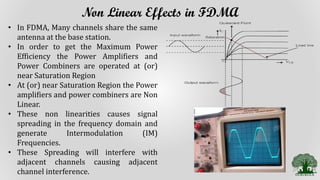
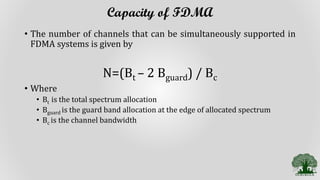
Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) is a multiple access technique that assigns individual frequency bands or channels to each user. FDMA avoids interference by ensuring each user is allocated a unique frequency band. While FDMA allows multiple users to access the channel simultaneously and has low inter-symbol interference, it requires tight RF filtering to minimize adjacent channel interference and duplexers, increasing costs. Non-linear effects from power amplifiers can also cause intermodulation frequencies, interfering with adjacent channels. The capacity of an FDMA system is calculated based on the total spectrum allocation, guard band allocation, and channel bandwidth.