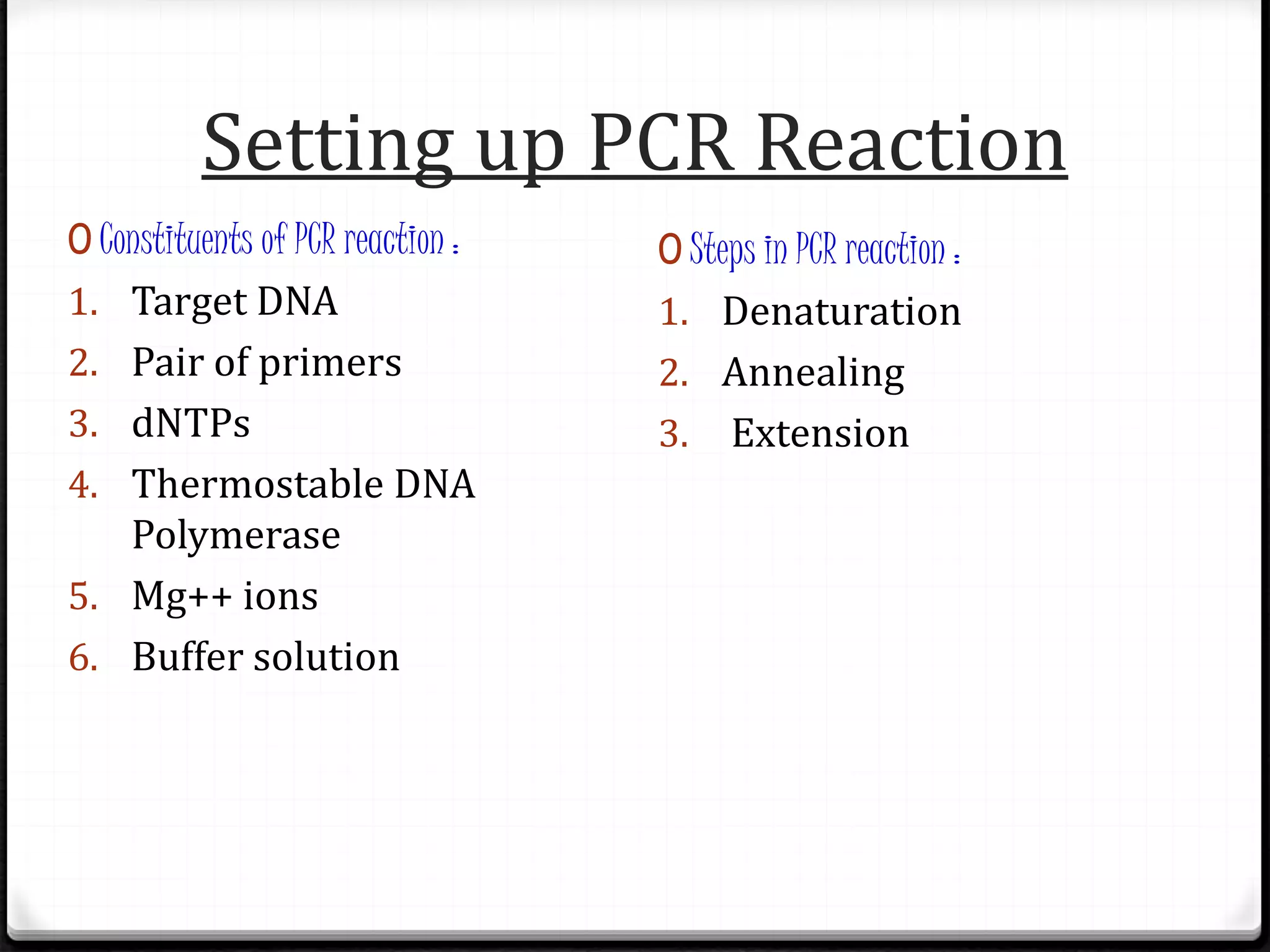
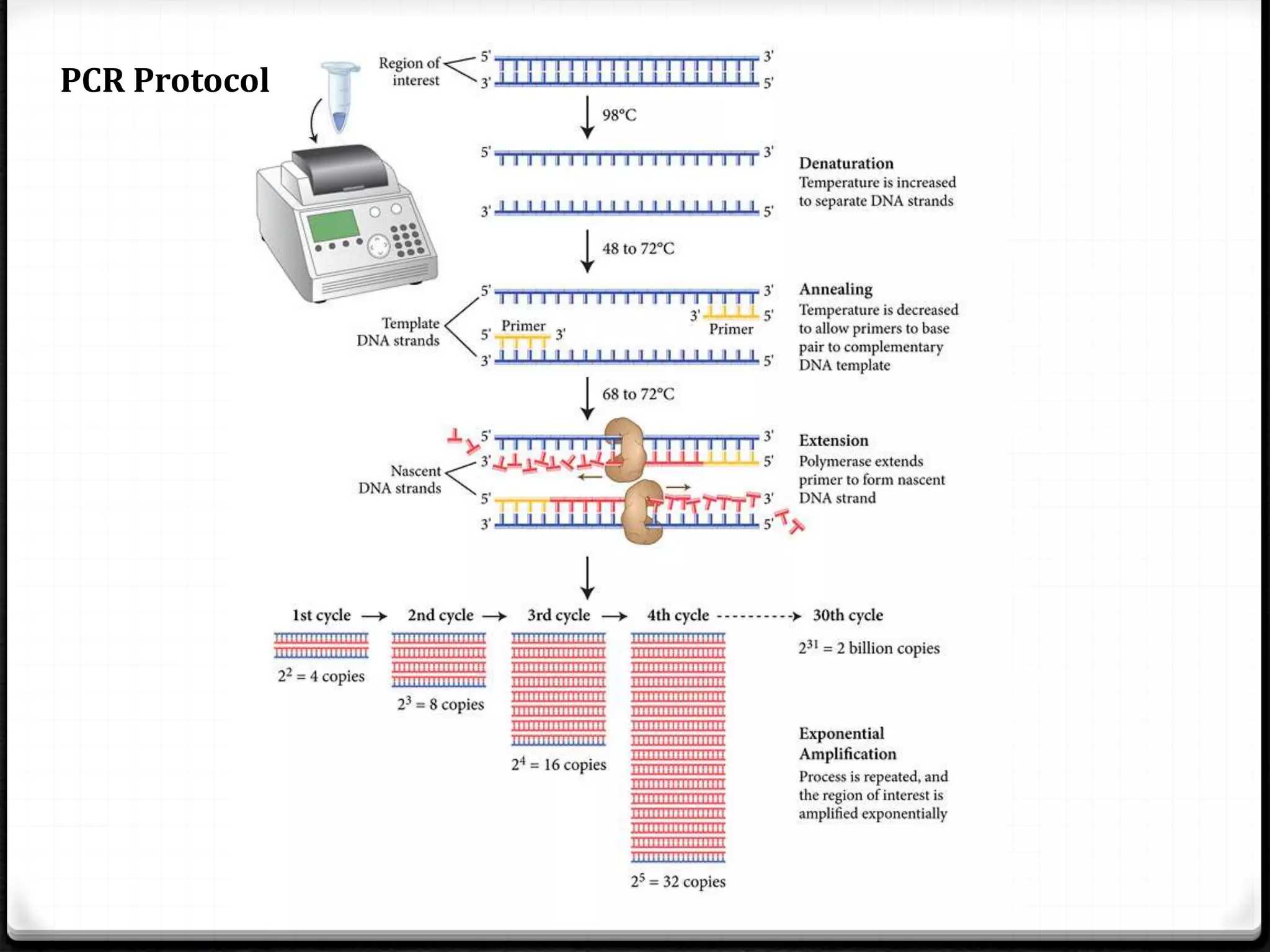
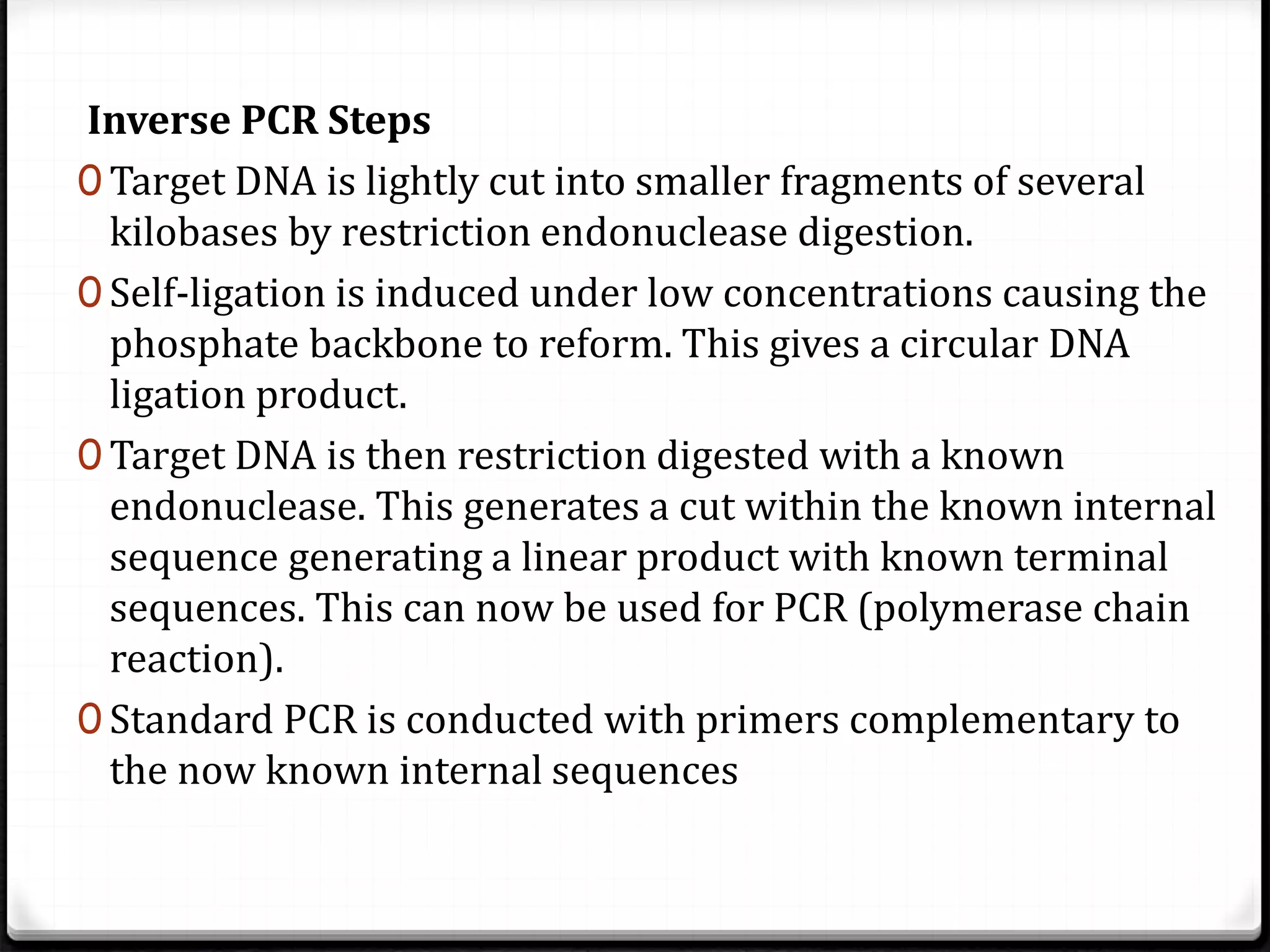
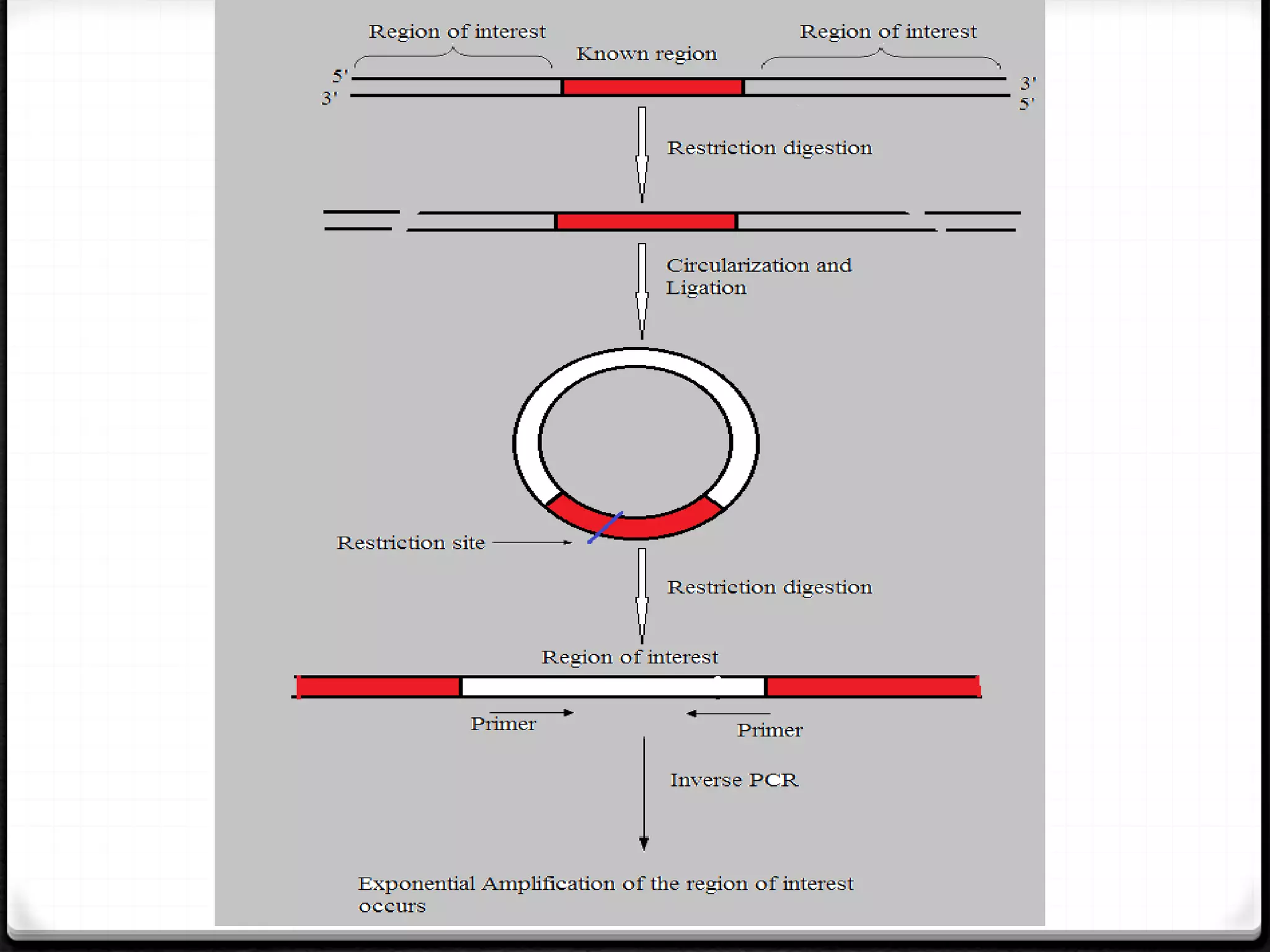
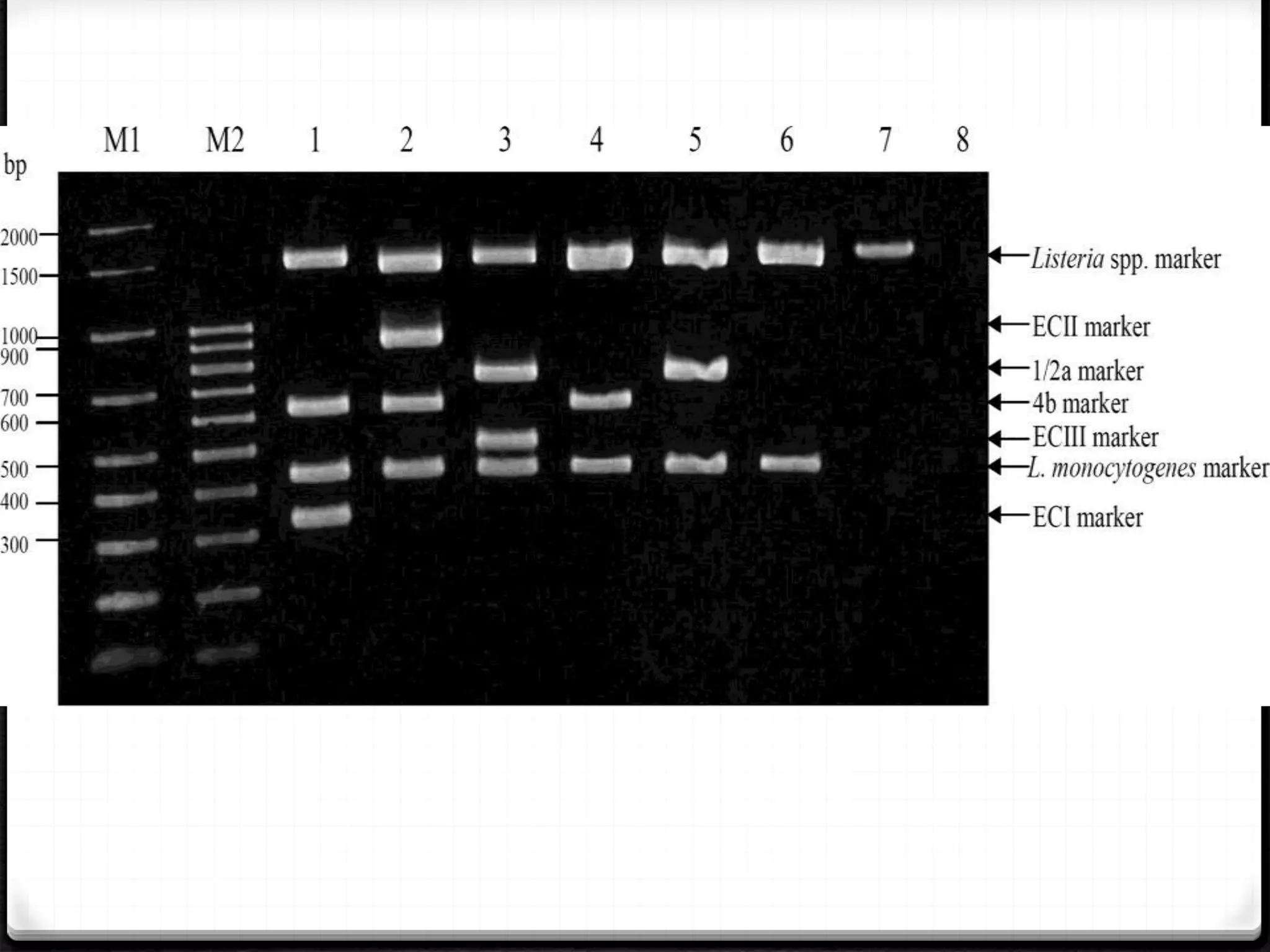
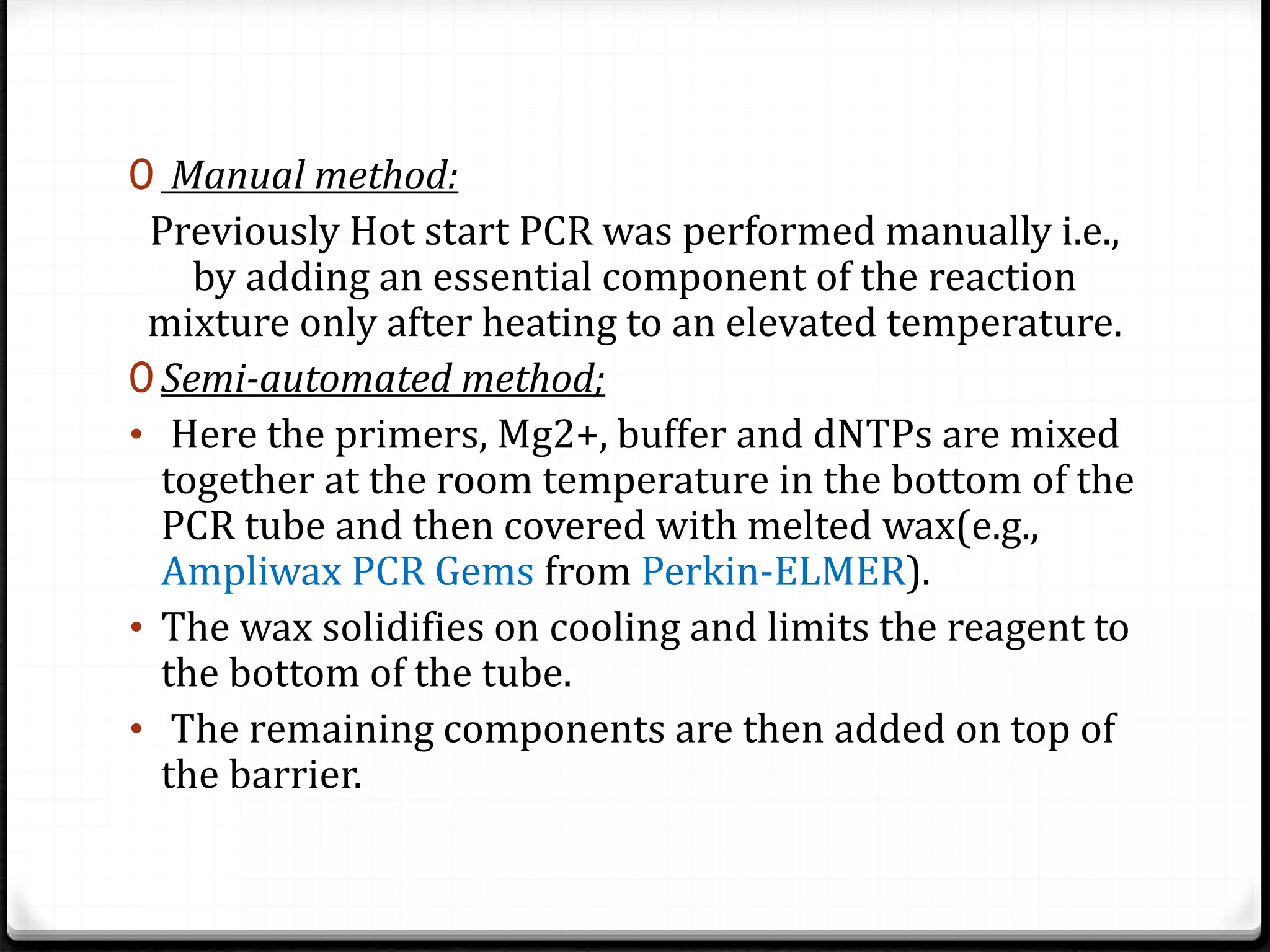
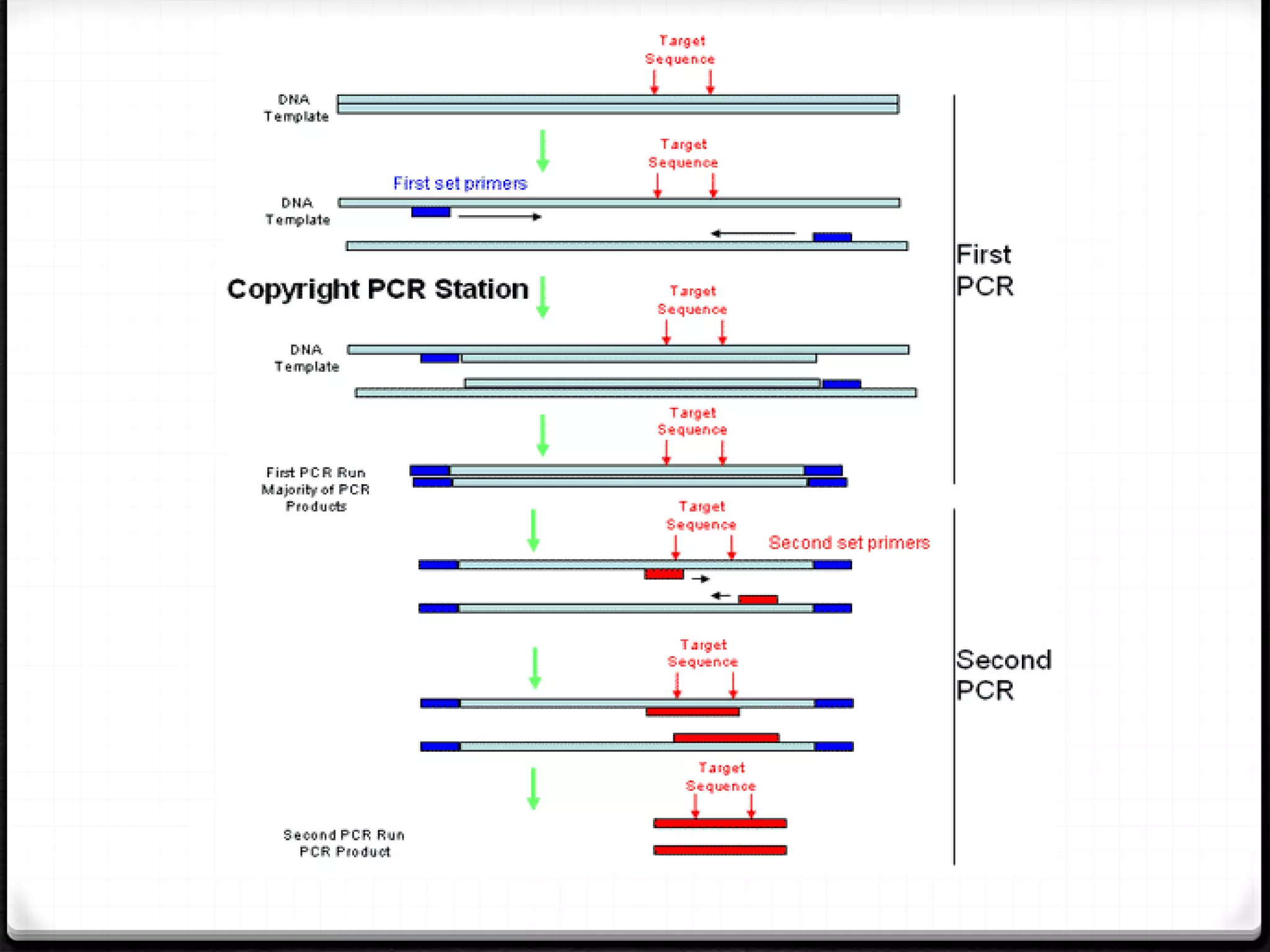
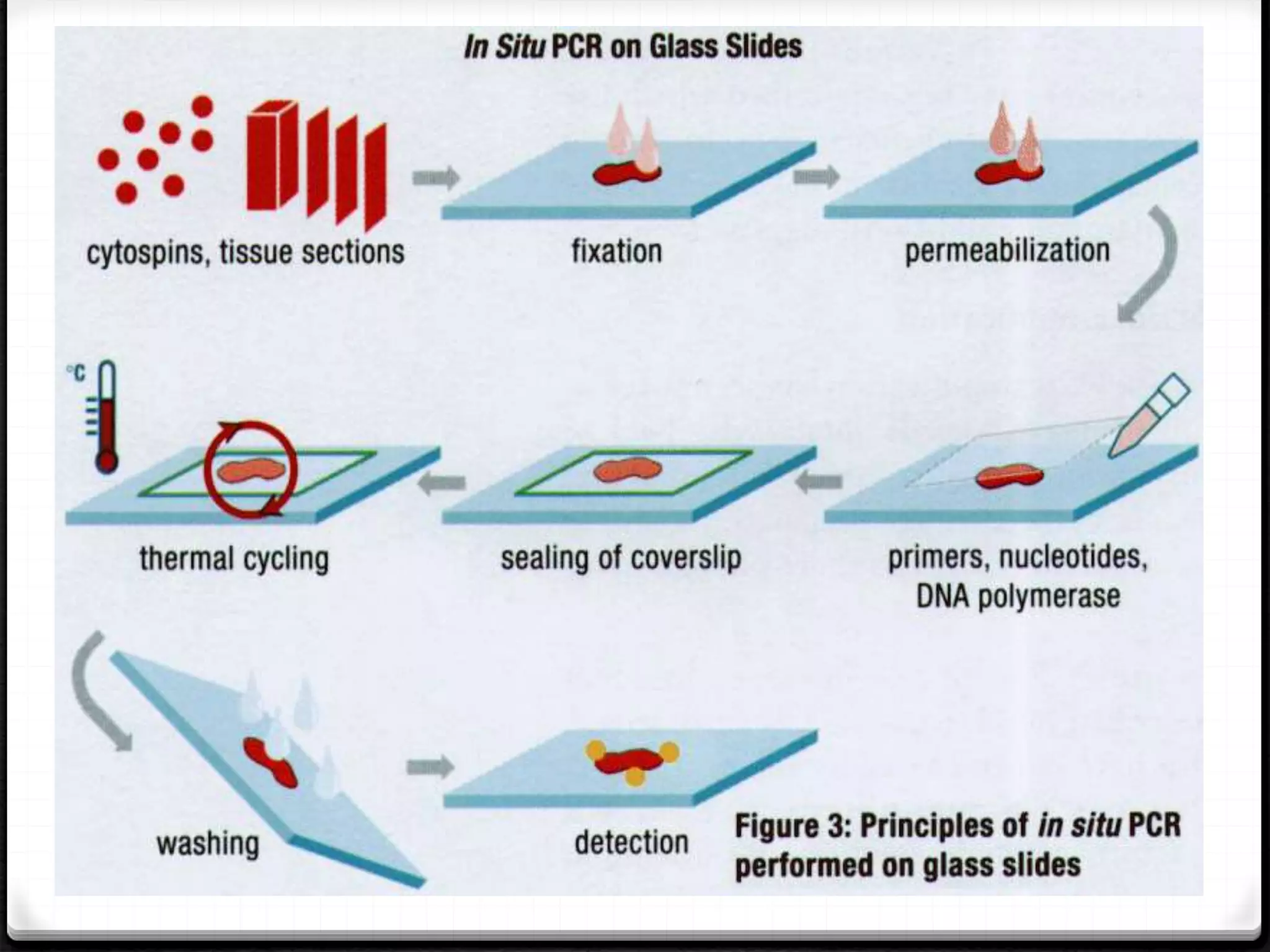
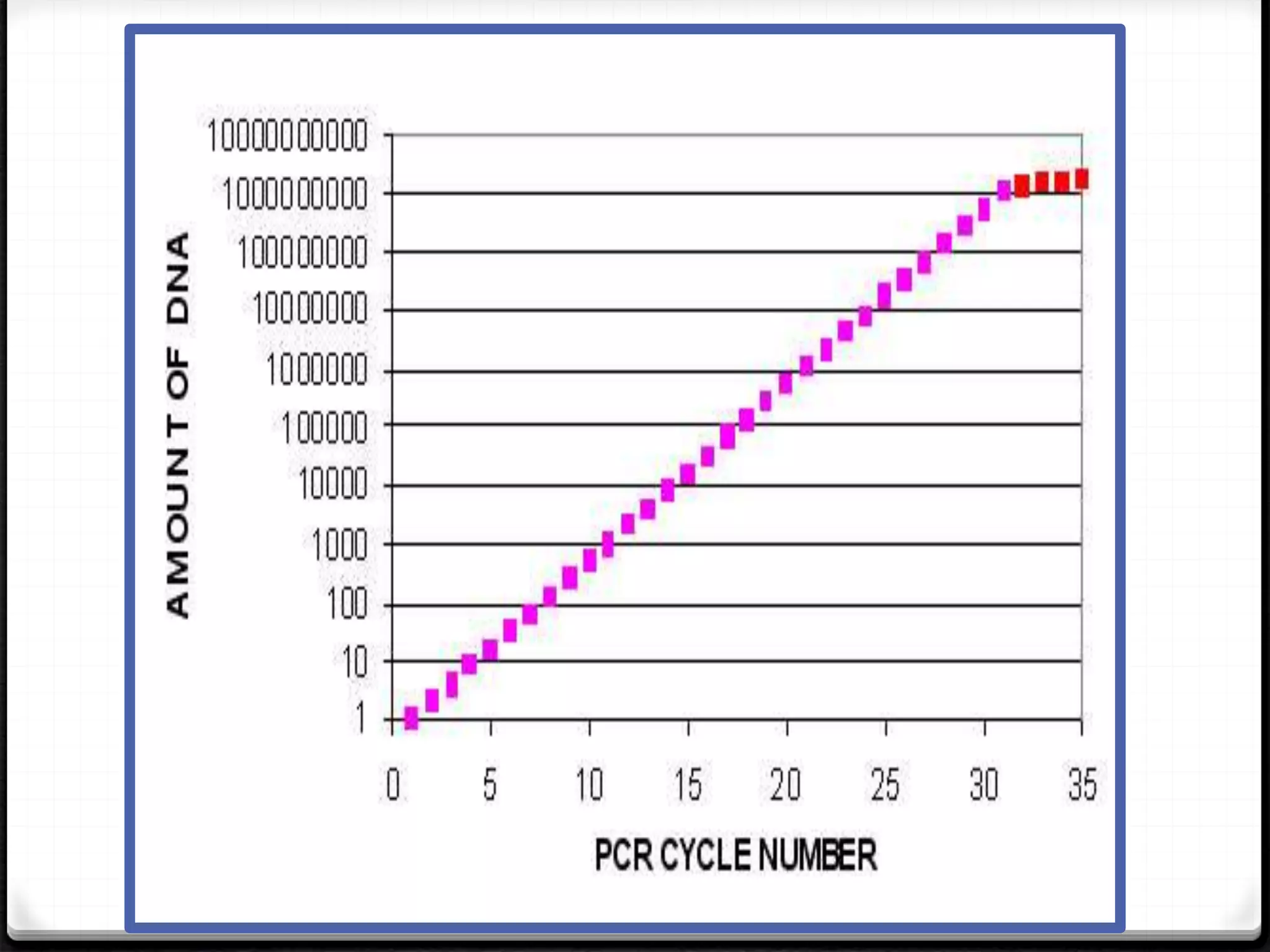
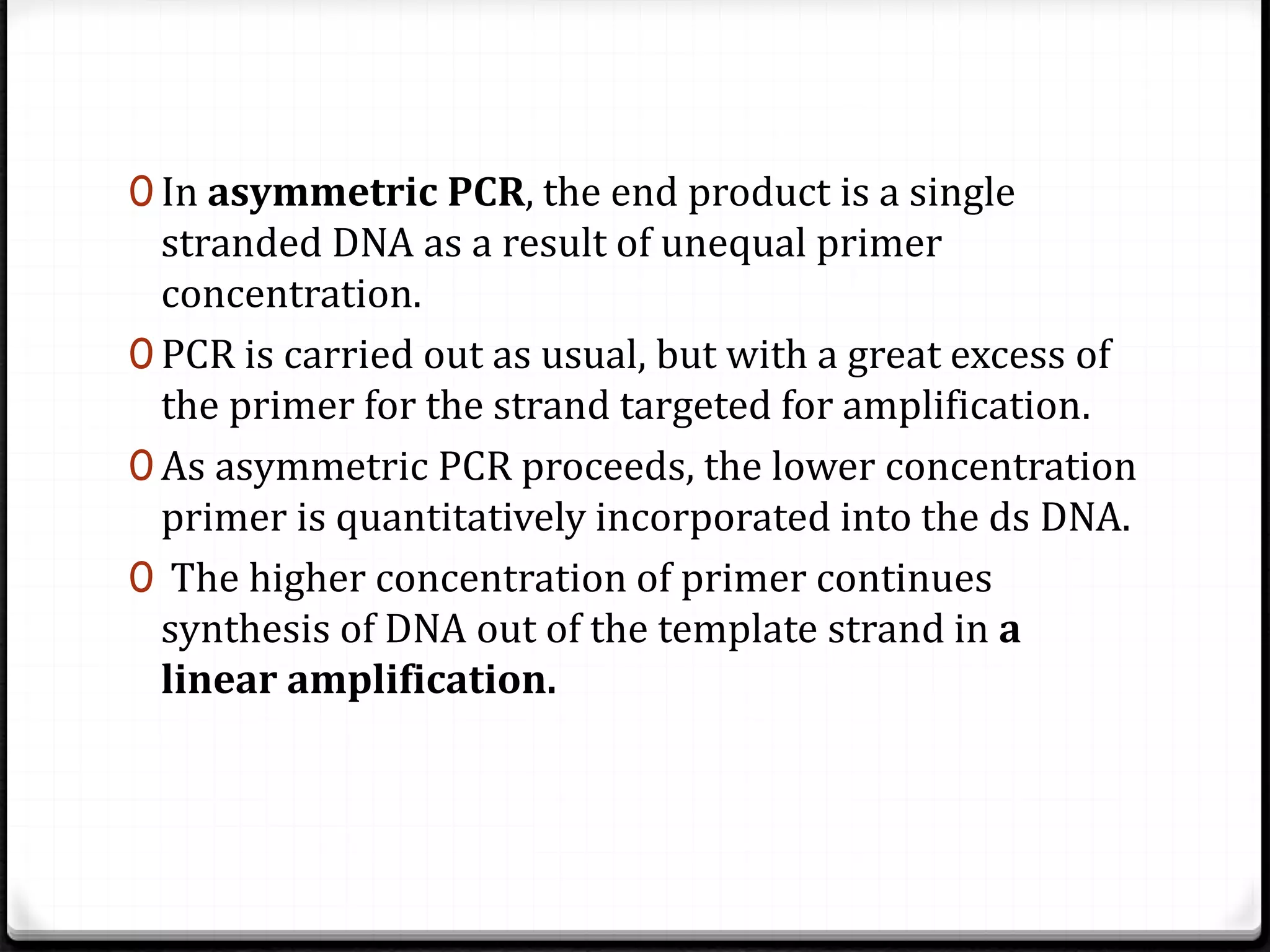
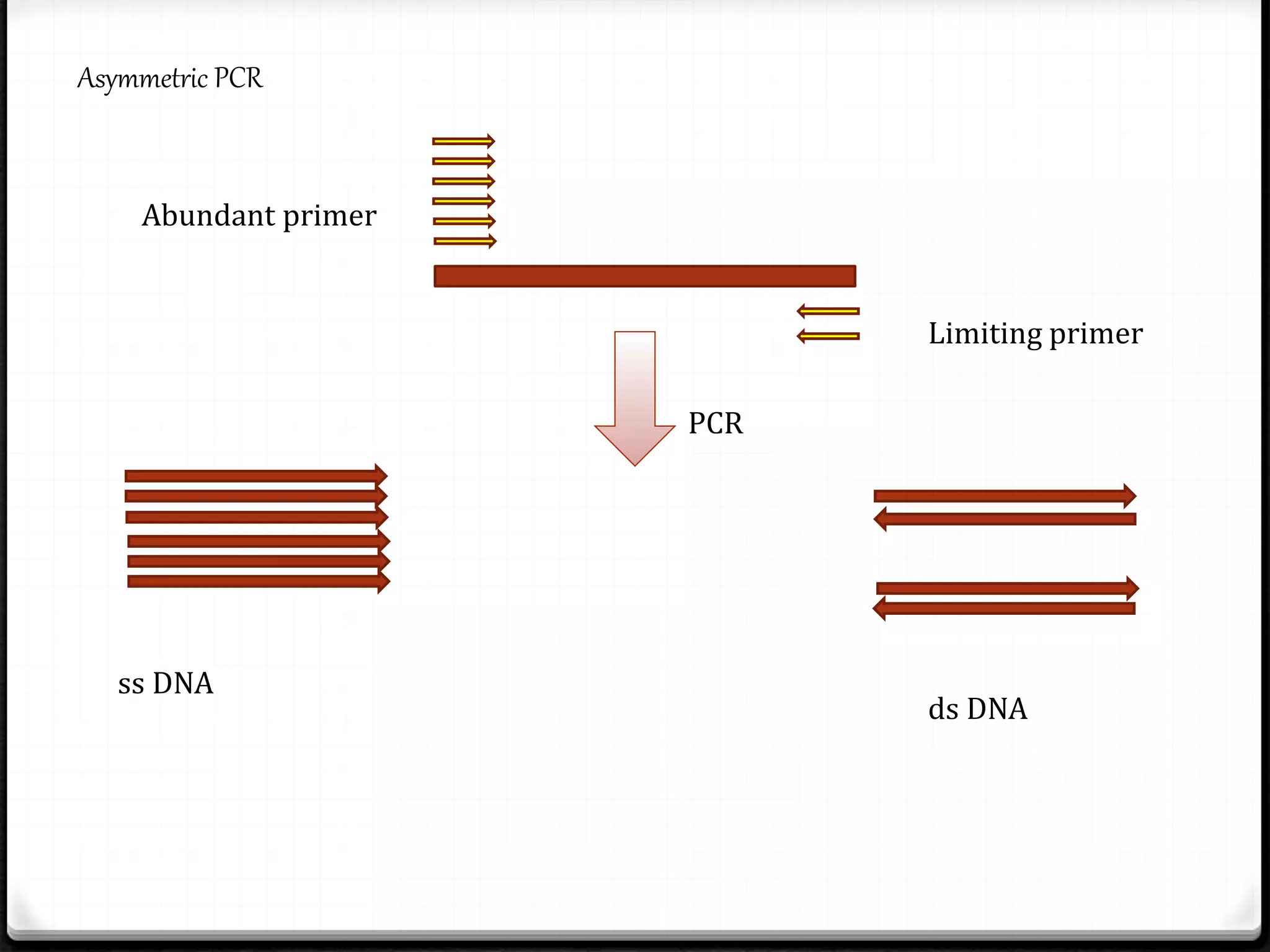
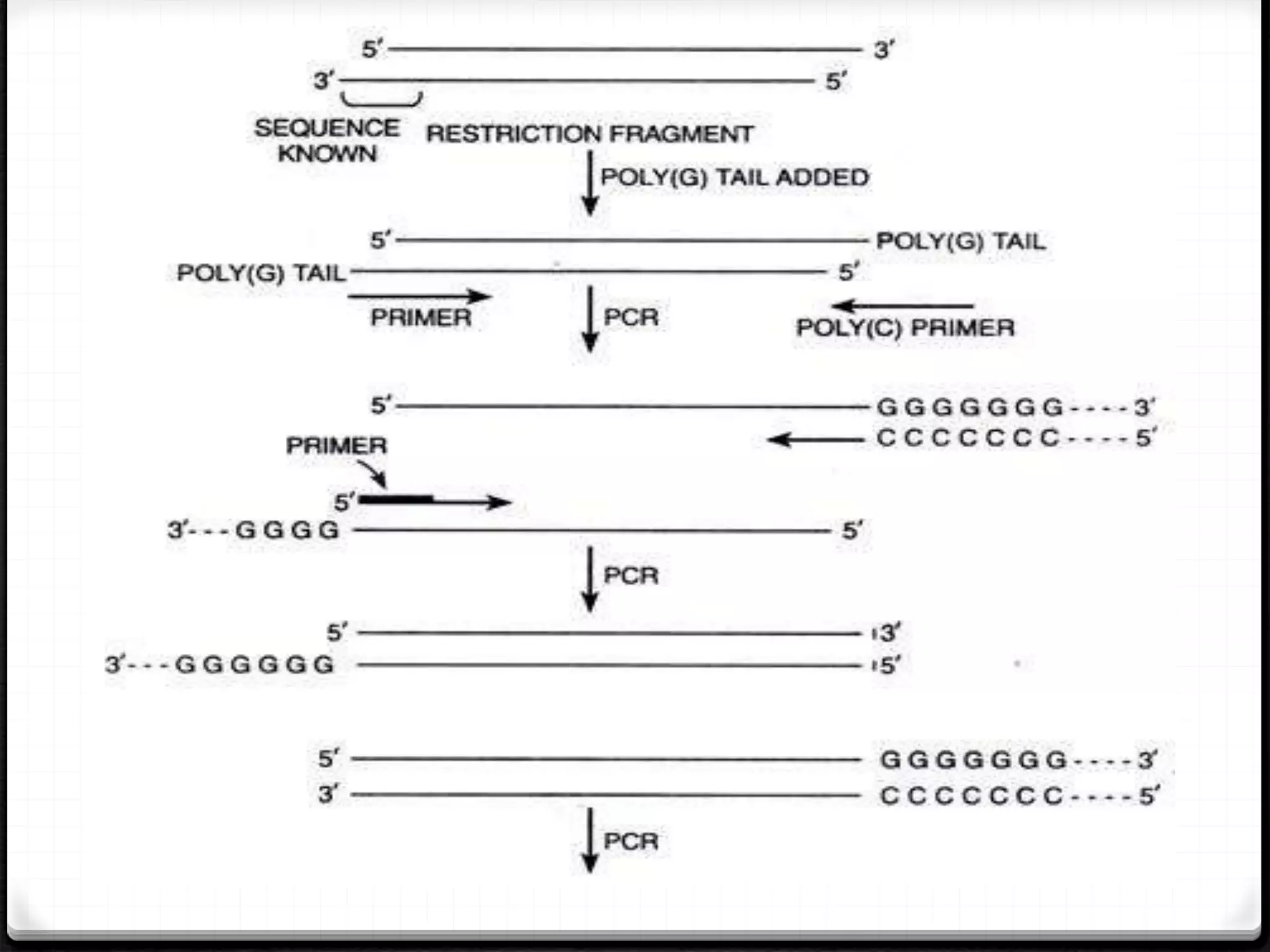
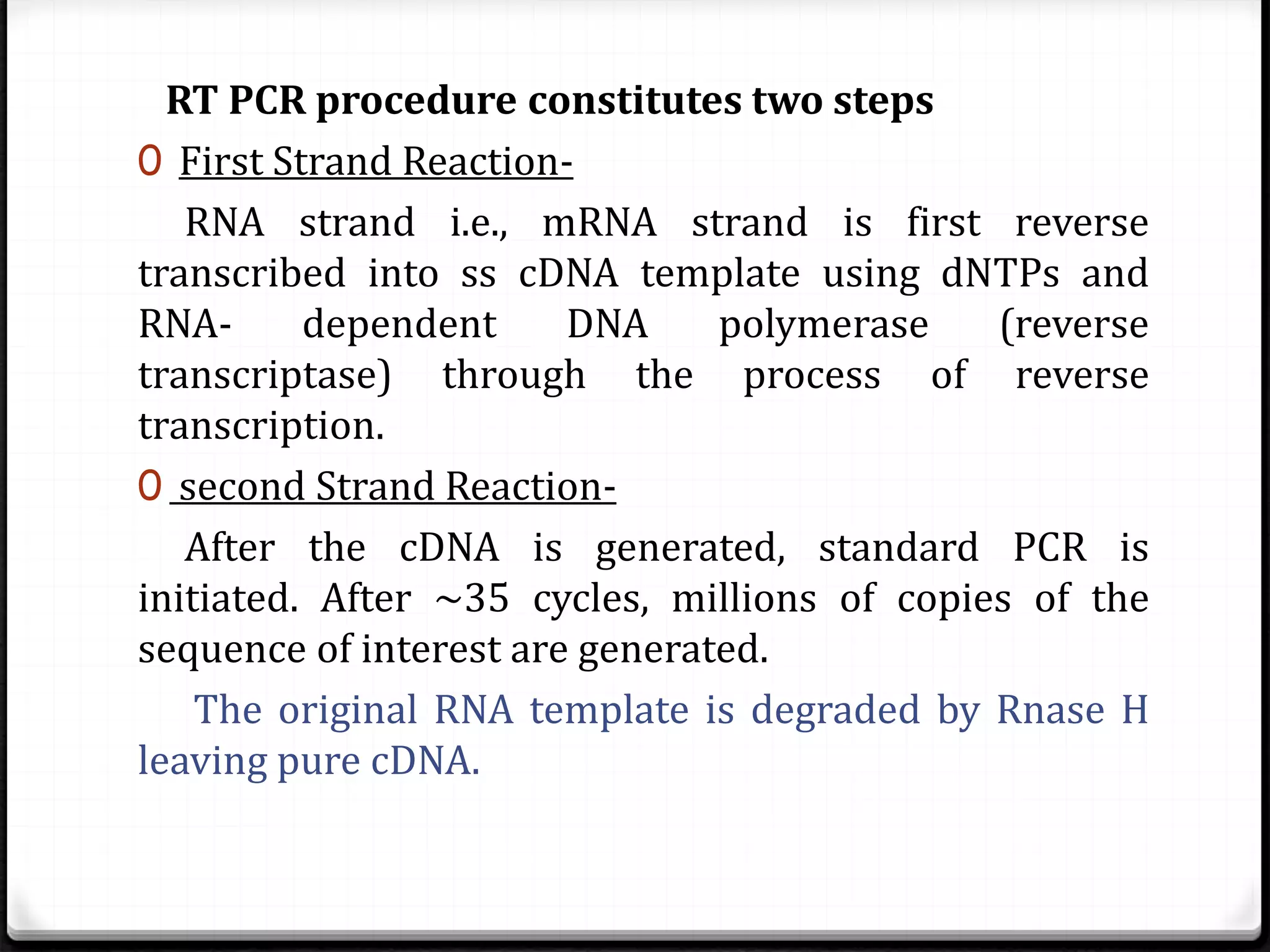
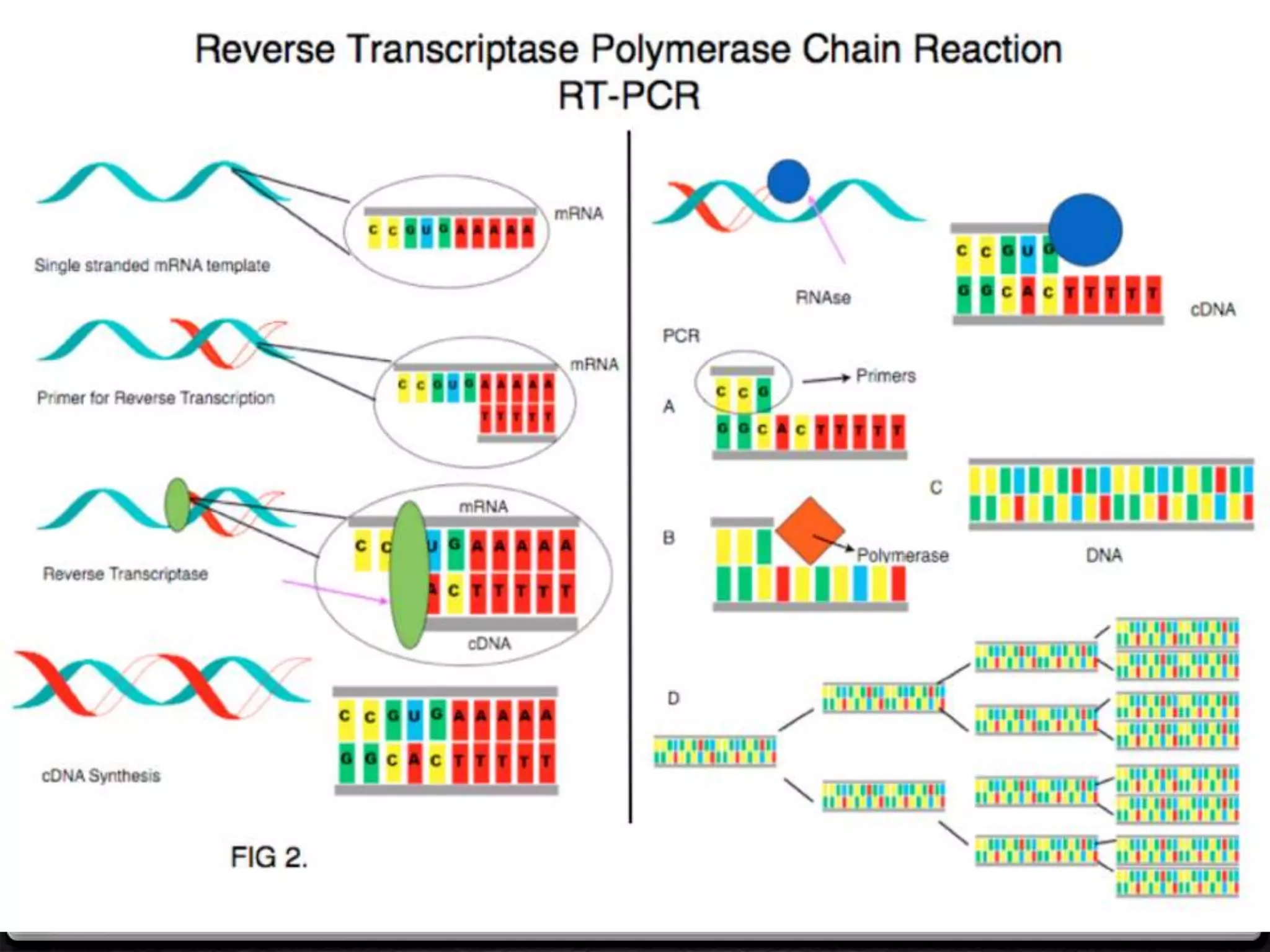
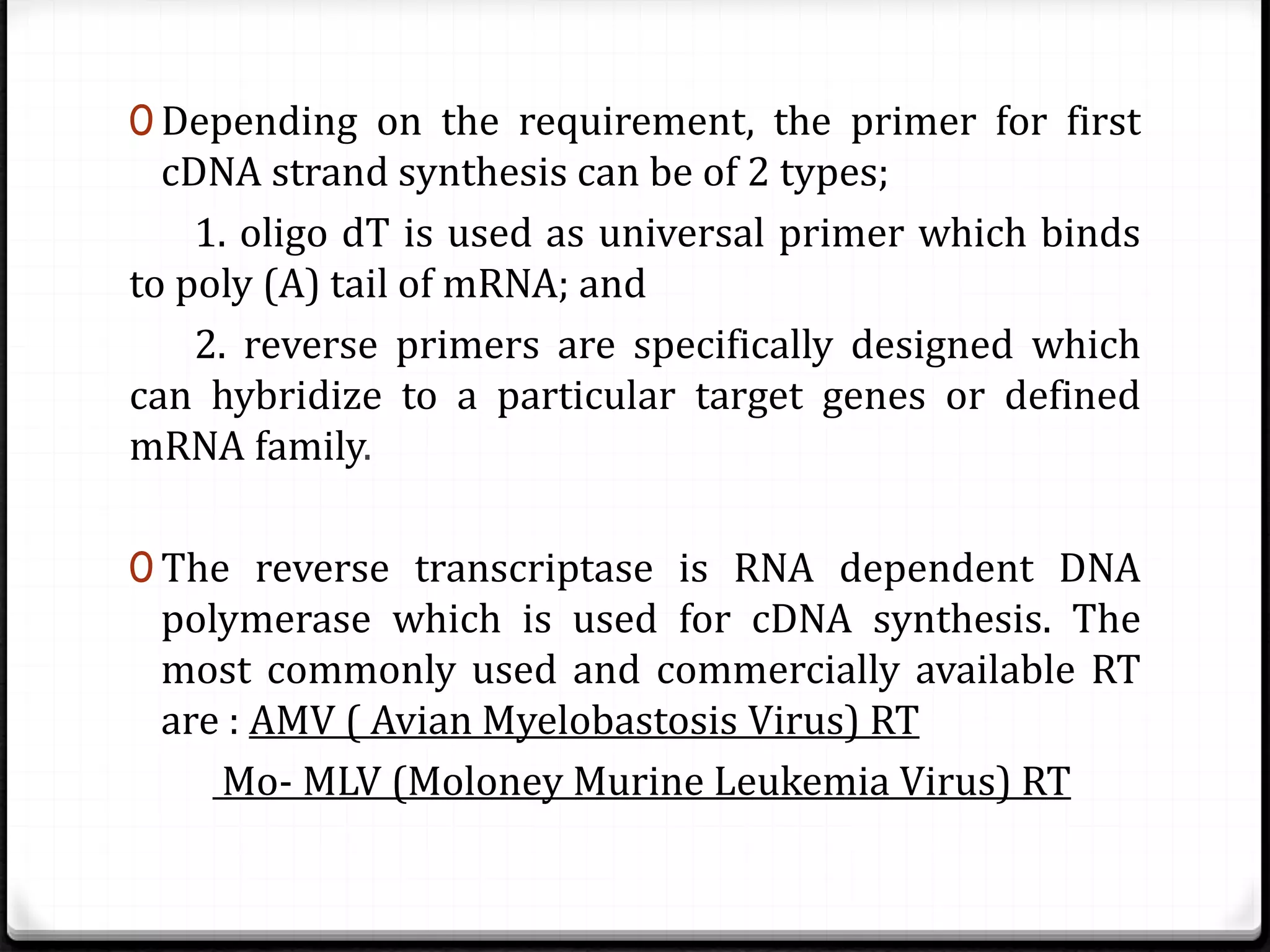
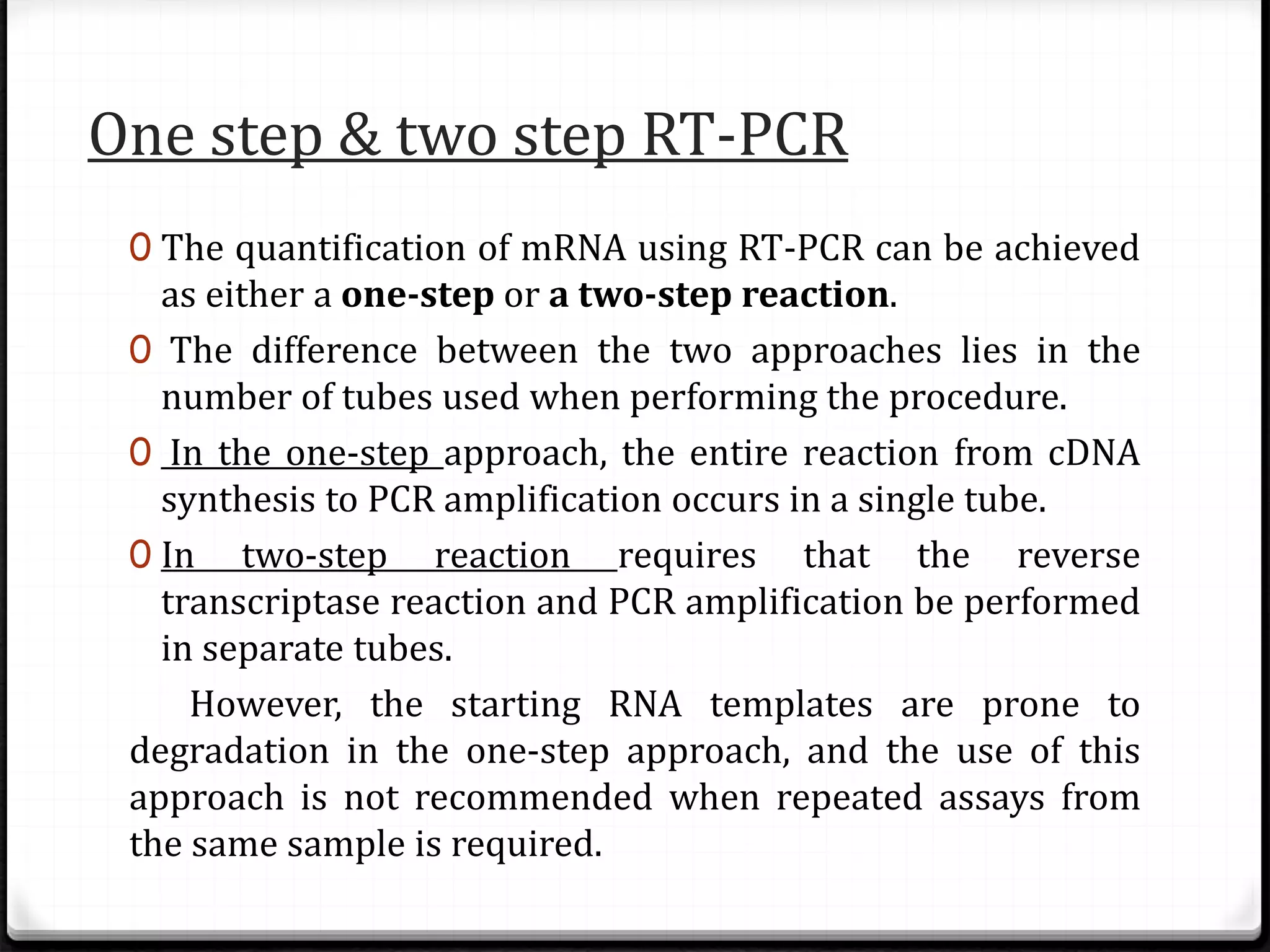
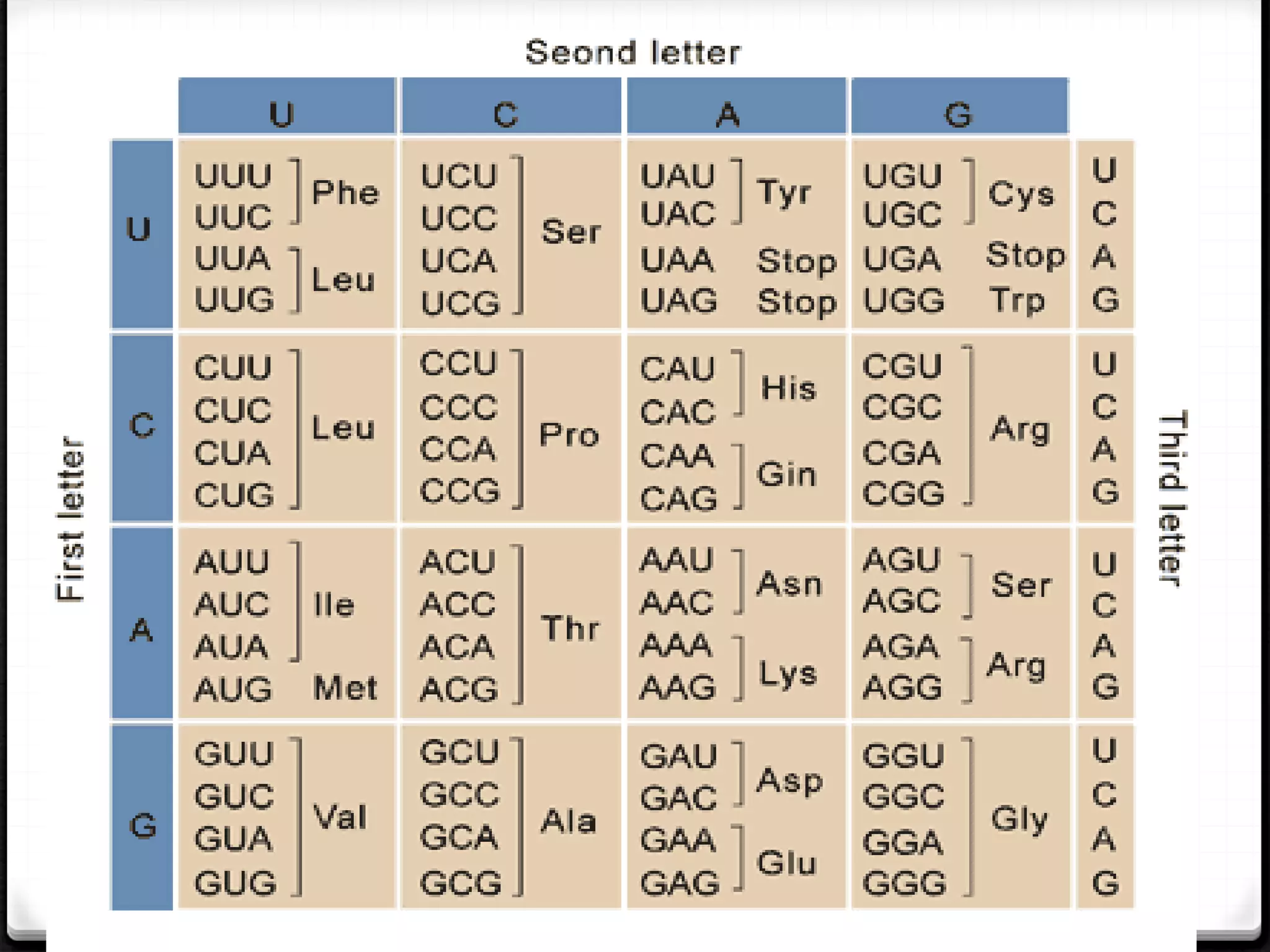
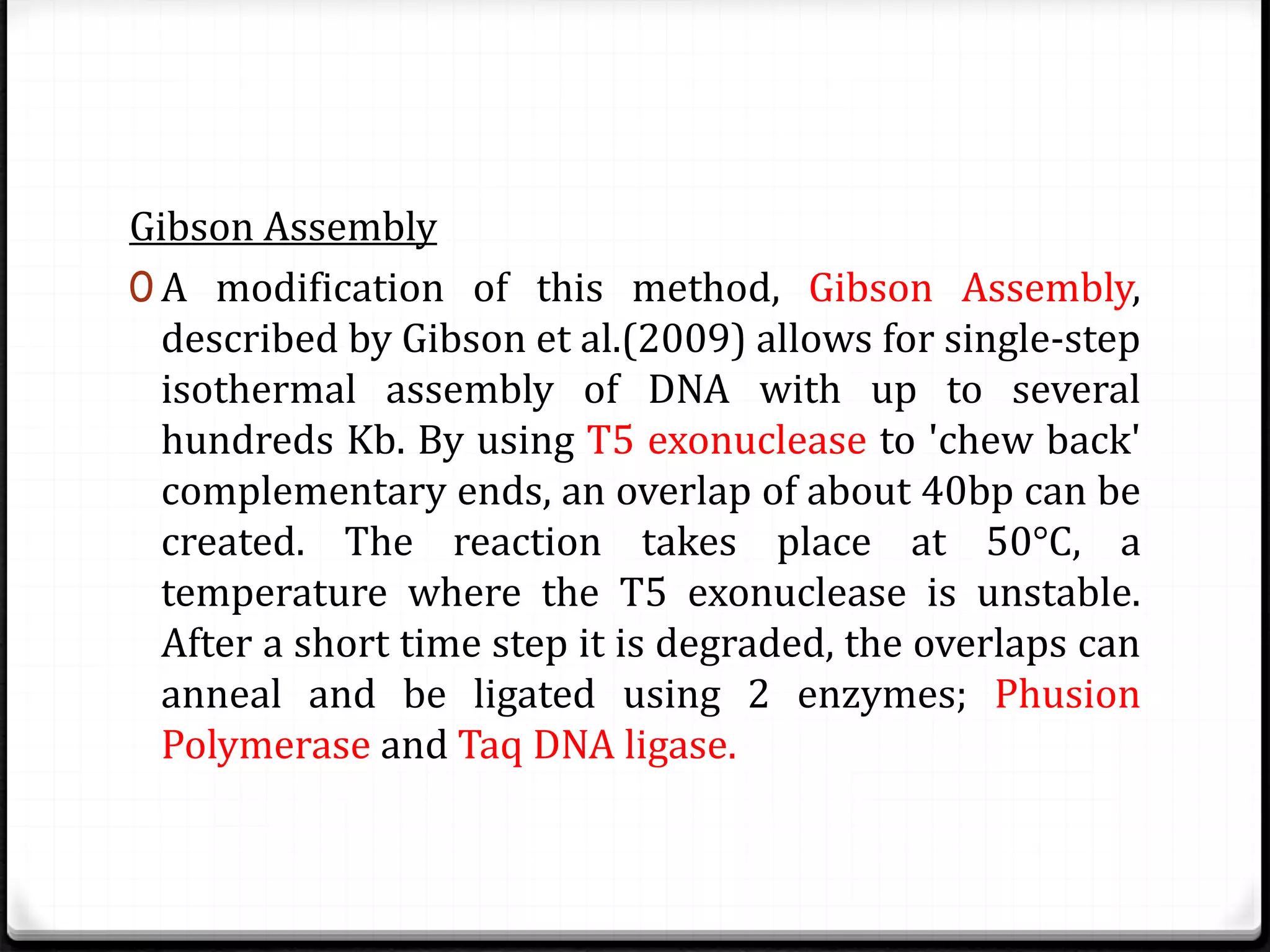
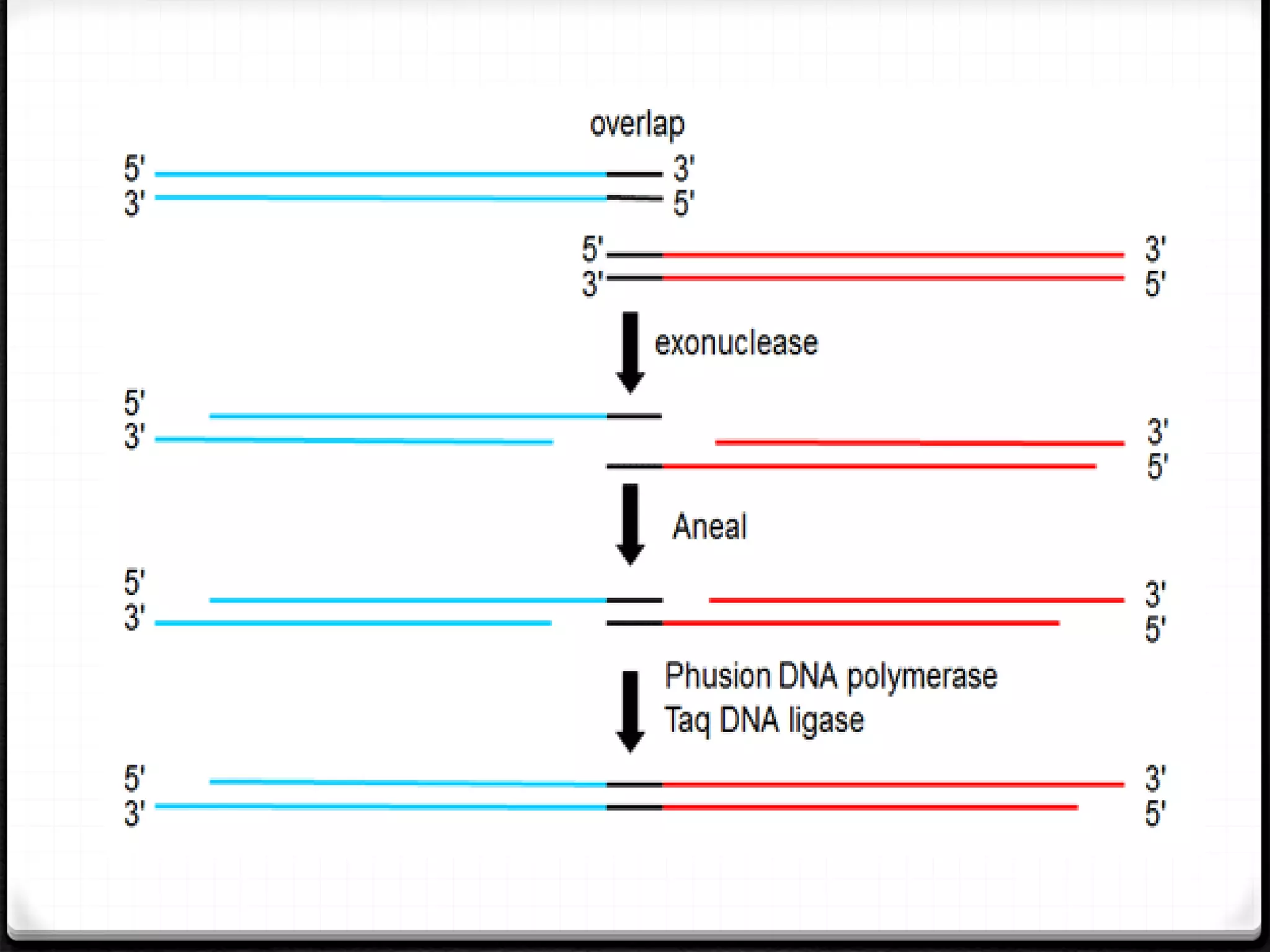
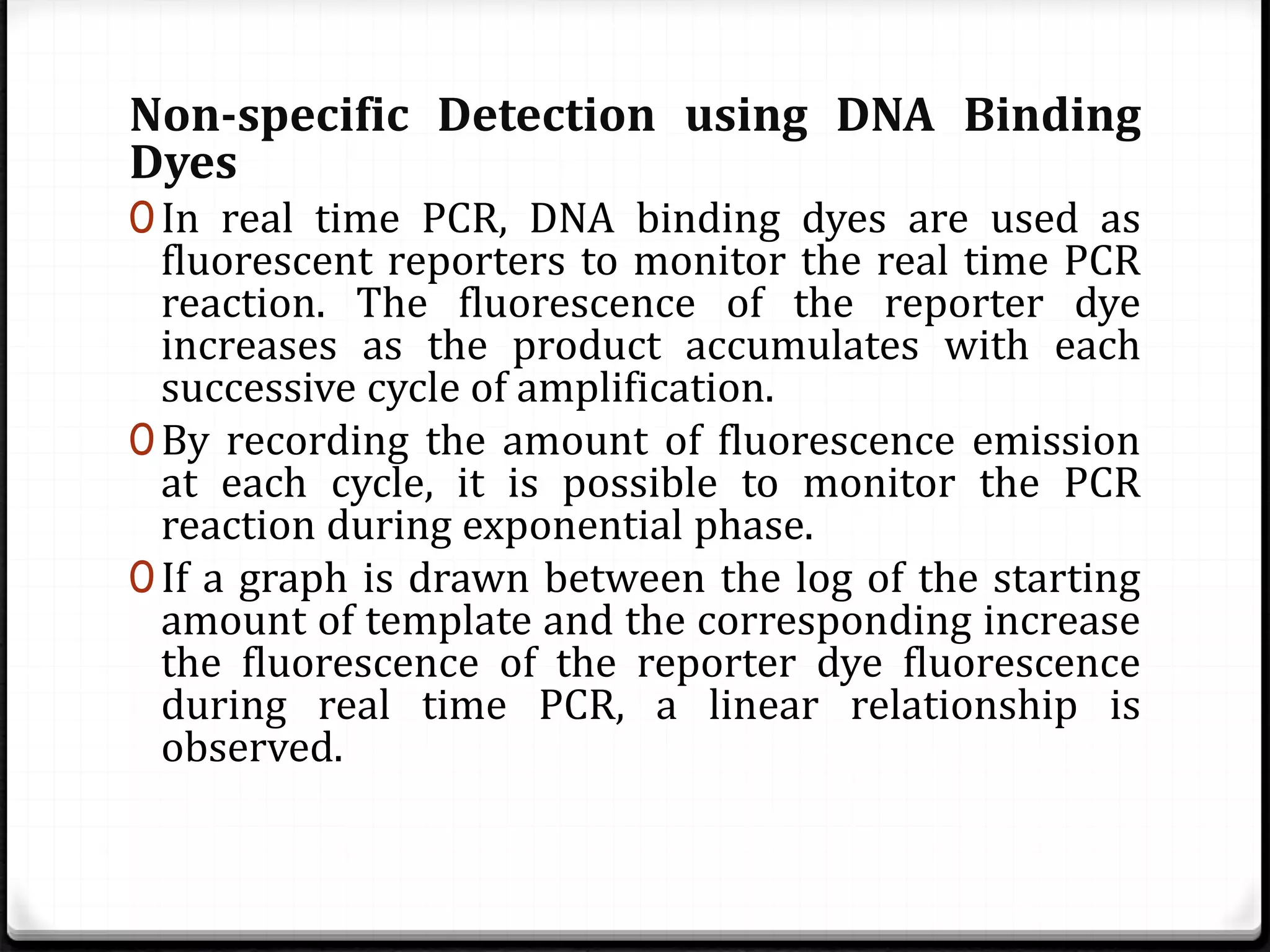
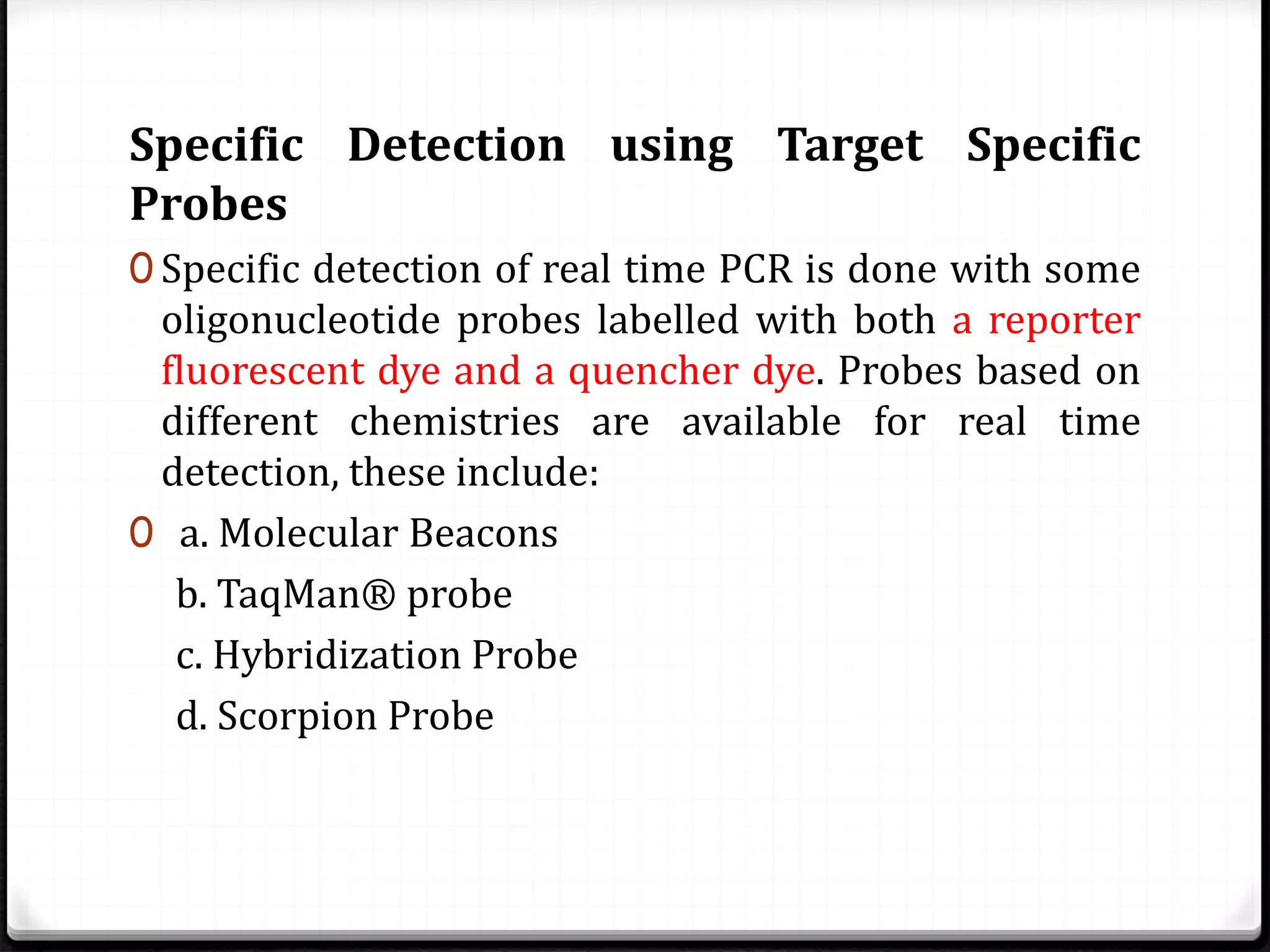
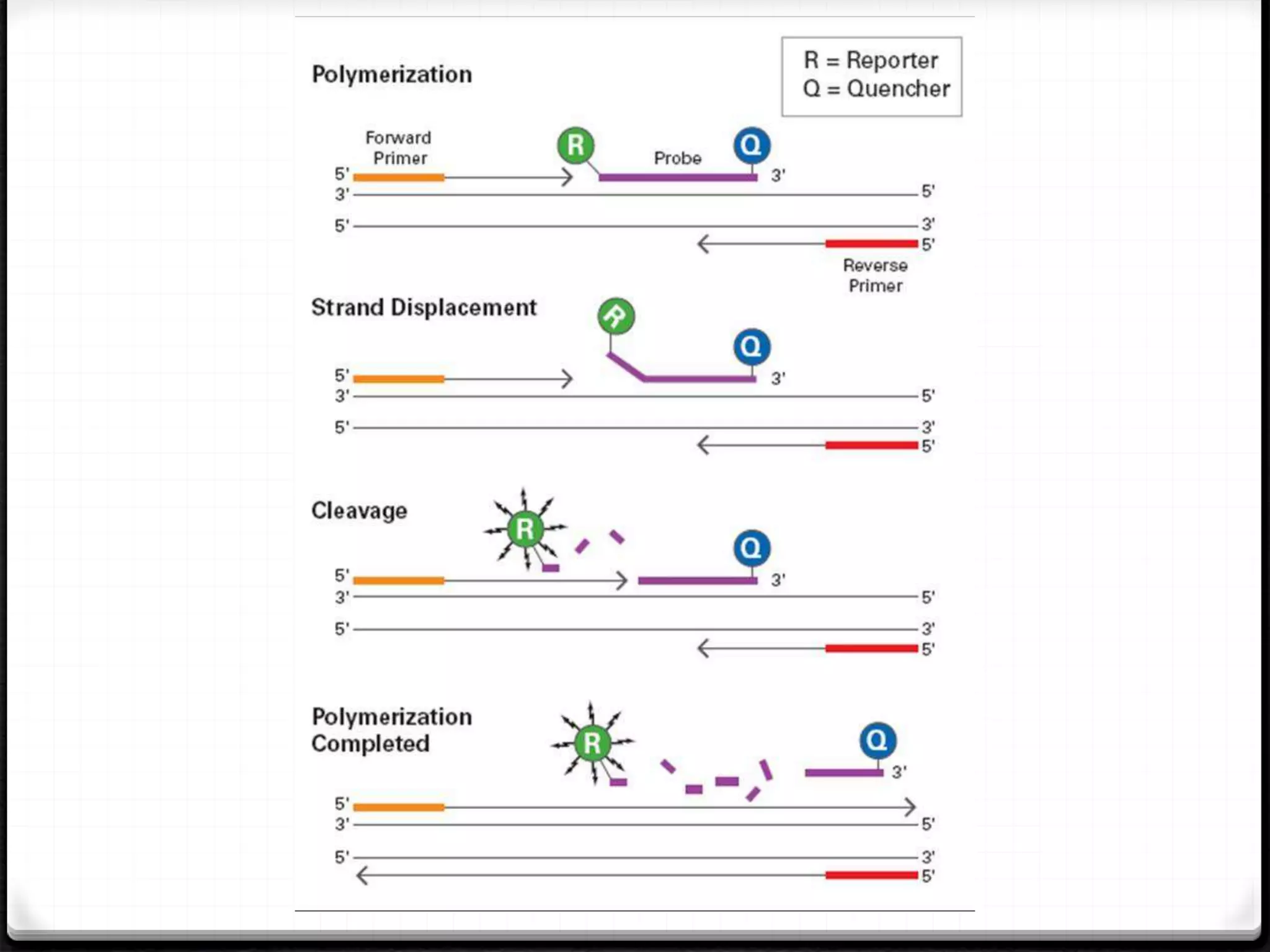
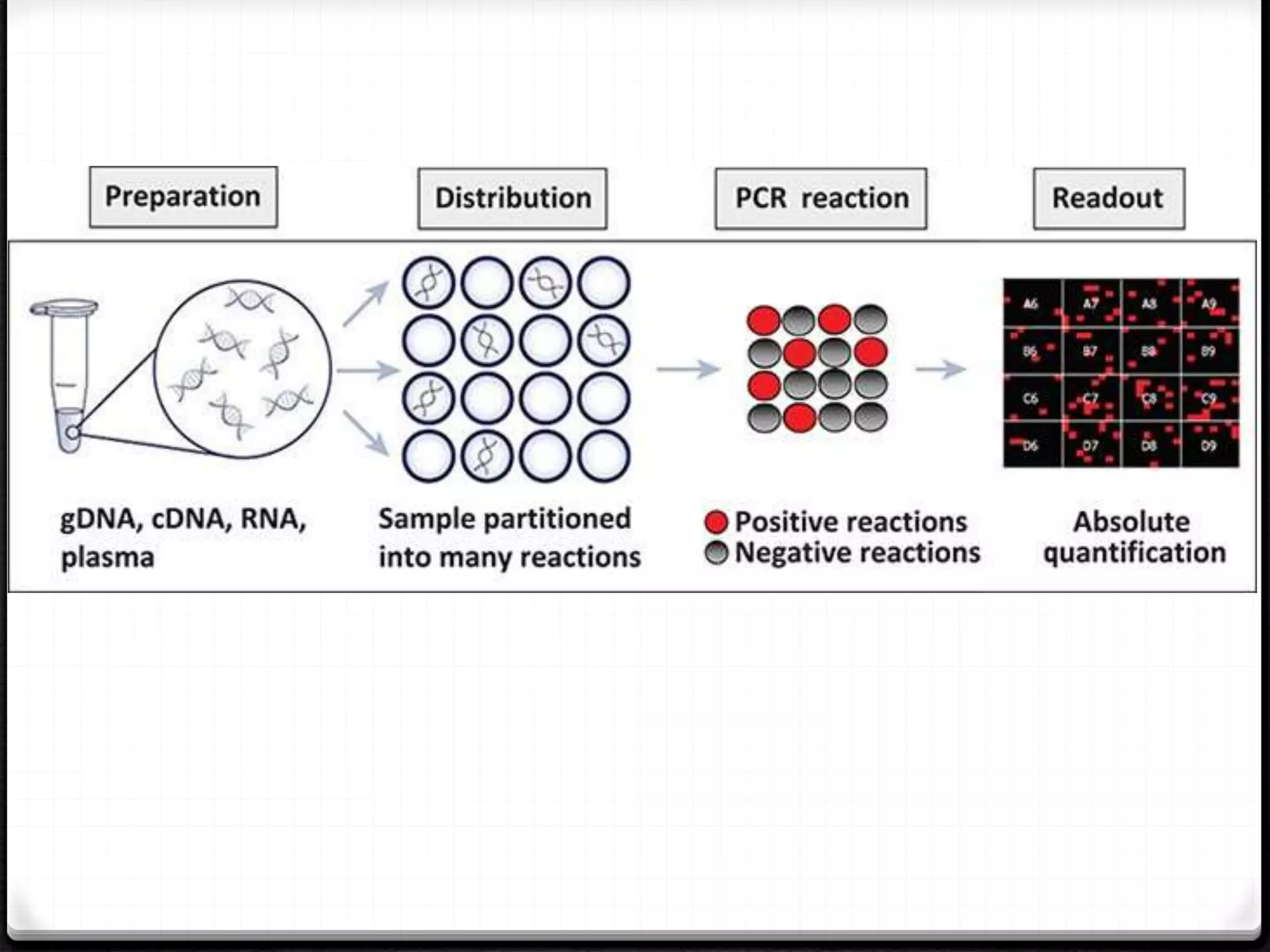
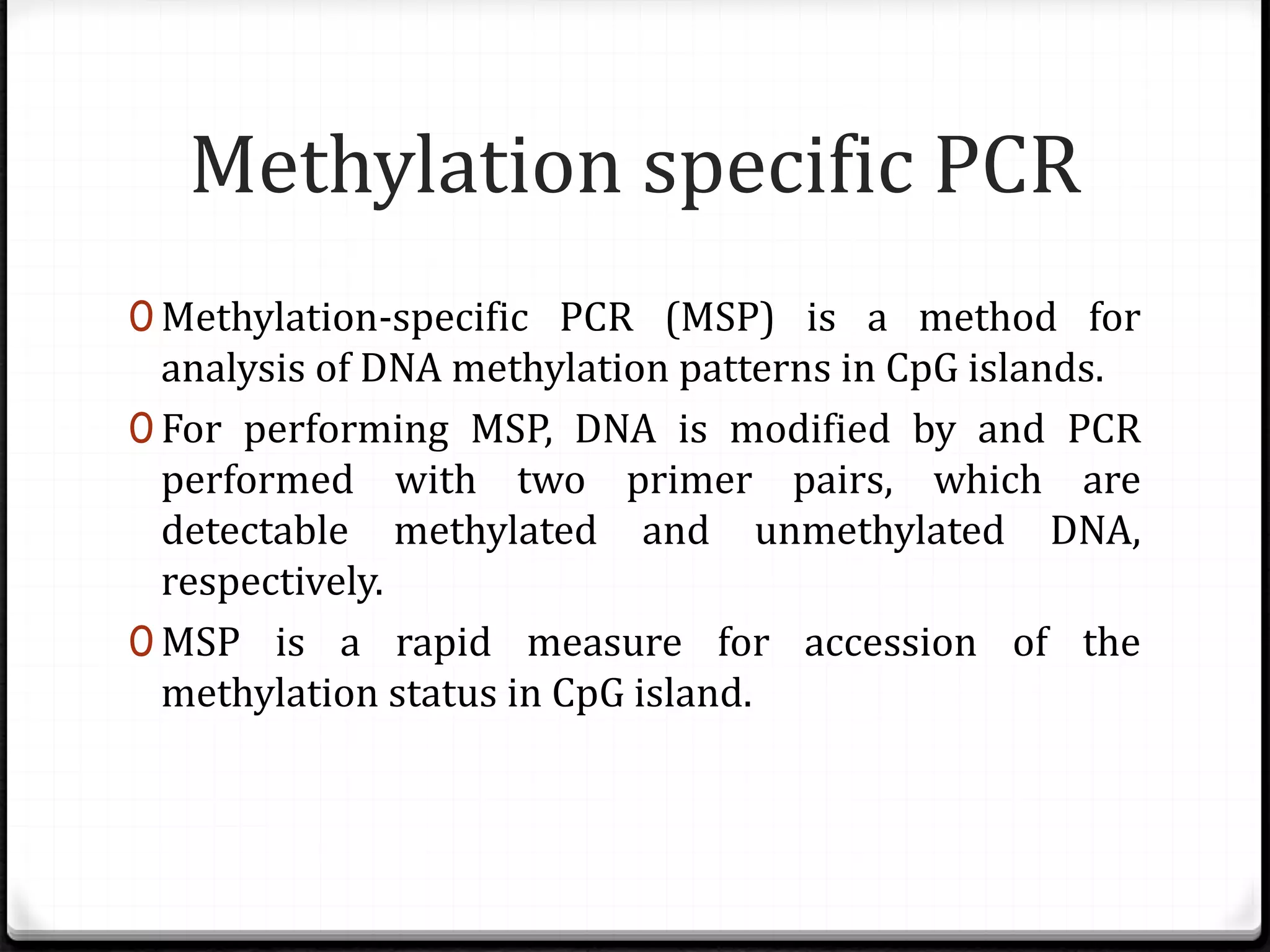
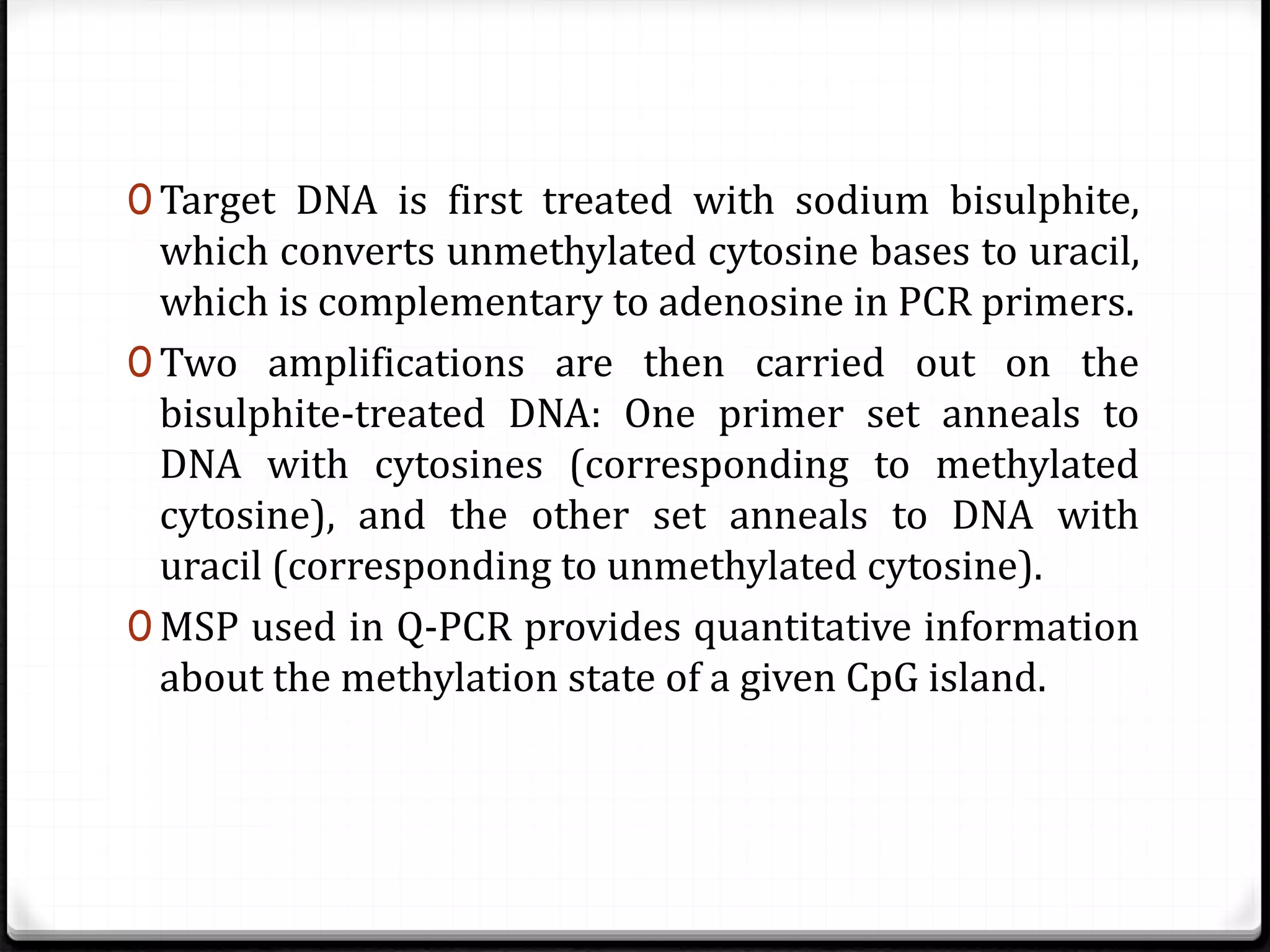
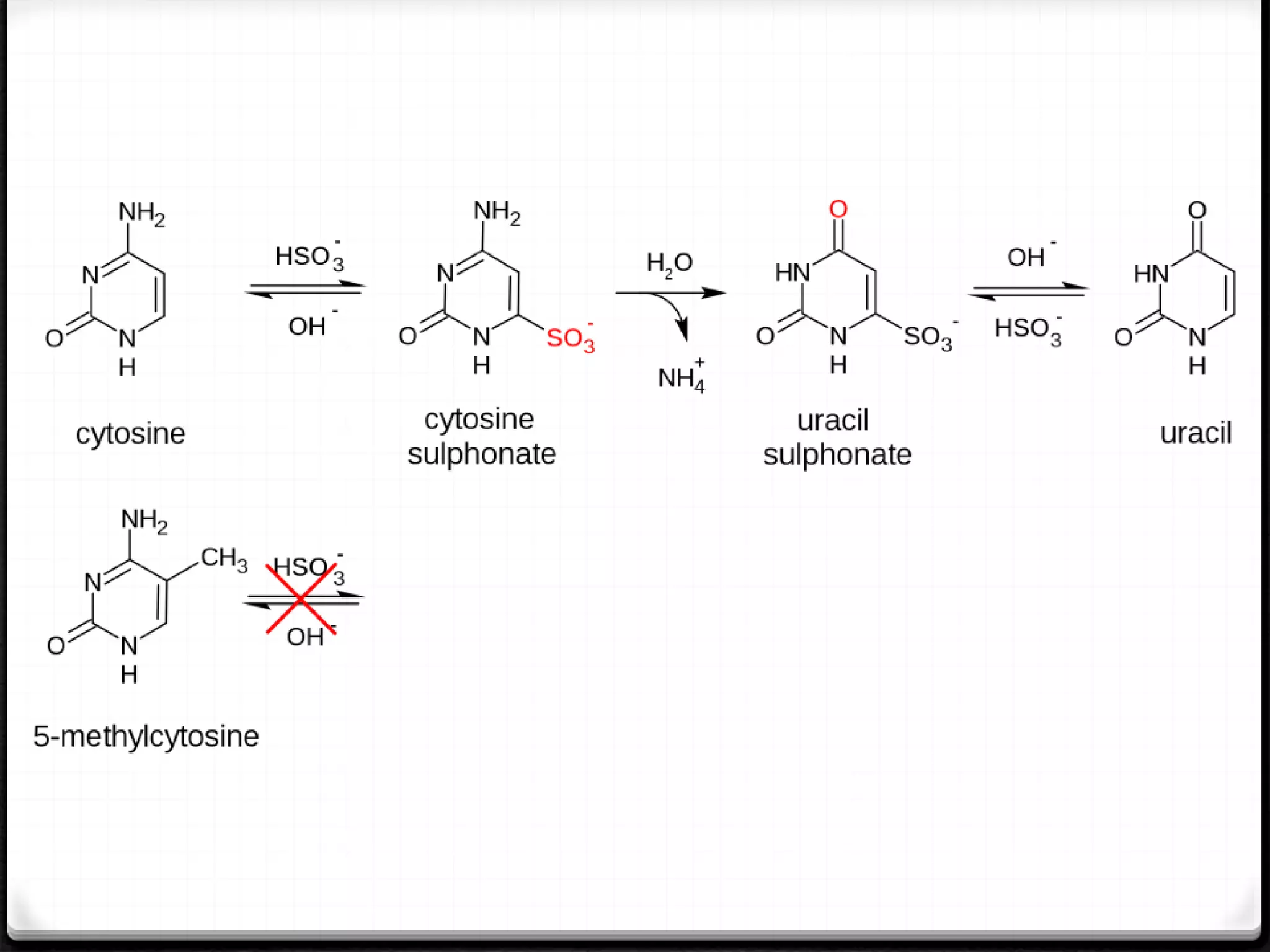
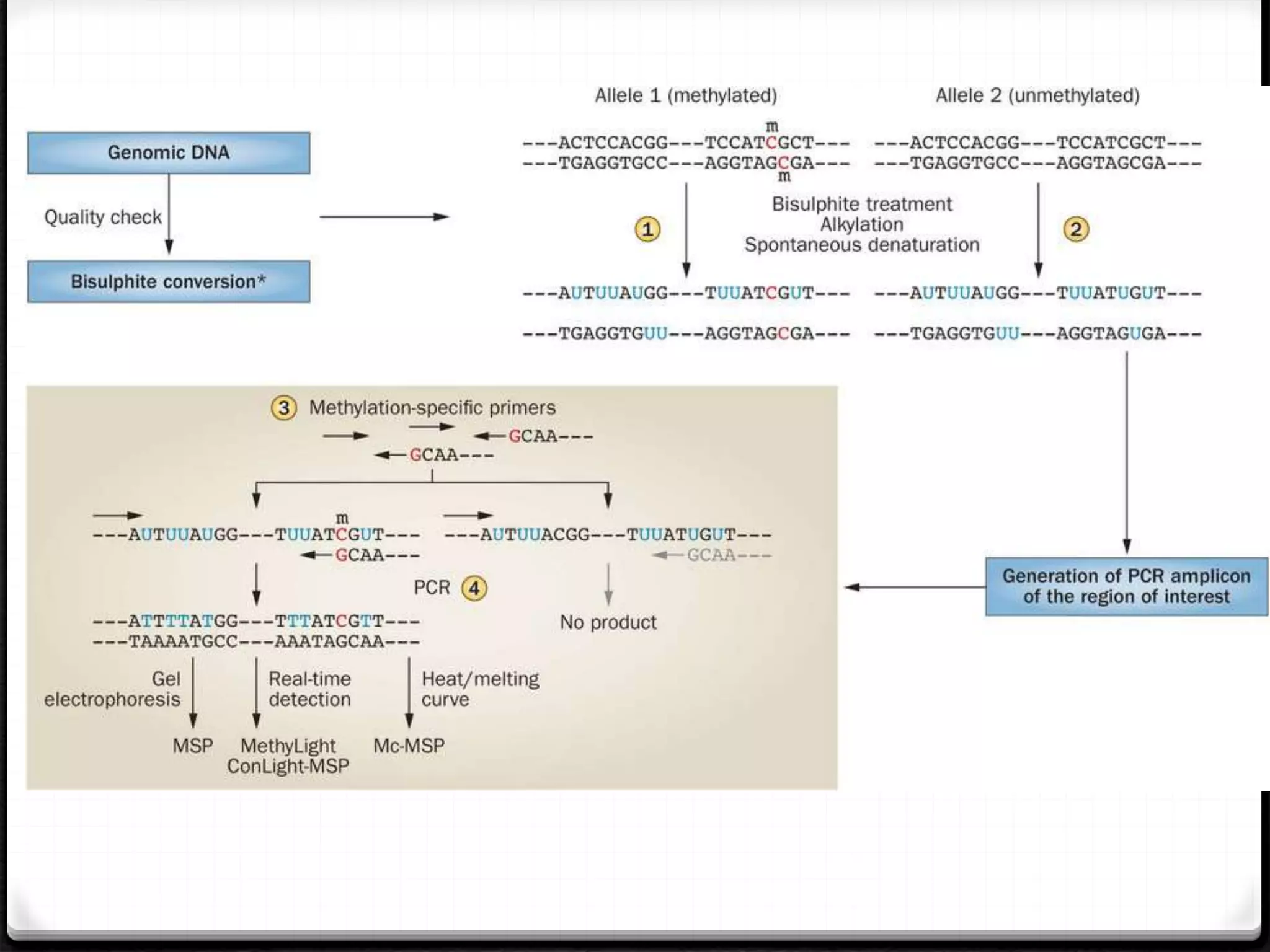
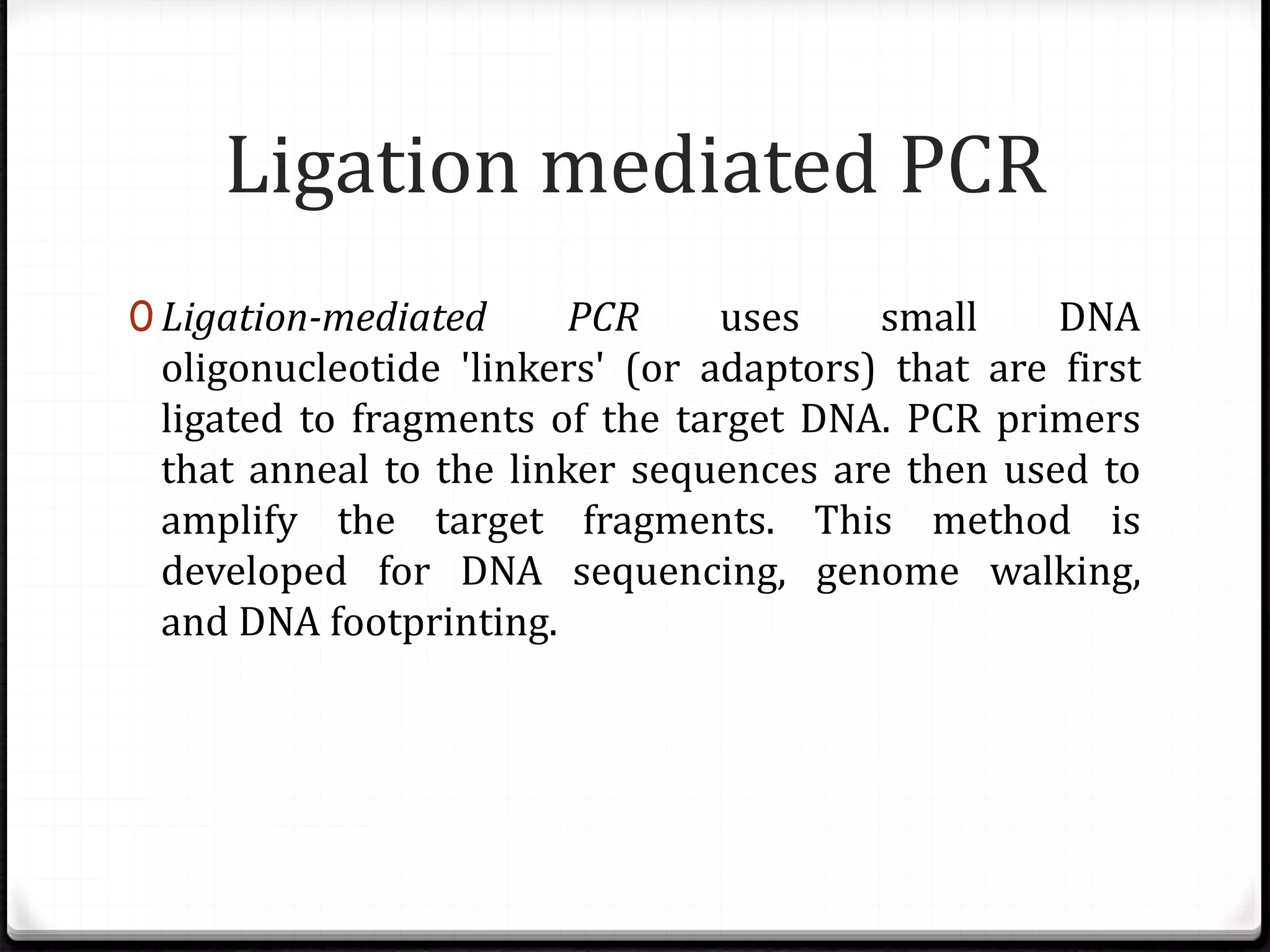
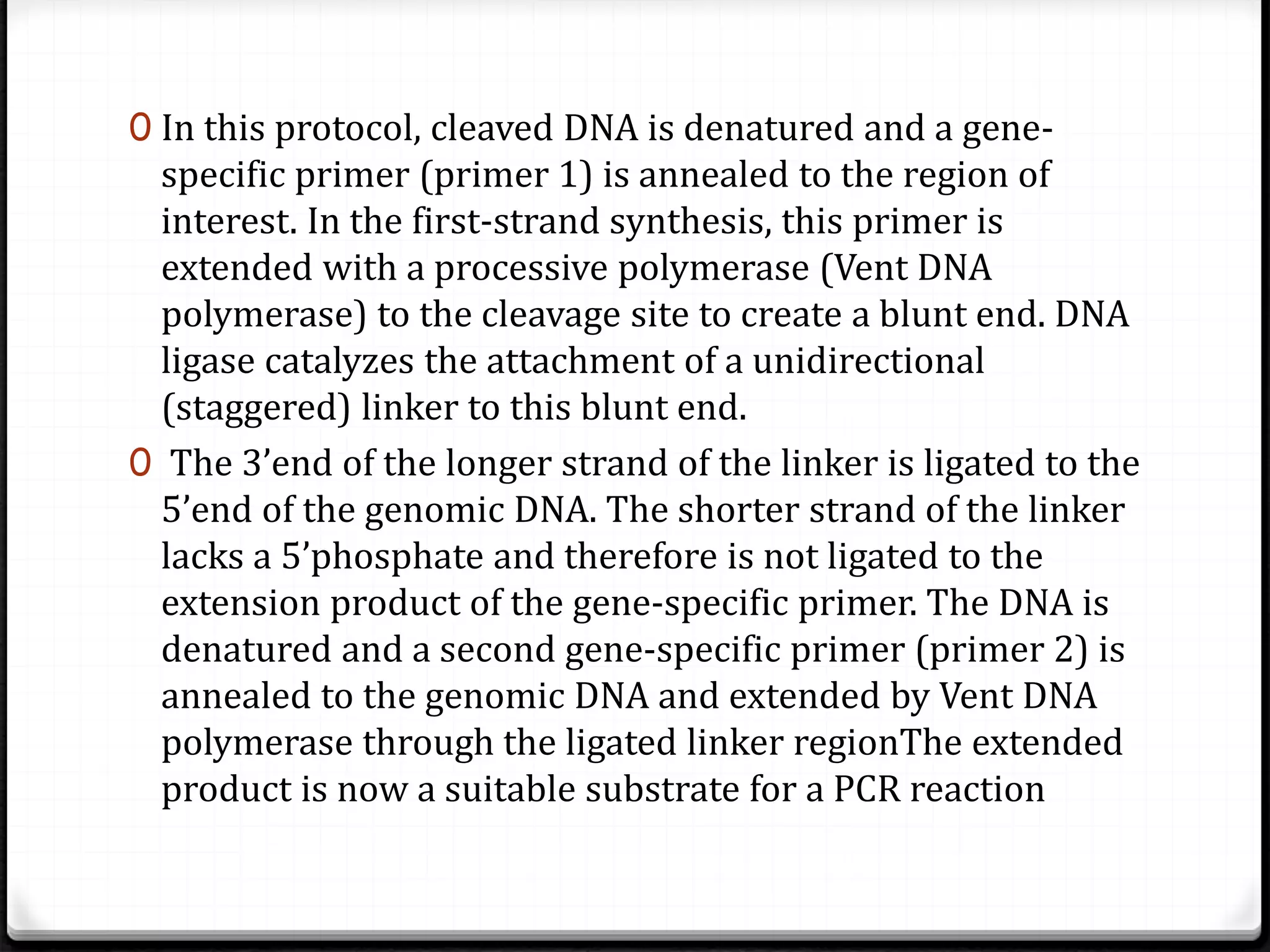
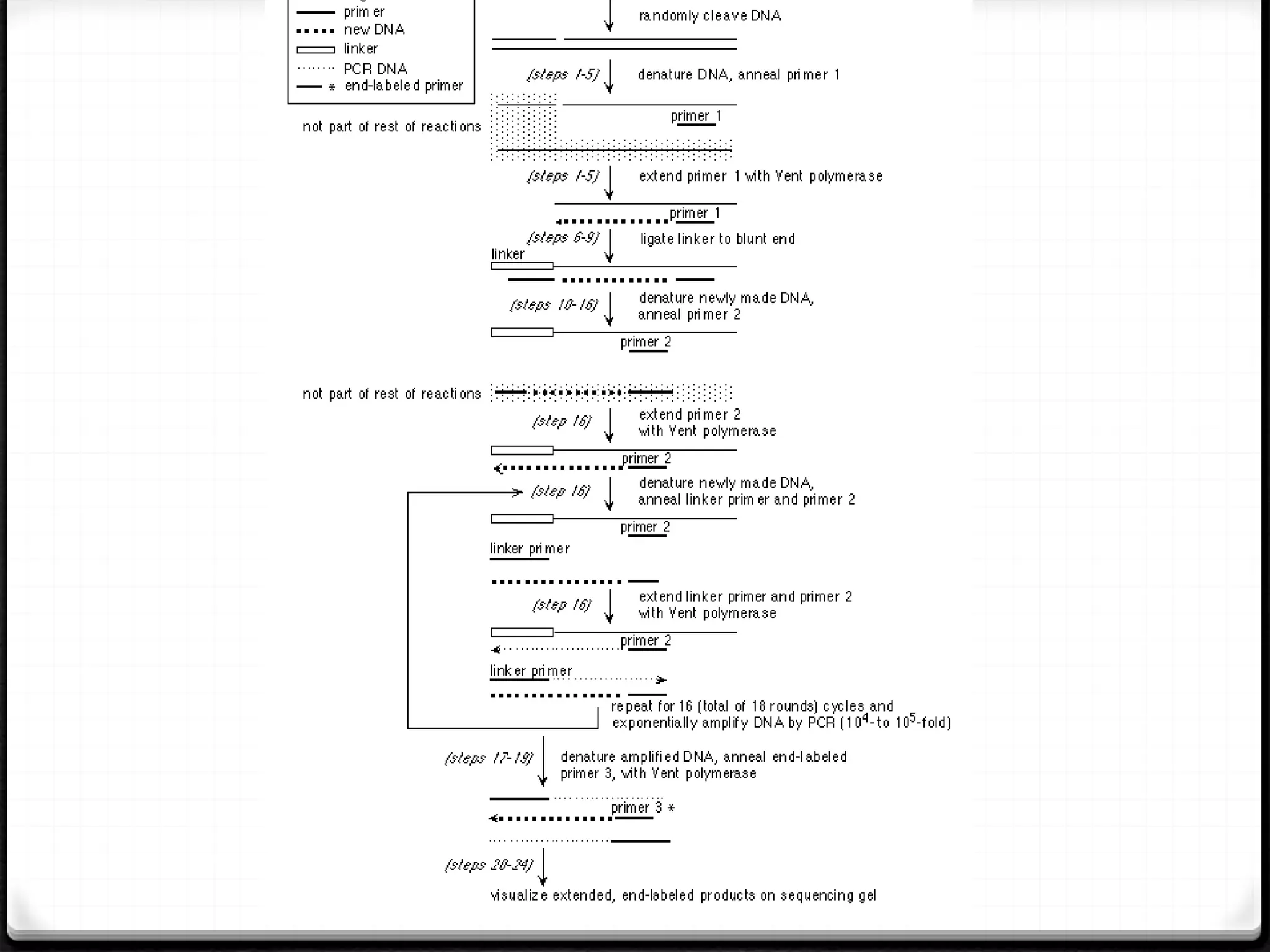
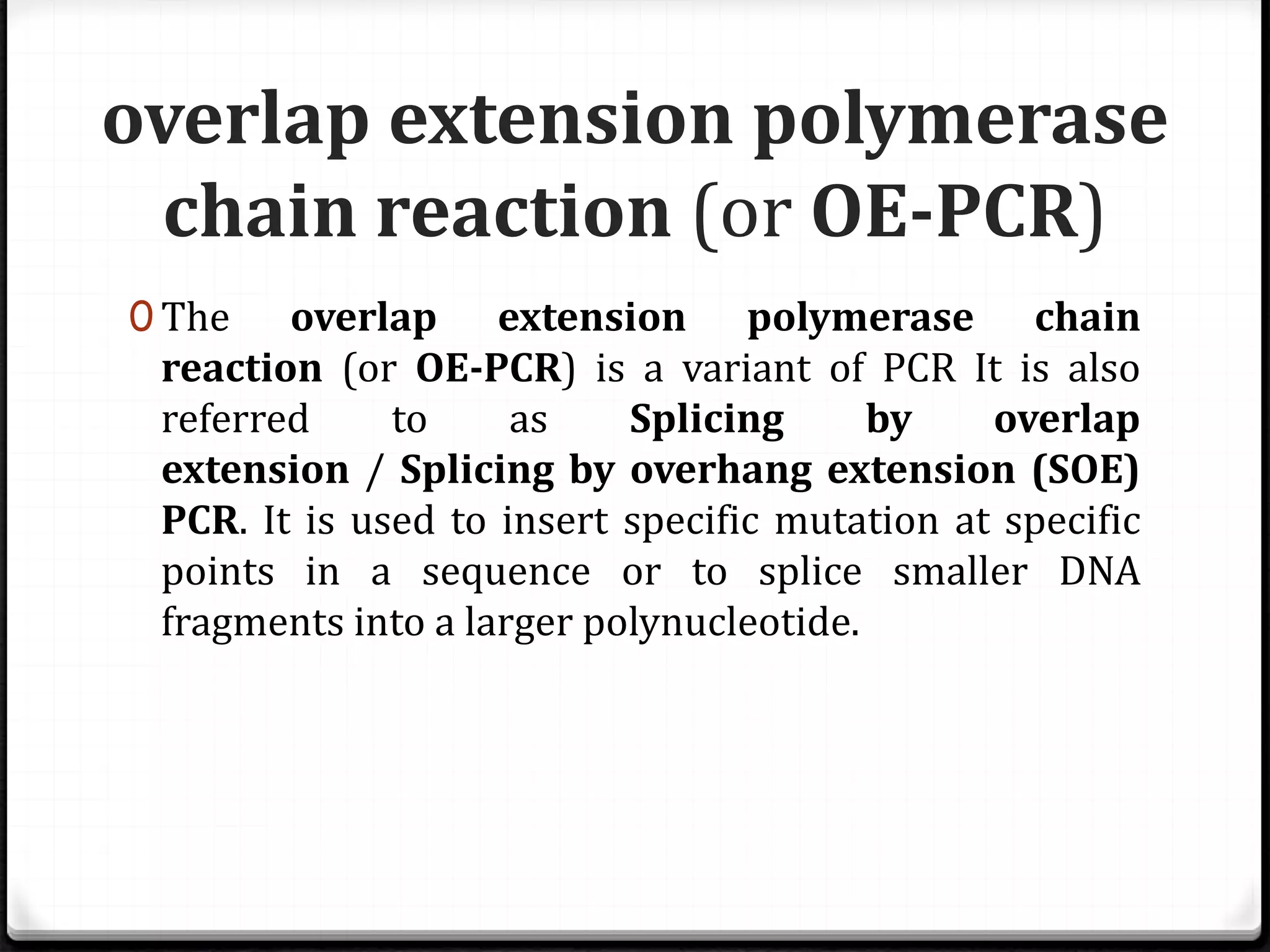
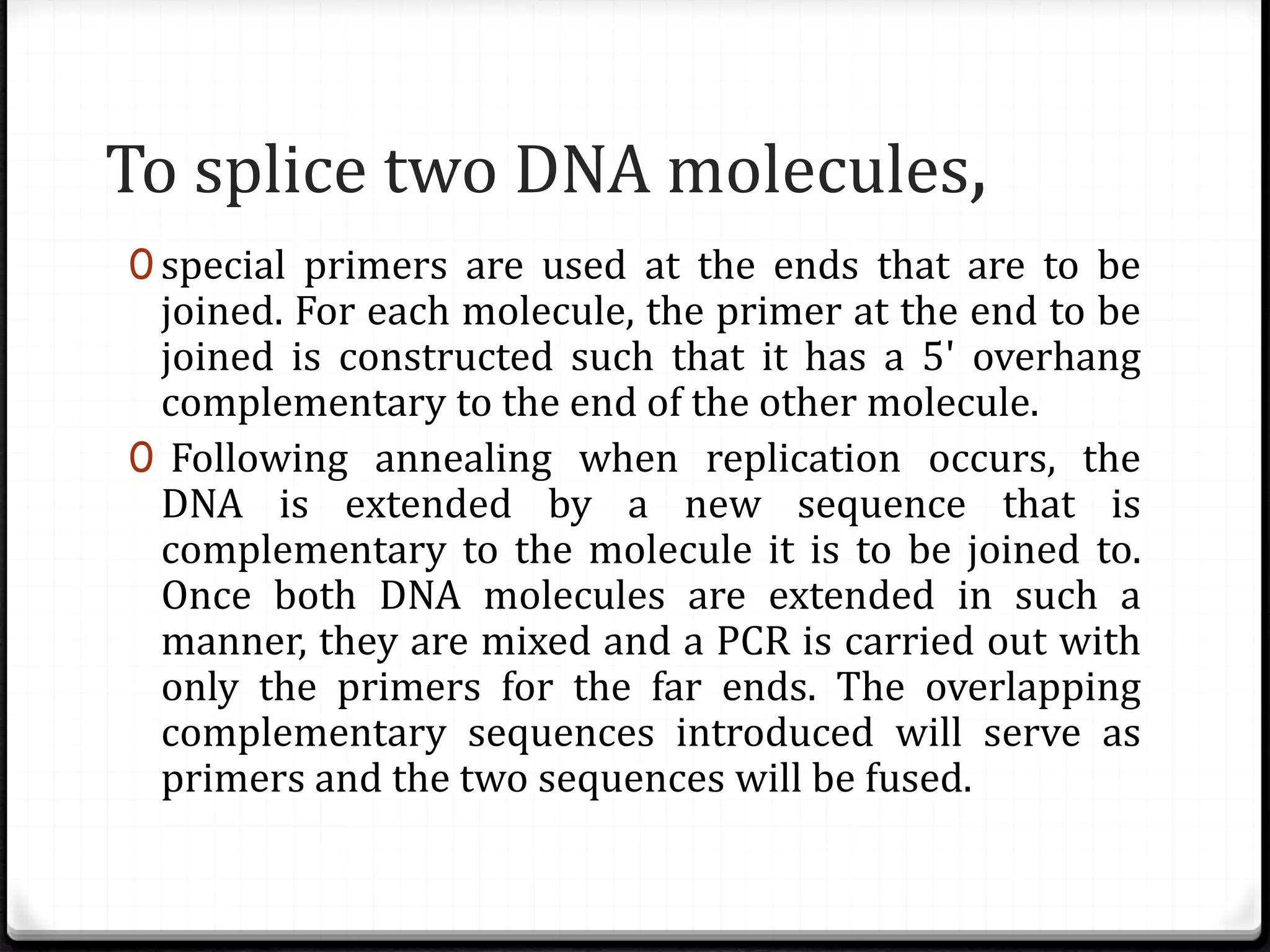
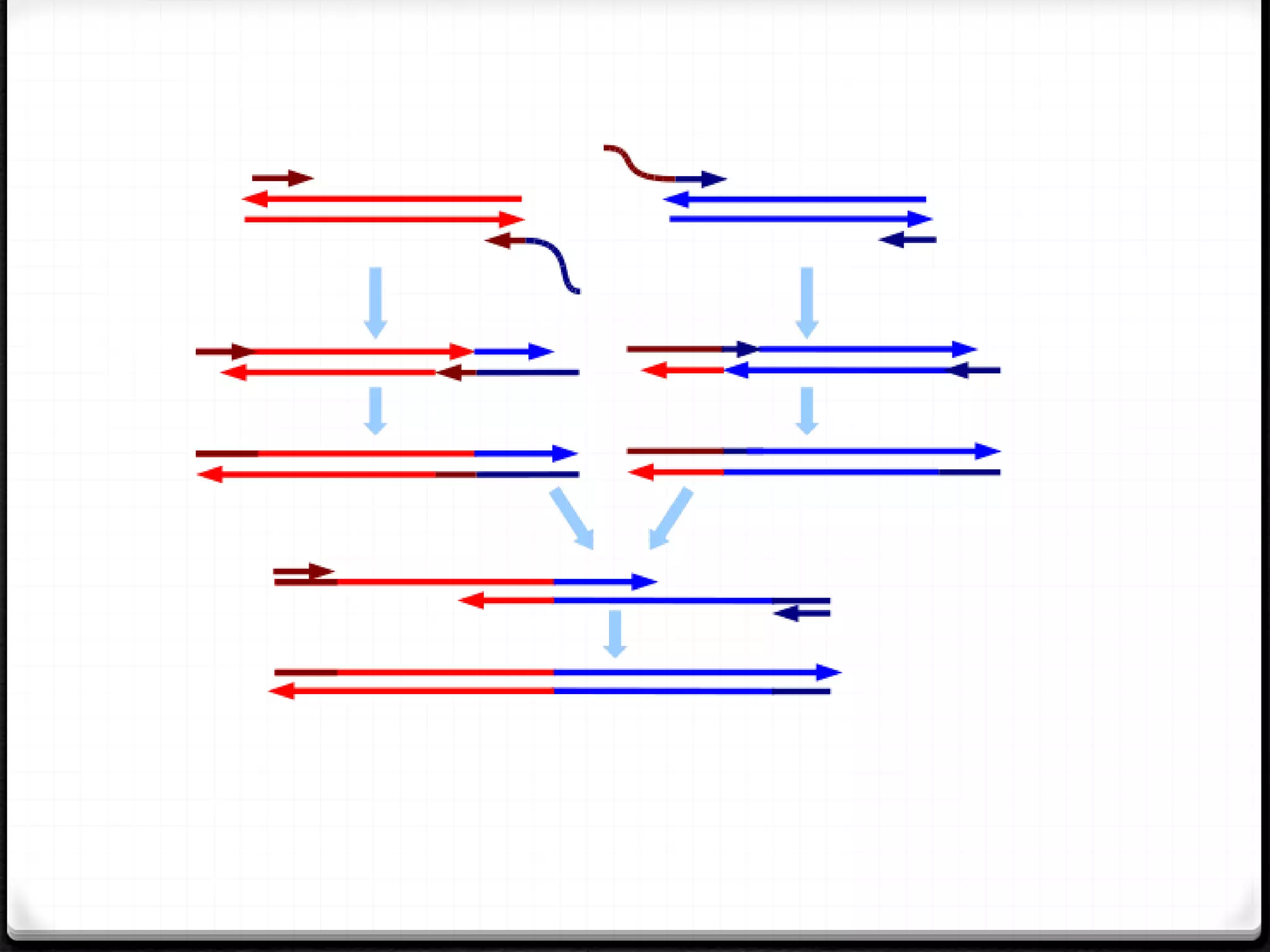
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a technique for amplifying specific DNA sequences exponentially, allowing for the identification and manipulation of genetic material. Developed by Kary Mullis in 1983, PCR utilizes DNA polymerase to enable reactions that can be adapted for various applications, including inverse, multiplex, and real-time PCR, among others. The document elaborates on different types of PCR, their methodologies, and significance in molecular biology.