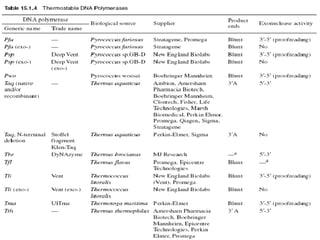
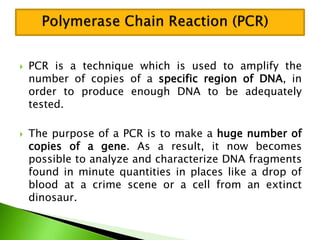
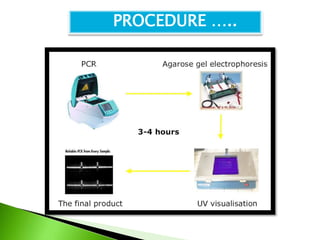
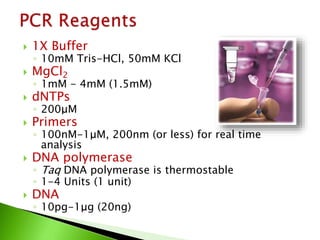
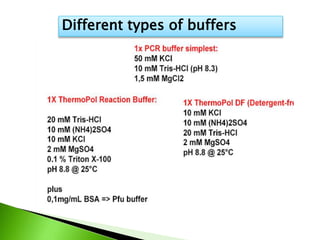
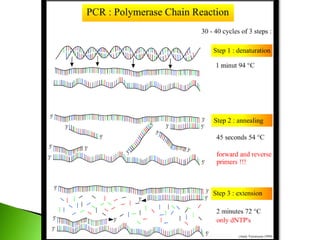
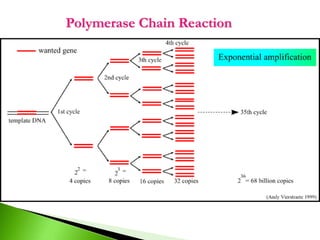
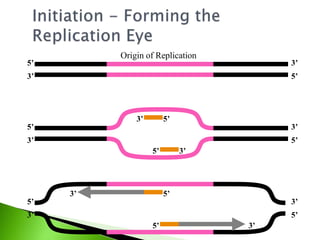
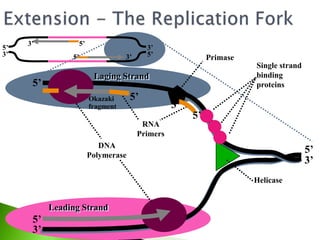
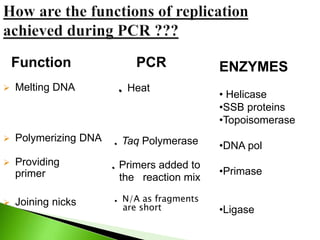
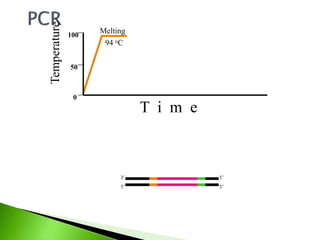
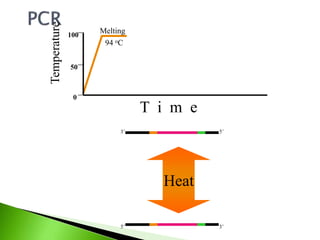
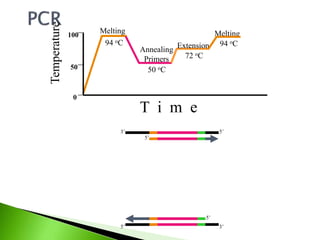
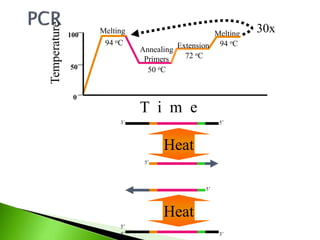
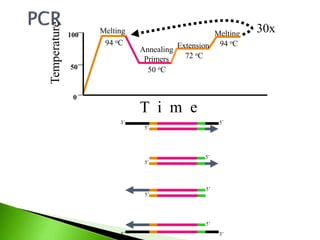
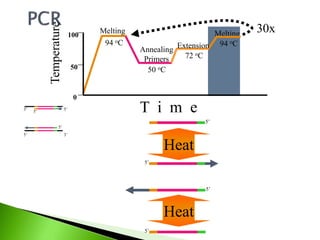
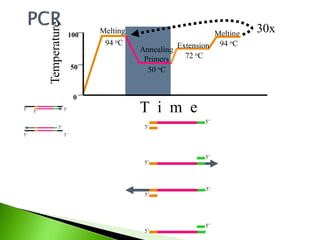
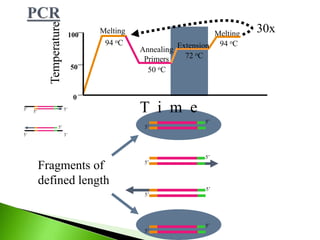
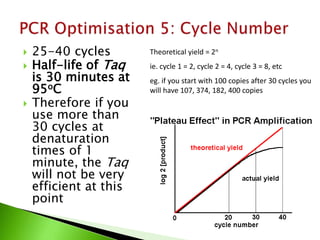
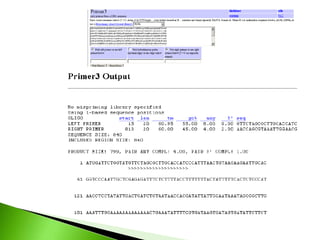
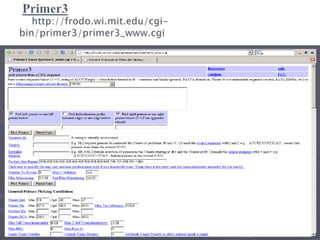
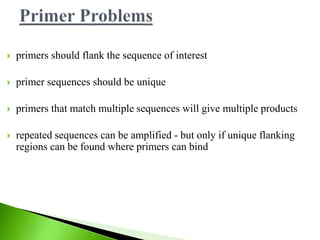
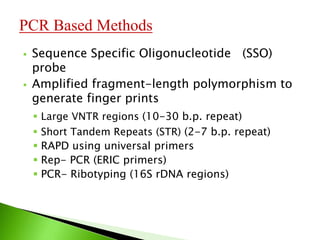
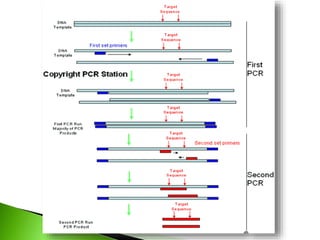
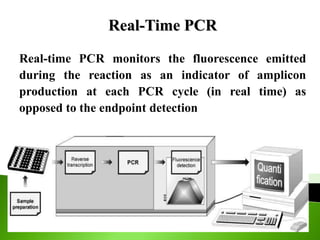
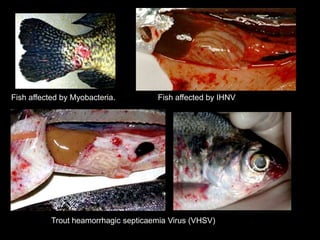
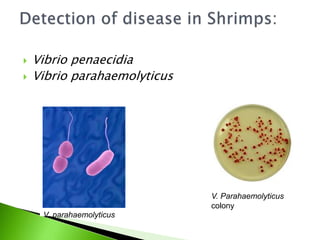
The document discusses the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) technique. It was invented by Kary Mullis in 1985. PCR allows for targeted amplification of specific DNA sequences. It works by using DNA polymerase to make copies of a targeted region of DNA defined by primer sequences. Through repeated heating and cooling cycles, millions of copies of the target DNA can be produced, allowing it to be analyzed. Taq polymerase, an enzyme from thermophilic bacteria, is used as it is heat-stable and allows the reaction to take place.