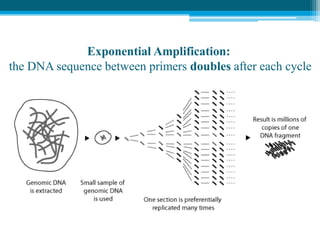
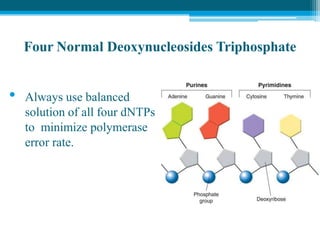
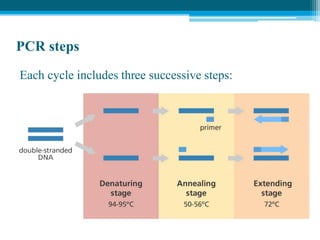
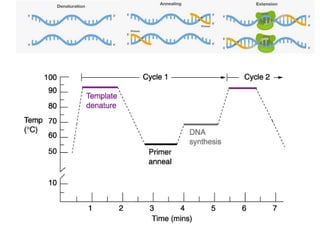
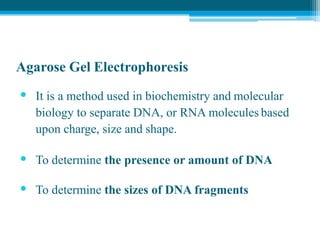
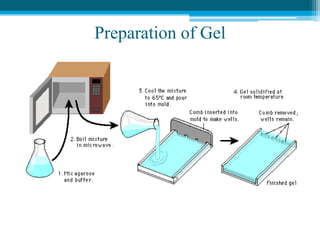
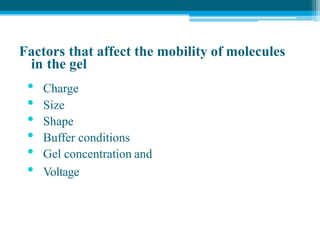
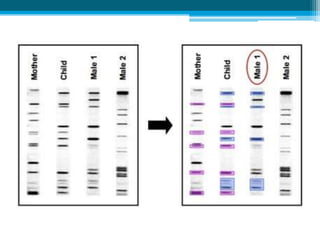
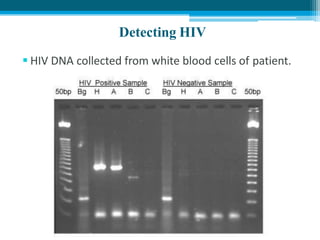
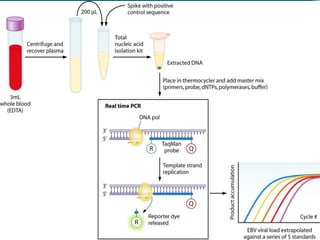
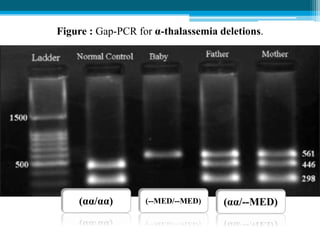
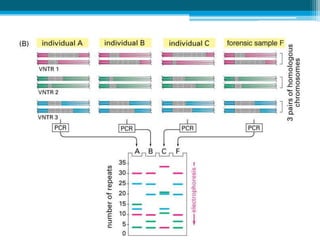
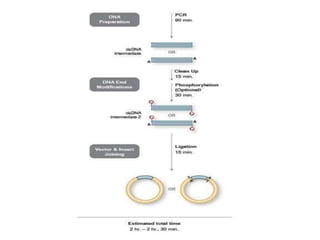
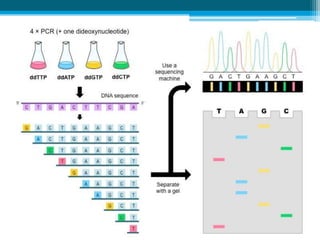
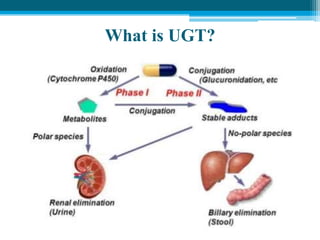
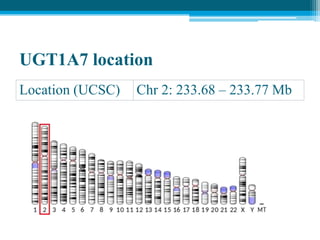
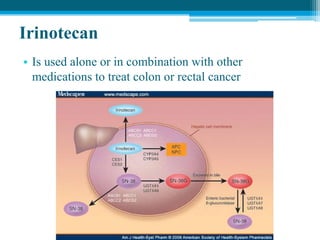
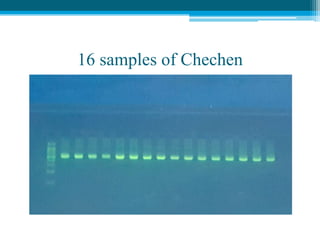
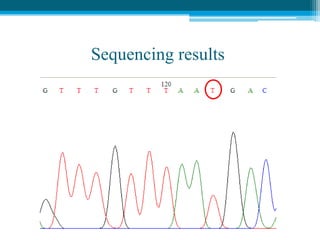
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify specific DNA sequences. It allows targeted DNA sequences to be selectively amplified millions of fold in a few hours. PCR consists of repeated cycles of heating and cooling of the DNA sample to denature and replicate the targeted sequence using DNA polymerase and primers. The amplified DNA can then be analyzed using gel electrophoresis. PCR has many applications including DNA cloning, gene expression analysis, DNA fingerprinting, paternity testing, and detecting infectious diseases and genetic mutations. The researcher aims to identify novel single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the UGT1A7 gene in Circassian and Chechen subpopulations compared to Jordanians which may impact the metabolism of ir