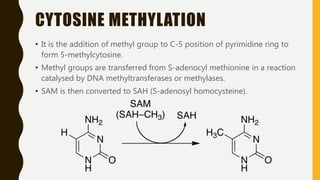
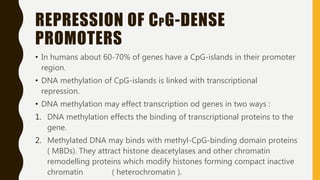
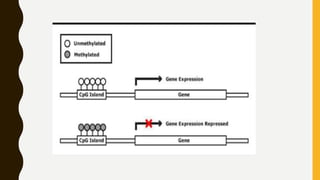
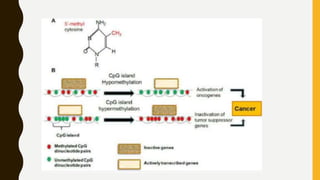
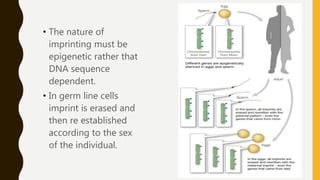
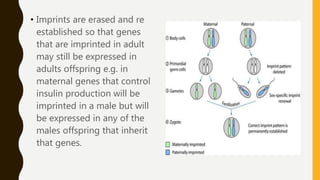
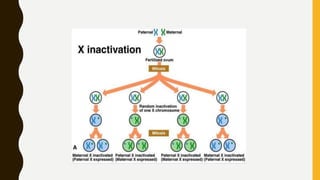
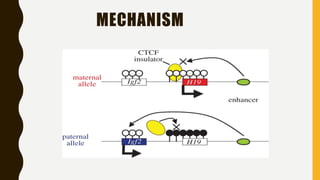
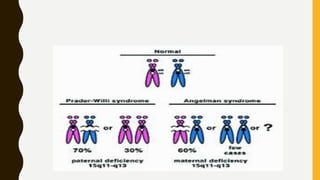
DNA methylation involves the addition of methyl groups to cytosine bases in DNA. It is an epigenetic process that plays an important role in normal development and diseases like cancer. Cytosine methylation occurs most widely and involves the addition of a methyl group to the C-5 position of cytosine. Methylation can repress gene expression by interfering with transcriptional protein binding or recruiting chromatin remodeling proteins. In cancer, aberrant methylation can lead to silencing of tumor suppressor genes or activation of oncogenes. Genomic imprinting involves differential gene expression based on parental origin through epigenetic mechanisms like methylation. Around 1% of genes show imprinting including IGF2 and H19. Imprinting errors