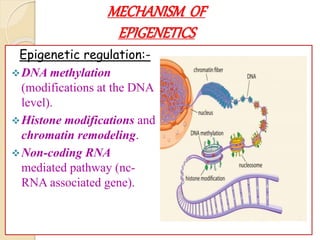
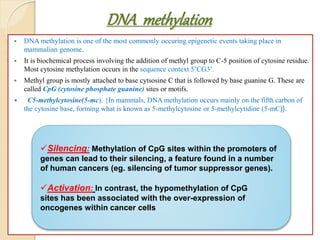
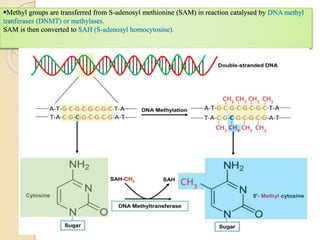
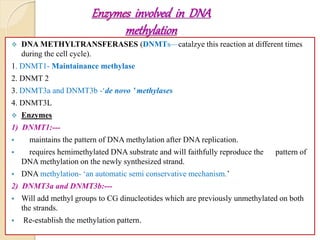
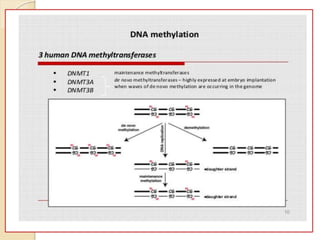
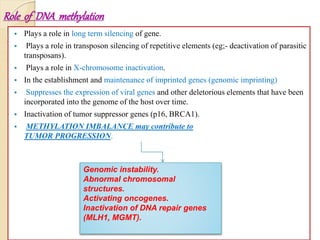
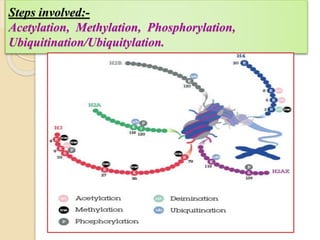
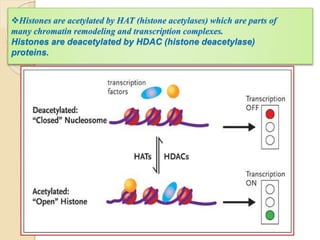
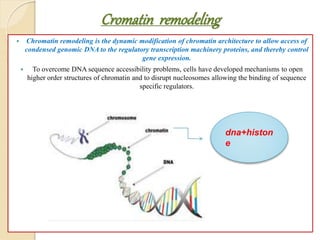
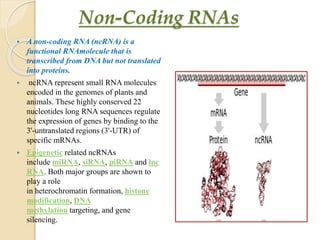
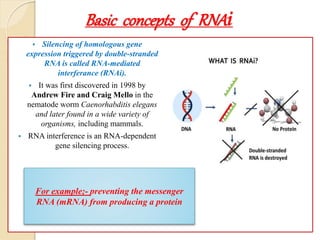
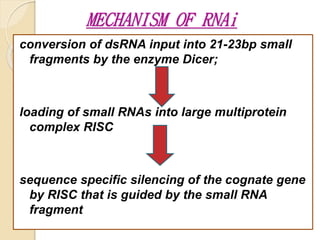
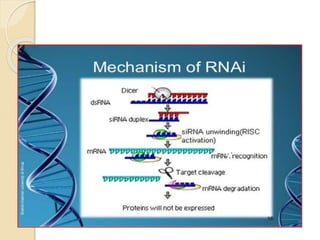
Mugdha Rangnath's seminar topic is on epigenetics. The document defines epigenetics as heritable changes in gene expression that do not involve changes to DNA sequence. It discusses several epigenetic mechanisms including DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNA pathways. DNA methylation involves adding methyl groups to cytosine bases and can lead to gene silencing or activation. Histone modifications like acetylation and methylation can increase or decrease gene expression. Non-coding RNAs like miRNAs regulate genes by binding to mRNA. These epigenetic changes influence gene expression and cellular differentiation.