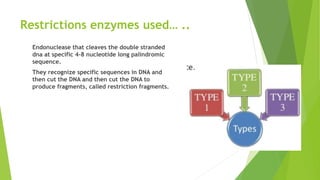
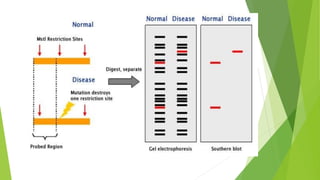
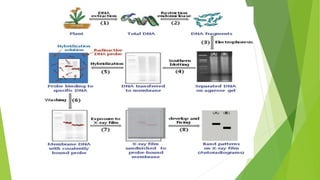
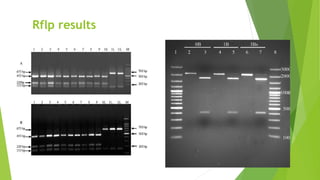
The document provides an overview of the Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) technique used for DNA analysis, which differentiates organisms based on DNA cleavage patterns. It outlines the process of RFLP, including the steps of DNA digestion, gel electrophoresis, and hybridization, as well as its applications in forensics, genetic mapping, and disease detection. The advantages and disadvantages of RFLP are also discussed, highlighting its effectiveness and challenges.