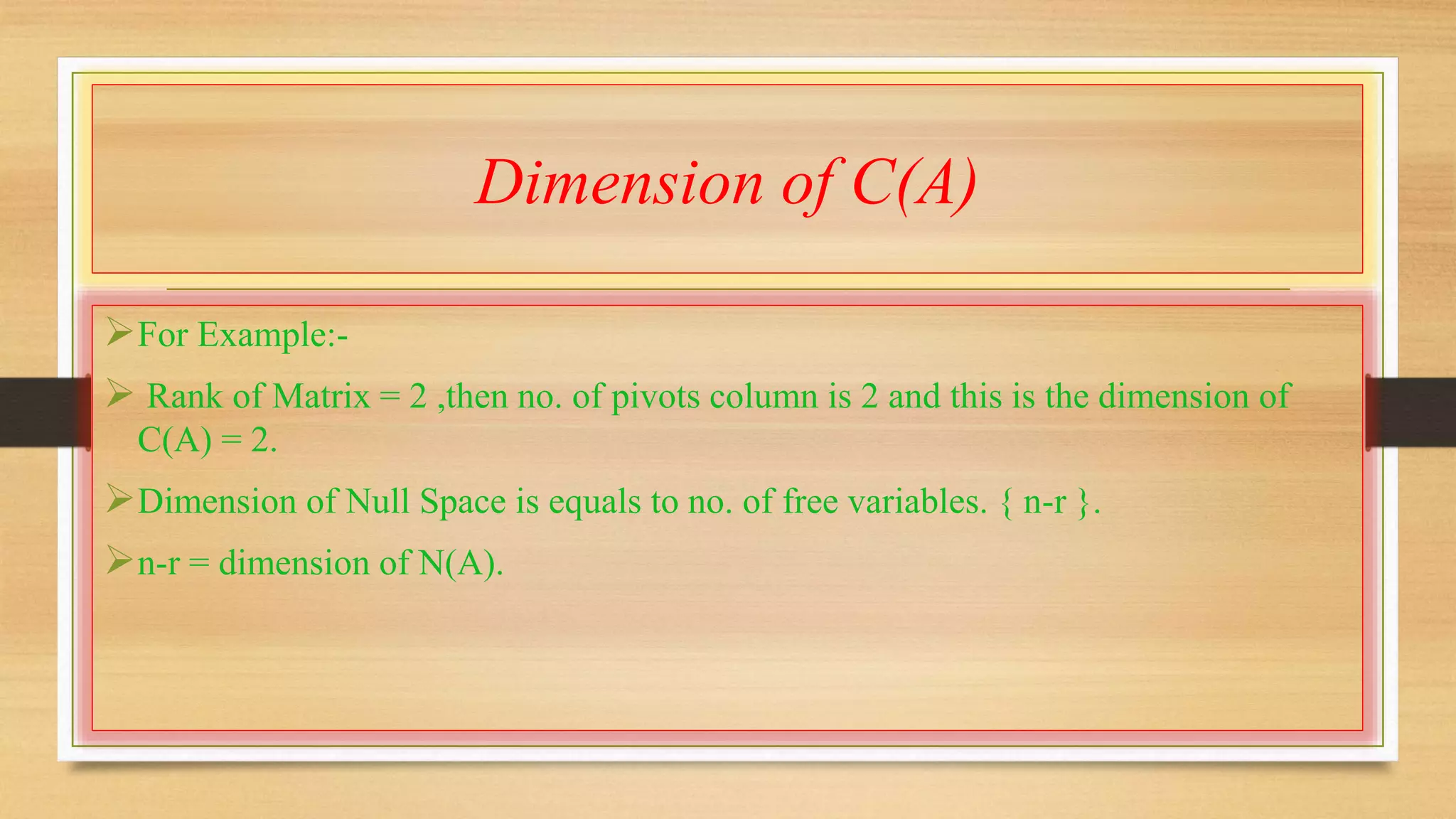
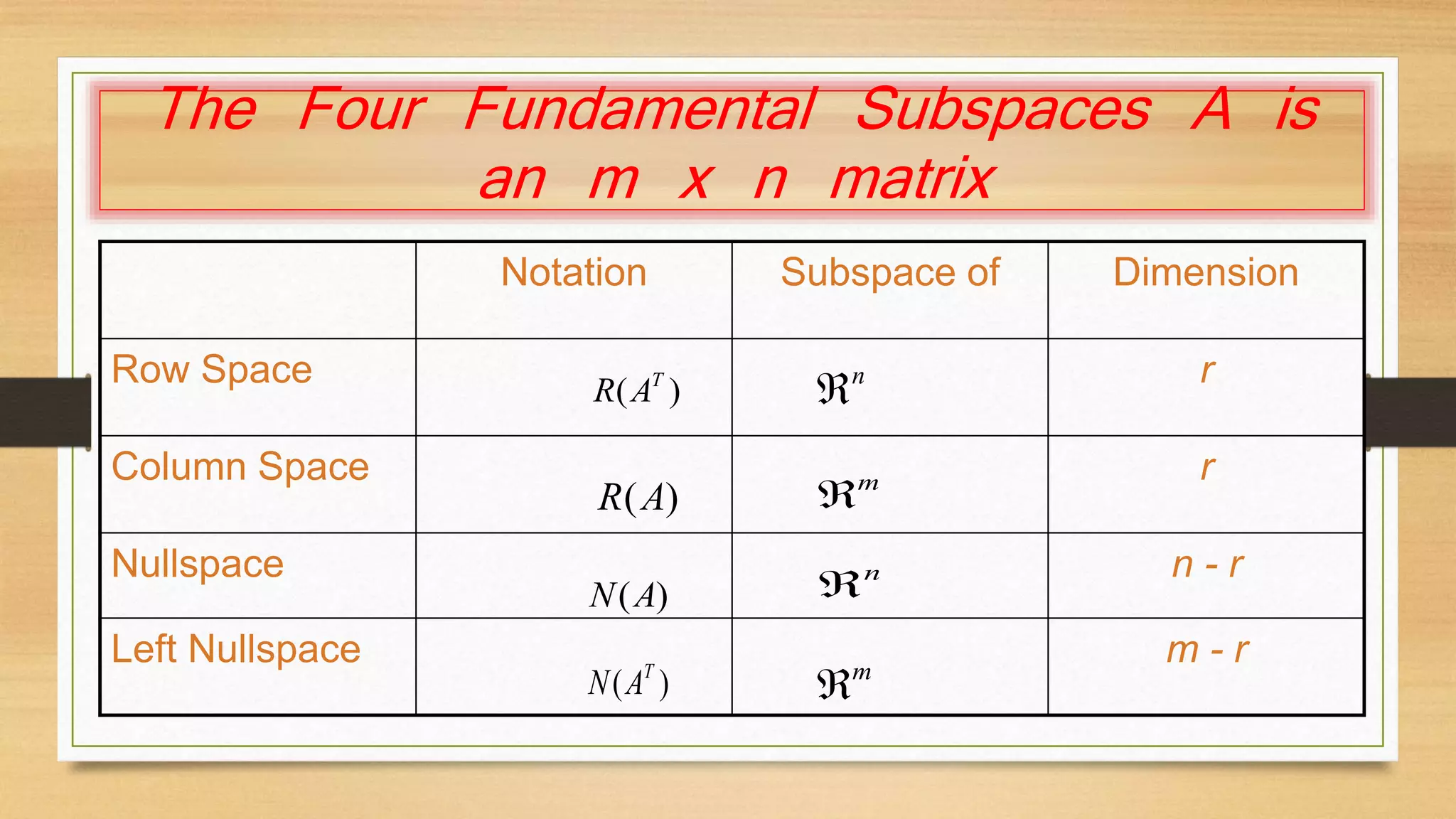
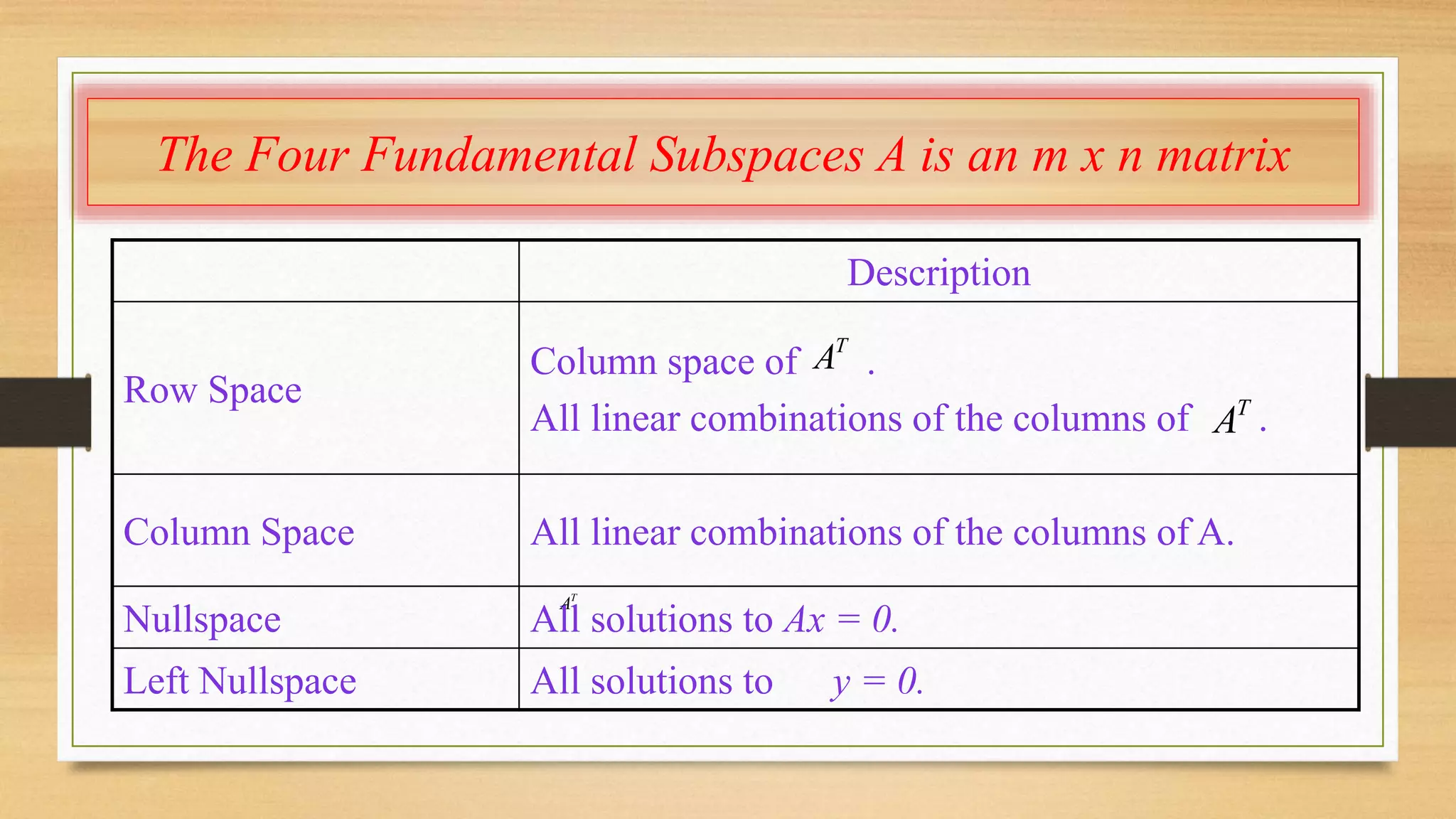
This document discusses linear independence, basis, and dimension in linear algebra. It defines linear independence as vectors being linearly independent if the only solution that produces the zero vector is the trivial solution with all coefficients equal to zero. A basis is defined as a set of linearly independent vectors that span the vector space. The dimension of a vector space is the number of vectors in any basis of that space. The dimensions of the four fundamental subspaces (row space, column space, nullspace, and left nullspace) of a matrix are defined in terms of the rank of the matrix.