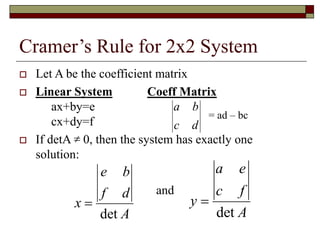
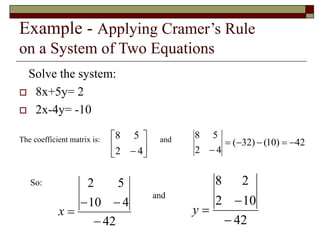
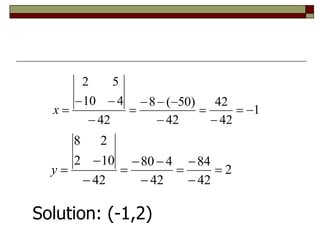
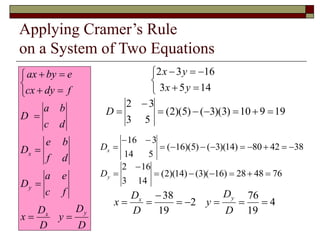
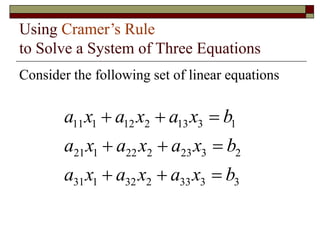
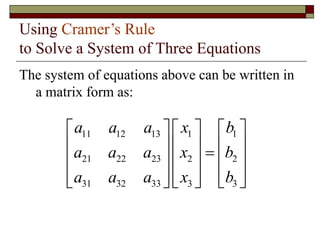
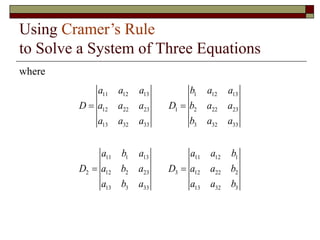
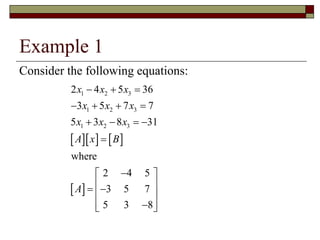
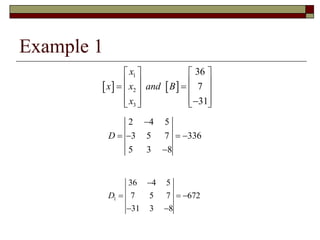
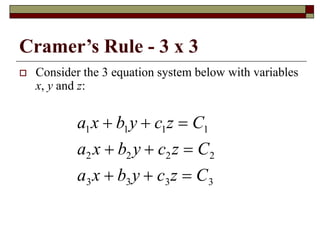
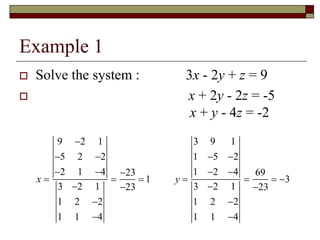
Cramer's Rule is a method for solving systems of linear equations. It uses determinants of coefficient matrices. For a system of two equations, the solutions are determined by taking the determinants of the coefficient matrix and matrices with the constant terms replacing coefficients in the numerator. For three equations, the solutions are similarly determined using 3x3 determinants. Cramer's Rule will fail if the determinant of the coefficient matrix is zero, indicating the system is dependent with no unique solution.