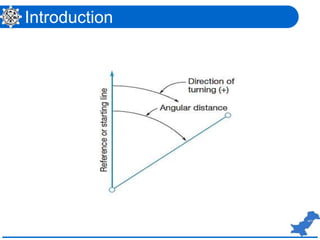
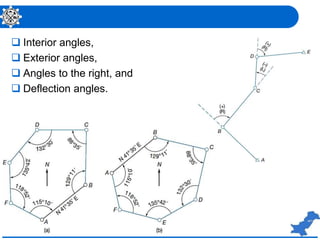
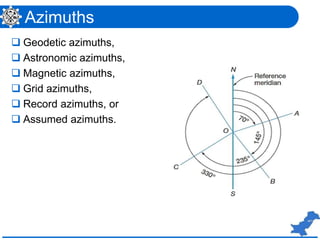
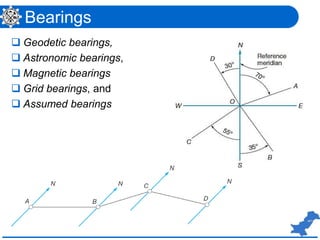
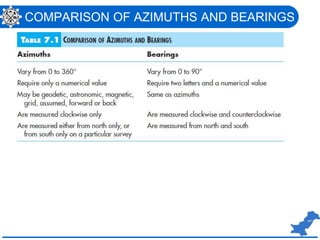
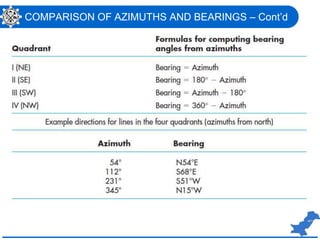
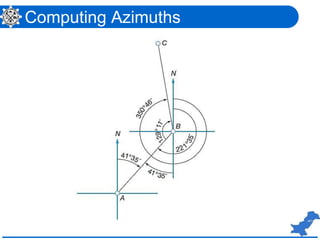
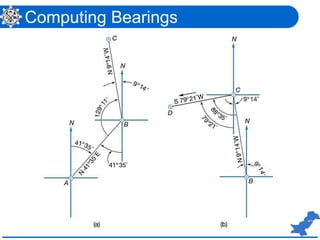
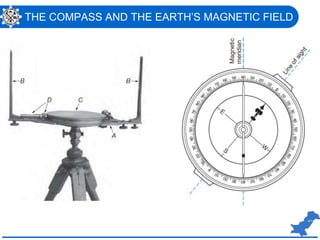
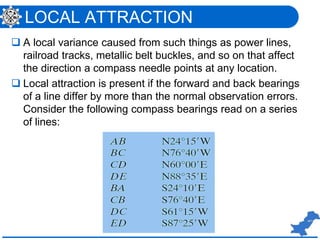
The document is a lecture on surveying focusing on angles, azimuths, and bearings presented by Dr. Mahmood Arshad from the University of Engineering & Technology. It covers definitions and comparisons of various types of angles and azimuths, methods of computing them, and discusses the impact of magnetic declination on readings. Additionally, it highlights the influence of local attraction on compass readings and encourages students to solve relevant problems as homework.